2023 Vol. 5, No. 37
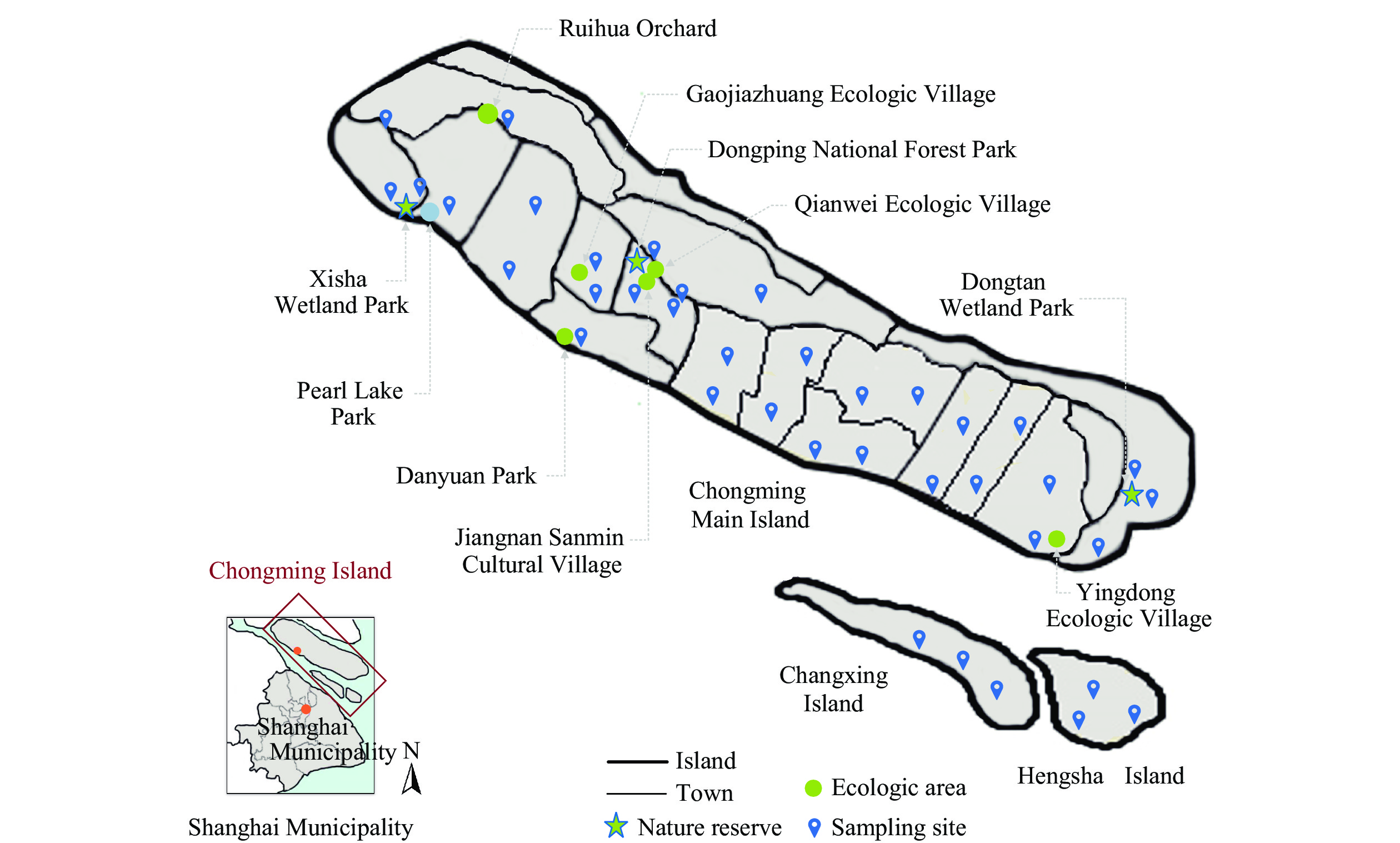
Although ticks and tick-borne diseases are prevalent throughout China, there remains a knowledge gap regarding their biology and potential risk of distribution to human and animal populations on Chongming Island. The island, being China’s third largest and a crucial component in the ecological preservation of the Yangtze Delta region, has yet to be comprehensively studied in this context.
In this study, employing molecular methodologies, a significant prevalence of Haemaphysalis (H.) longicornis and H. flava ticks — widely recognized for their high pathogenicity — is reported from Chongming Island. Additionally, the identification of two previously unreported species on the island, namely, H. doenitzi and H. japonica, expands our understanding of both the range and evolution of tick species.
The populations of humans and animals in nearly all 18 towns on Chongming Island are potentially at risk for transmission of tick-borne infectious agents. As a result, there is a pressing necessity for public health alerts, proactive tick surveillance, and effective screening of suspected clinical cases of tick-borne diseases within the Chongming population.
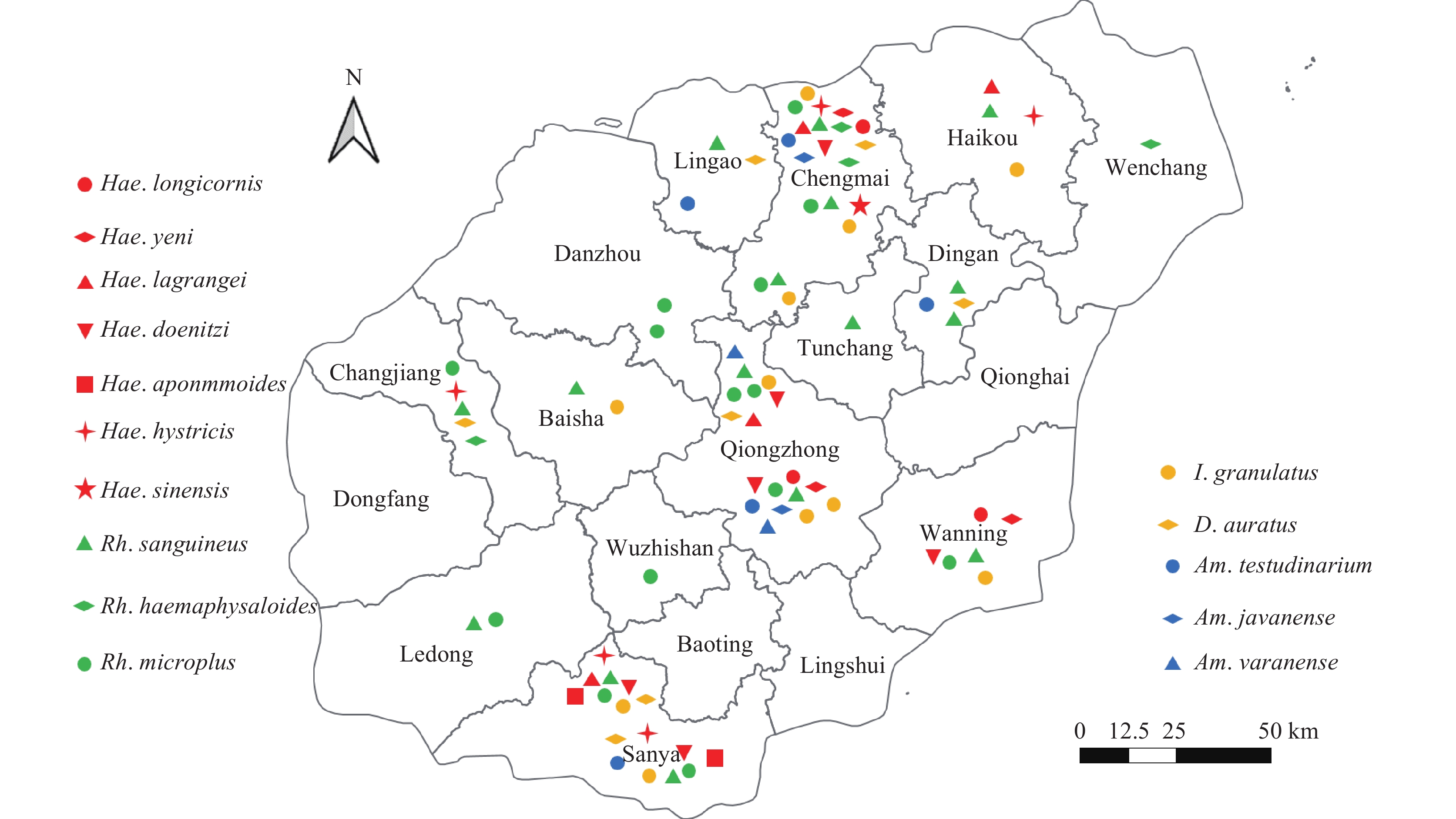
China’s six tropical regions include Guangdong Province, Yunnan Province, Hainan Province, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (SAR), Macau SAR, and Taiwan, China. Hainan, seated in the southernmost tropical region of China, is home to ticks that remain active throughout all four seasons. This heightens their potential to transmit tick-borne diseases to both animals and humans. This study provides a succinct overview of the prevailing tick species’ spatial distribution and offers an outline of the range and dispersion of emerging tick-borne infections in tick vectors, animal hosts, and human populations within Hainan, China.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed