2023 Vol. 5, No. 35
Interpregnancy intervals (IPIs) that are either excessively long or short have been linked with an elevated risk of adverse perinatal outcomes. Presently, no pertinent guidelines have been established in China to provide clear direction with regard to optimal IPI.
A brief interpregnancy interval may elevate the risk of miscarriage, postpartum hemorrhage, and fetal distress among expectant women.
These results could inform prenatal consultations, guiding pregnant women towards an ideal interpregnancy interval of no less than 24 months.
Maintaining a healthy diet and appropriate weight during pregnancy is crucial for both the expectant mother and the fetus. Unhealthy eating behaviors (UEBs) such as eating out frequently are becoming increasingly prevalent across the globe. However, there is a dearth of research investigating the relationship between UEBs and gestational weight gain (GWG) specifically in the context of Chinese women.
The study revealed that a majority of pregnant women reported experiencing one or more UEBs such as eating fast, eating three meals irregularly, eating away from home, and skipping breakfast. A positive association was also observed between the number of UEBs and elevated odds of experiencing excessive GWG.
The uptake of emerging UEBs is prevalent among pregnant women in China. It is recommended that healthy eating behavior become the focal point of gestational weight management in clinical practice. Moreover, preconception care should take into account customized health education and promotion programs.
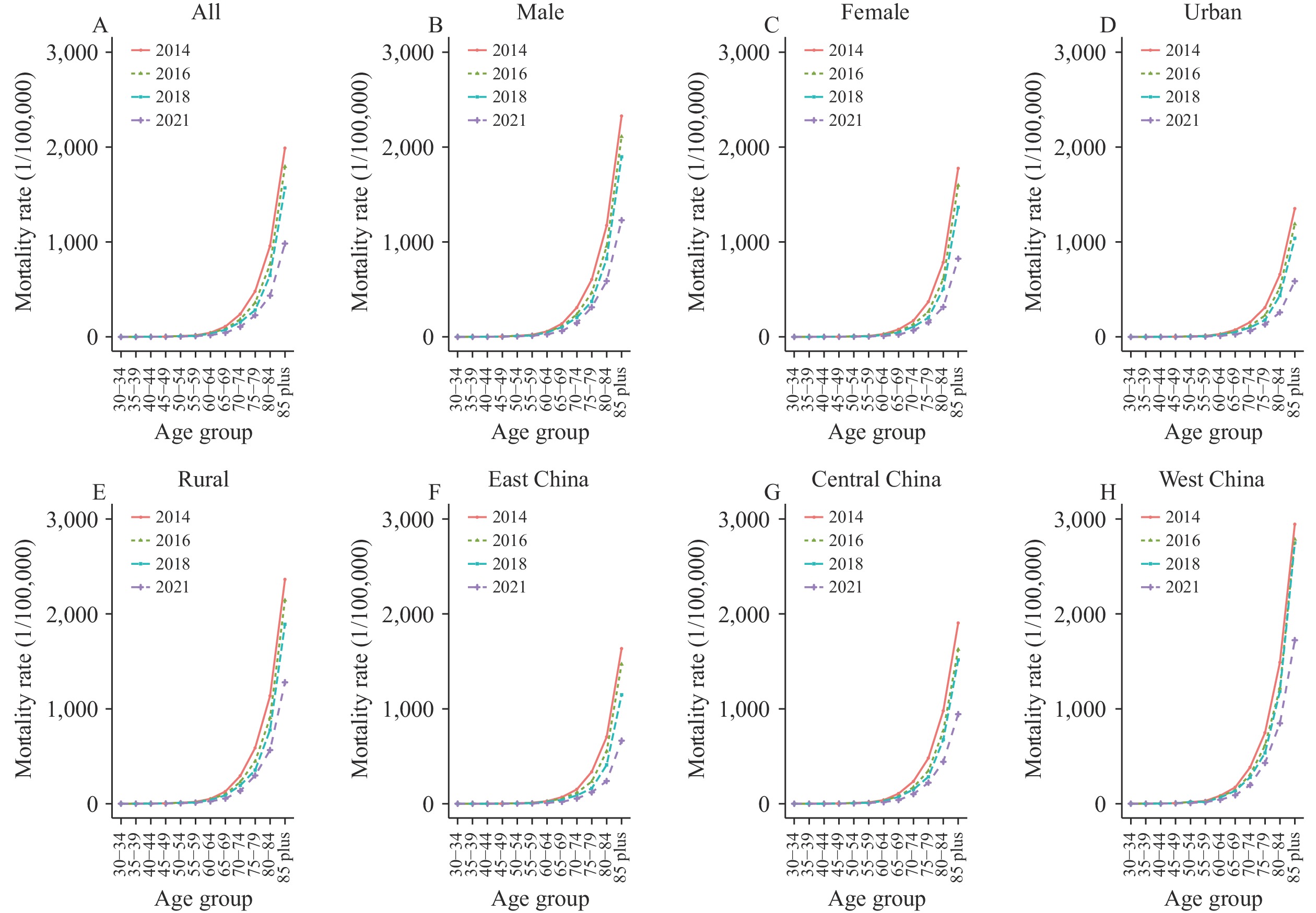
Over the latter half of the previous century, pulmonary heart disease (PHD) emerged as a significant public health issue in China. However, the current mortality rate is unknown. Utilizing the Multiple Cause of Death database, the present study aims to investigate the current state and progression of PHD-associated death in China.
Data from the China National Mortality Surveillance System were used to analyze progression in mortality rates attributable to PHD from 2014 to 2021. To standardize population structure for each year during the investigation period, demographic information from the 2020 census was employed as the reference population. Age-standardized mortality rates (ASMR) were determined based on sex, urban-rural area, and region. To identify trends in ASMR, a joinpoint regression analysis was executed.
The ASMR of PHD exhibited a marked decrease, falling from 61.68 per 100,000 in 2014 to 28.53 per 100,000 in 2021. This downward trend was observable in both genders, all regions, and both urban and rural settings. The greatest ASMR values were documented in the western region. Comparative observations revealed a higher ASMR in rural areas versus urban ones and in males versus females. PHD-associated deaths predominantly occurred among older individuals, particularly those aged 80 and above. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) emerged as the principal underlying cause of death PHD-associated mortalities, accounting for between 87.41% and 93.42% of cases throughout the period 2014–2021.
There was a declining trend in PHD mortality in China from 2014 to 2021, with COPD accounting for a significant proportion of these deaths. Given the high prevalence of COPD and the escalating population aging in China, PHD remains a significant health concern that warrants further attention.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed