2025 Vol. 7, No. 34
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) nonoccupational post-exposure prophylaxis (nPEP) clinics are specialized healthcare facilities that provide urgent medical interventions to individuals with potential high-risk HIV exposures. This study analyzed utilization patterns of HIV nPEP services in China and examined factors associated with medication adherence among consultees, providing evidence to inform further implementation and optimization of HIV nPEP interventions.
We analyzed nPEP case data collected from the national nPEP data information system between November 1, 2022, and November 1, 2024, using SPSS 29.0 software. Chi-square tests were applied to analyze characteristics of nPEP consultees, and logistic regression models were used to identify factors influencing medication adherence and follow-up compliance among those who initiated treatment.
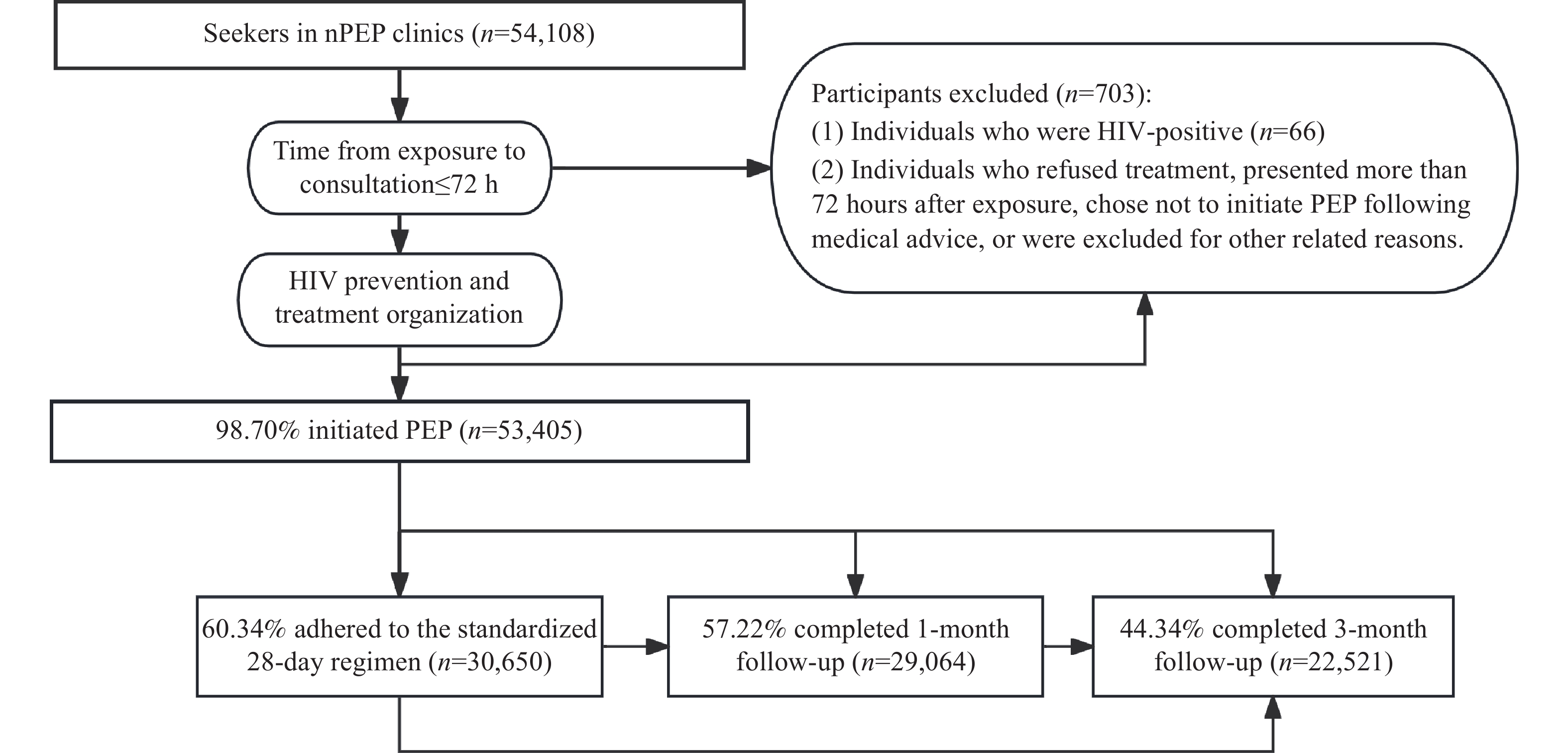
As of November 1, 2024, 924 nPEP clinics nationwide received 54,108 consultees, with 53,405 (98.70%) initiating medication. Most individuals seeking services were male (88.63%), classified as high-risk (83.11%), and heterosexual with multiple partners (67.66%). The “BIC/FTC/TAF” regimen was selected by 63.07% of recipients. Nearly all users (99.03%) completed medication evaluation within 72 hours post-exposure. Among medication users, 60.34% (30,650) adhered to the full 28-day regimen, and 60.10% (30,509) completed either one-month or three-month follow-ups. Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified gender, exposure risk assessment results, exposure population classification, individual preferences, and medication regimen as significant factors influencing both 28-day medication adherence and follow-up compliance (P<0.05).
nPEP clinic consultees in China are predominantly young male heterosexual individuals with multiple sexual partners, with most selecting the Biktarvy regimen. However, both current 28-day medication adherence and follow-up compliance rates remain suboptimal. High-risk men and those receiving the Biktarvy regimen demonstrate superior medication adherence and follow-up compliance compared to other groups. Further research is needed to develop targeted interventions to improve medication adherence and follow-up rates among nPEP recipients. Enhancing adherence and follow-up should be prioritized in future interventions, supported by continuous monitoring to inform timely intervention strategy adjustments.
Diagnosing tuberculosis (TB) in HIV-infected individuals presents significant challenges due to difficulties in obtaining specimens containing adequate quantities of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic performance of the IP-10 mRNA assay independently and in combination with established diagnostic tests for Mtb detection.
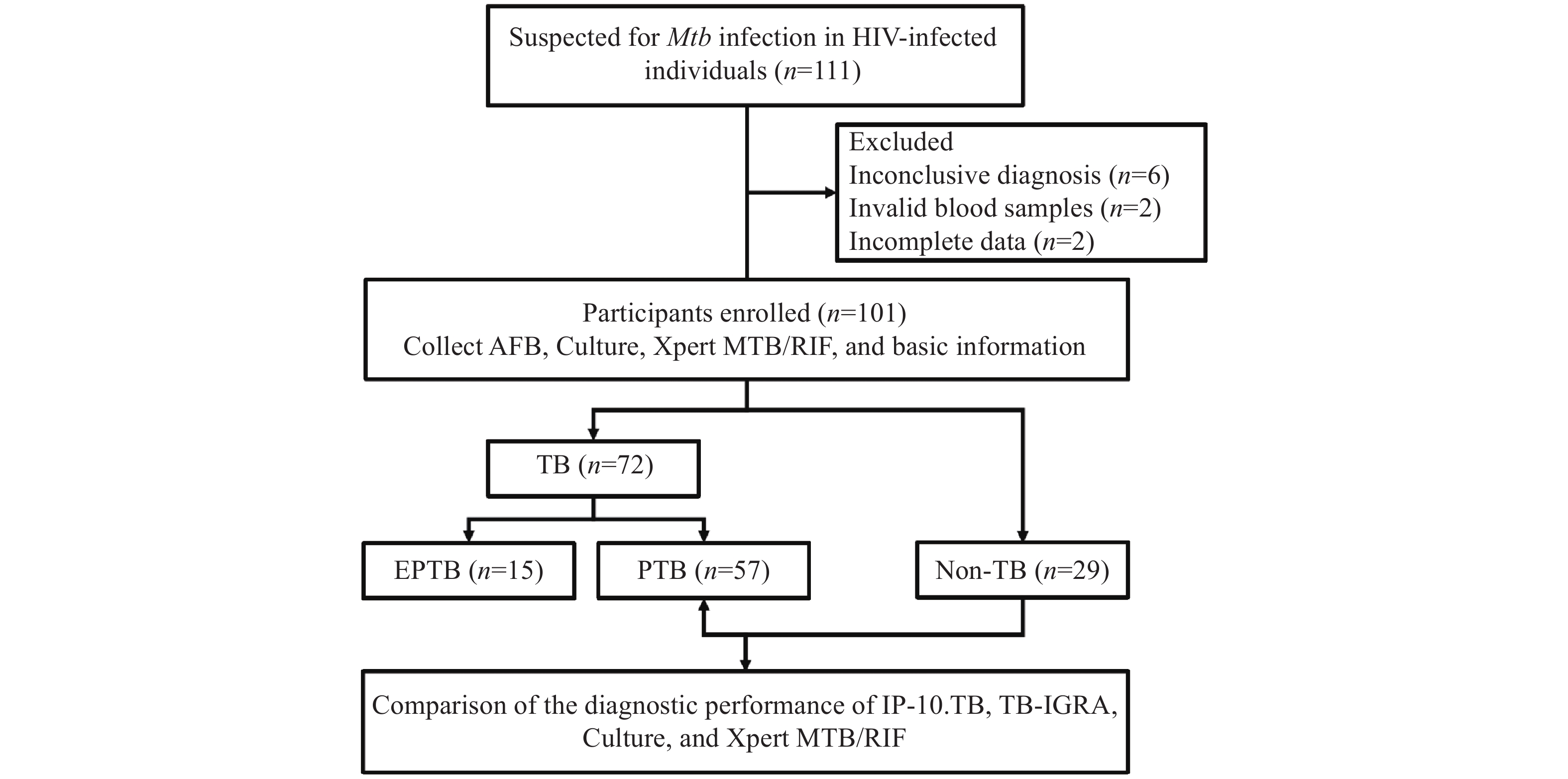
The study cohort comprised 111 HIV-infected individuals who presented with TB at Beijing Youan Hospital from 2022 to 2024. Participants were categorized into confirmed TB, probable TB, or non-TB groups according to the diagnostic criteria for tuberculosis (WS288-2017). The performance of the IP-10 mRNA release assay was evaluated by the STARD guidelines on blood samples collected after enrollment.
The IP-10 mRNA release assay demonstrated significantly higher sensitivity than interferon-γ release assays (IGRAs) and culture methods for confirming pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) diagnosis while maintaining comparable specificity. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis revealed that the diagnostic performance of the IP-10 mRNA release assay used in parallel with Xpert MTB/RIF significantly exceeded that of the IP-10 mRNA release assay alone (0.731 vs. 0.687, P=0.02). Among HIV-infected individuals, the IP-10 mRNA release assay showed superior performance compared to IGRAs for diagnosing extrapulmonary tuberculosis.
The IP-10 mRNA release assay exhibited excellent diagnostic performance and demonstrates substantial potential as an auxiliary tool for diagnosing TB in HIV-infected individuals. The combined application of IP-10.TB and Xpert MTB/RIF further enhance diagnostic efficacy.
Trainees in the China Field Epidemiology Training Program (CFETP) constitute a vital workforce in addressing global public health emergencies. Developing intercultural communication competence is essential for their future participation in international public health efforts. However, within China’s existing public health training system, this aspect has not yet received adequate attention or been systematically strengthened.
This study is the first to evaluate and investigate the intercultural communication competence of domestic CFETP trainees. There are 77 trainees that demonstrated strong cognitive (Score rates: 86.57%) and emotional (87.22%) competencies. However, behavioral (79.42%) competence, particularly language proficiency, can be improved. Further analysis indicated that international experience, duration of time spent abroad, and foreign language proficiency had a significant impact on their intercultural communication competence.
This study examined the current state of intercultural communication competence among public health professionals and the factors influencing it. It highlights the key obstacles and practical challenges trainees face in intercultural communication while providing essential data to inform the development of targeted strategies for improving competence and refining training programs.
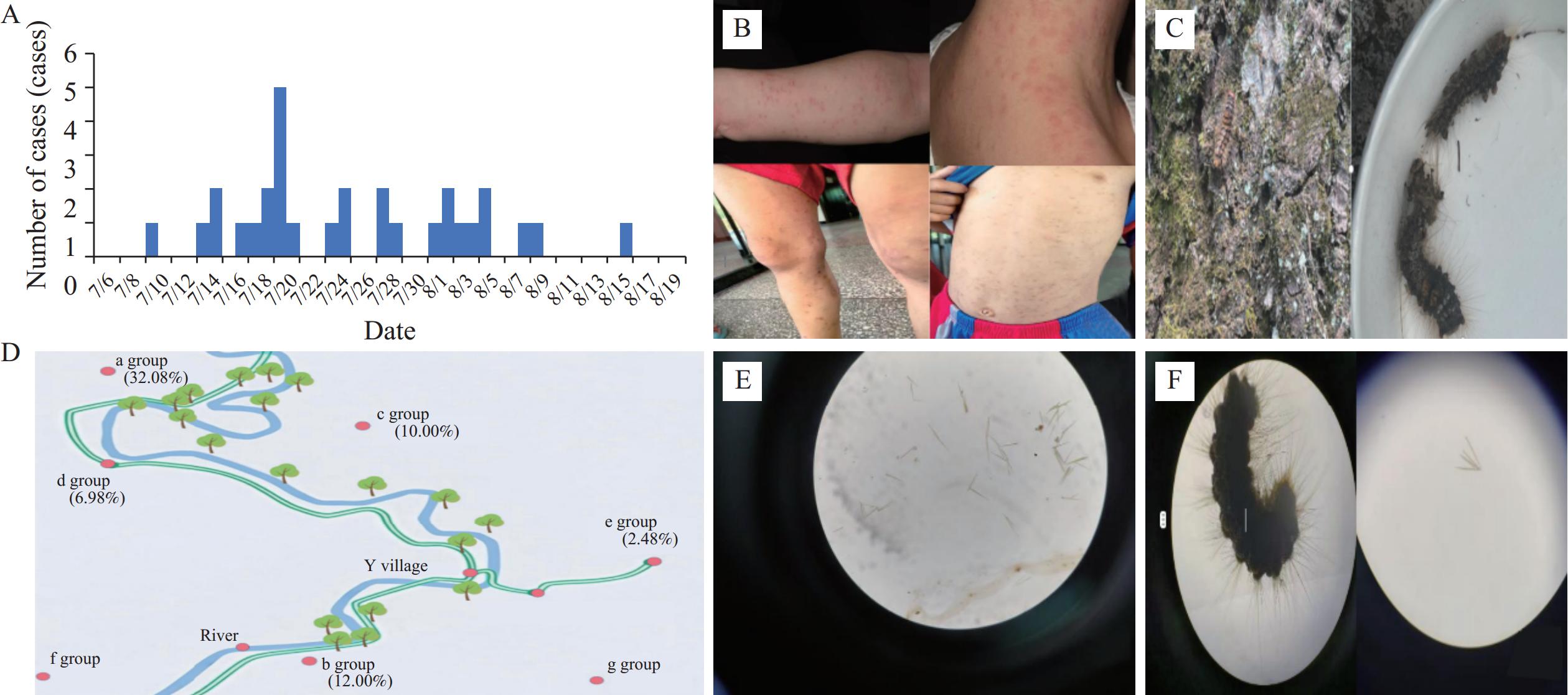
Redoa leucoscela (R. leucoscela) Collenette (Lepidoptera: Erebidae), releases urticating setae during larval molting. These setae disperse through aquatic and aerial pathways and can trigger allergic reactions upon dermal contact. Clinical manifestations include pruritic dermatitis with stinging sensations and papular lesions; untreated cases may progress to systemic reactions or secondary infections.
Between July 10 and August 16, 2024, a dermatitis outbreak caused by R. leucoscela occurred in Y Village, Tongren City, Guizhou Province. A total of 32 cases were identified, including 30 residents and 2 tourists. This report provides the first epidemiological evidence linking R. leucoscela larvae to dermatitis outbreaks through rigorous case-control methodology.
During peak R. leucoscela larvae infestation periods, local authorities must implement integrated dermatitis surveillance and larval eradication programs, coupled with prominent warning signage in high-risk zones (riversides, swimming areas) advising against water contact and minimizing exposure to P. stenoptera tree foliage to prevent outbreak recurrence. Concurrently, health promotion campaigns must prioritize eco-awareness education for tourism stakeholders and the public, advocating for eco-conscious tourism behaviors to minimize anthropogenic habitat disruption, thereby achieving sustainable tourism-conservation synergy.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed