2024 Vol. 6, No. 1
The global efforts to address the hepatitis C virus (HCV) are progressing, but there are still significant gaps in the diagnosis and treatment of HCV, leading to an increasing number of deaths related to HCV.
An extensive investigation was conducted to assess HCV RNA diagnosis, treatment uptake, and associated factors among individuals infected with HCV within Jiangsu Province. The study encompassed a large geographical area and utilized a substantial sample size.
Implementing focused interventions to improve the timely diagnosis of HCV RNA and increase the uptake of HCV treatment could effectively reduce the future burden of HCV-related health problems, deaths, and healthcare expenses. This is essential for achieving the global target of eliminating hepatitis C.
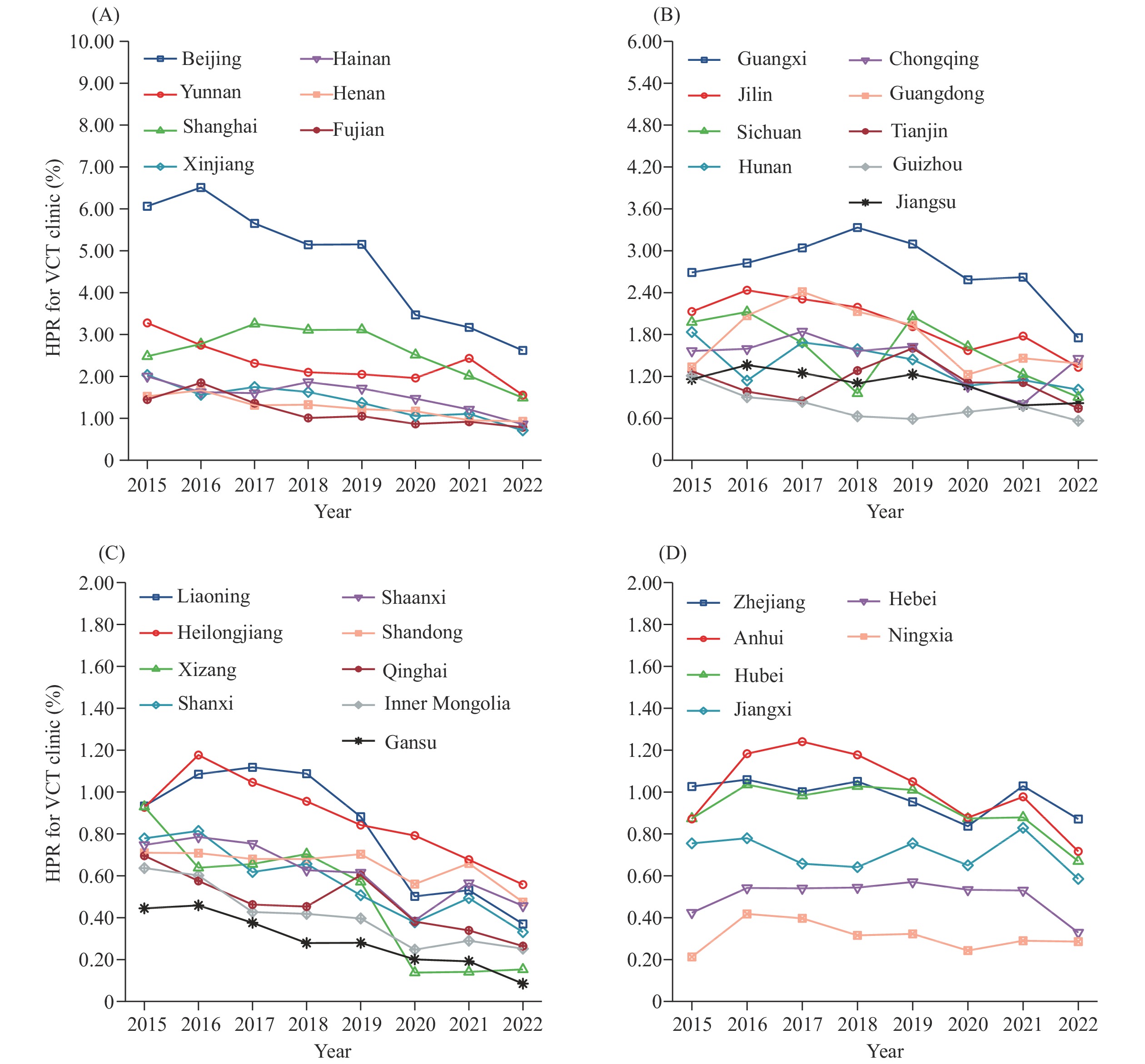
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) voluntary counseling and testing (VCT) clinics play a critical role in identifying and diagnosing HIV cases. This study aimed to describe the trend of HIV positivity rate (HPR) among Chinese VCT clinics between 2015 and 2022.
This study utilized data from the China Information System for Disease Control and Prevention to analyze the trend in the HPR for VCT clinics from 2015 to 2022. The HPR was calculated by dividing the number of newly-reported HIV cases by the number of HIV tests, multiplied by 100%. To identify temporal and spatial trends in the HPR, we employed joinpoint regression analysis and the Getis-Ord hotspot analysis.
From 2015 to 2022, VCT clinics in China performed a total of 22,075,386 HIV tests, leading to the identification of 260,353 HIV cases, resulting in a HPR of 1.18%. The HPR consistently declined over the study period, with an average annual percent change (AAPC) of −7.5% (95% confidence interval
VCT clinics in China have played a significant role in identifying HIV cases. The declining HPR observed in these clinics may indicates the progress has been made in some degree in mitigating HIV among high-risk populations. Therefore, it is crucial to further improving the utilization of VCT clinics for HIV testing.
This study aims to provide a theoretical foundation for the development and practical application of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) prevention and control policy systems in China by scrutinizing, analyzing, and synthesizing the evolution of Chinese policies in this domain.
Utilizing grounded theory, we employed NVivo12 software to perform text content analysis, mining, and coding classification, along with visualization techniques, on policy texts sourced from Chinese government platforms, including the official website of China’s State Council. We considered four analytical dimensions — time, subject, type, and object.
The National Health Commission and the State Council emerged as the primary entities engaged in policymaking for HIV/AIDS in China. We identified four distinct stages in the evolution of these policies, culminating in a novel ‘sun-shaped’ HIV/AIDS prevention and control policy network model with an emphasis on ‘knowledge, attitude, and practice’ at its nucleus, which aligns with national conditions and societal progress. Furthermore, the focal groups of these policies have been dynamically refined and updated over time.
Our findings introduce a ‘sun-shaped’ HIV/AIDS prevention and control policy network model specific to China. We observed a conceptual policy shift towards prioritizing overall human health rather than confining the focus to disease treatment. Additionally, in light of China’s growing elderly population, the imperative to address HIV/AIDS prevention and control among older adults is an issue that warrants increased attention.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed