2023 Vol. 5, No. 20
In China, patients with echinococcosis receive complimentary healthcare services, such as medical treatment, diagnostic examinations, and follow-up care. Despite this, no studies have been conducted to assess the quality of patient management to date.
This study reviewed the medical records of 899 patients who underwent albendazole treatment across 10 endemic counties. Out of 634 evaluable patient files, the proportion of patients with a ratio of actual follow-up and reexamination times to theoretical follow-up and reexamination times ≥0.8 were both low (21.92% and 23.19%, respectively).
This study identified weaknesses and specific issues in patient management and proposed feasible recommendations to enhance patient file documentation, follow-up, and reexamination.
The prevalence of rodent-adapted Bartonella species has been increasing significantly. However, the specific Bartonella species carried by Marmota himalayana (M. himalayana), a large rodent species, and the potential risk it poses to human populations remain unknown.
Bartonella washoensis (B. washoensis), associated with human endocarditis, was initially identified in M. himalayana, exhibiting a detection rate of approximately one-third and demonstrating a predilection for the heart and lungs. The discovery of the novel Sequence Type 22 has expanded both the isolation source and genetic lineage of B. washoensis.
Individuals residing within the M. himalayana plague focus are at an elevated risk for B. washoensis infection. Consequently, there is a pressing need for public health warnings and efficient clinical case identification in this population.
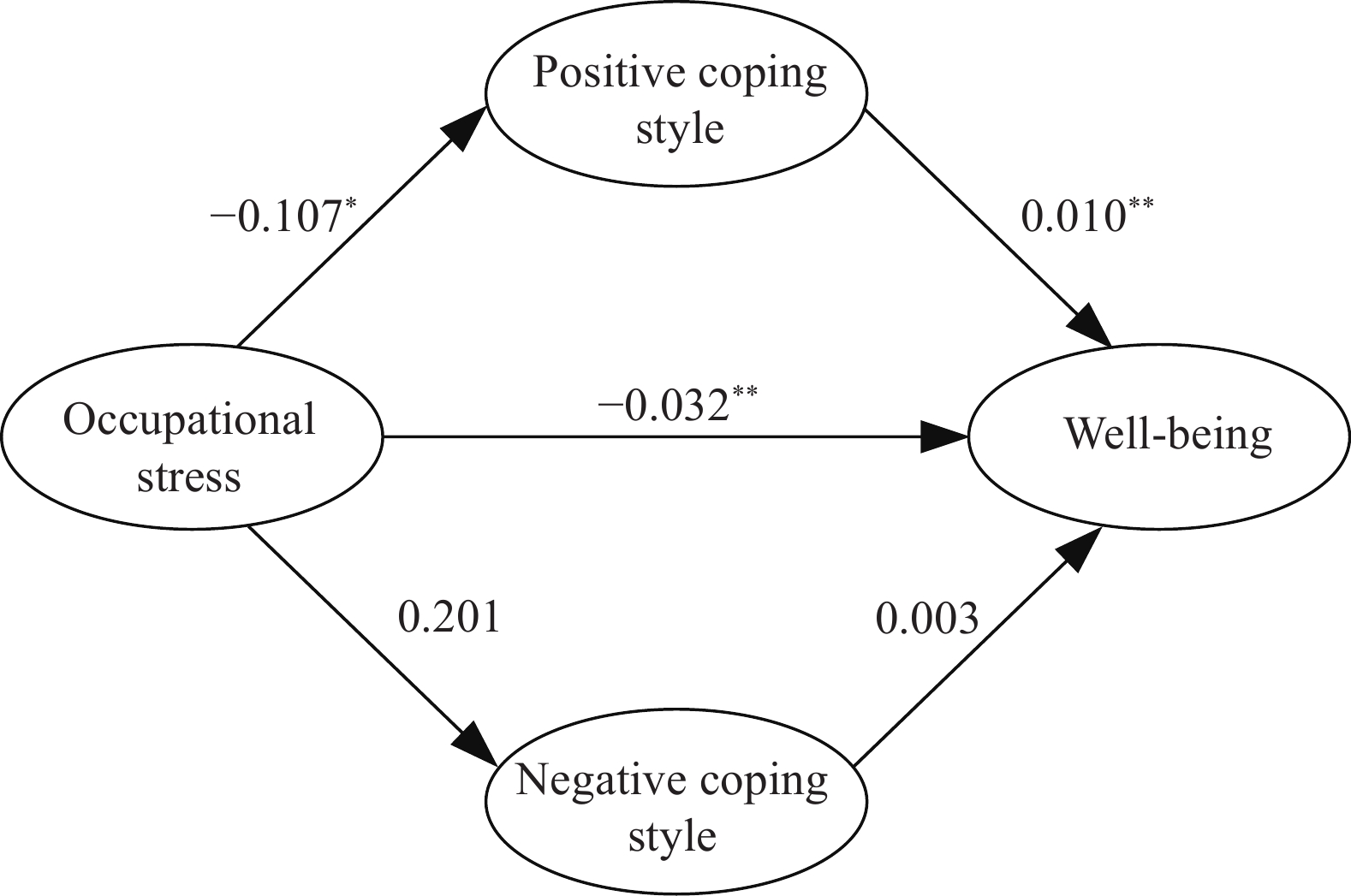
Prior research has primarily concentrated on occupational health concerns, including injuries and heatstroke, among couriers. Nevertheless, there has been a scarcity of emphasis on mental health aspects, with existing studies predominantly addressing the risk factors associated with occupational stress.
The present study demonstrated a significant association between occupational stress and well-being among couriers, with positive coping strategies acting as a mediating factor. Furthermore, the results indicate that implementing a positive coping style may mitigate the impact of occupational stress on well-being.
Future public policy initiatives should focus on promoting the well-being of couriers by fostering improvements in the workplace environment, reevaluating the organization of work, and delivering support to couriers in managing occupational stress.
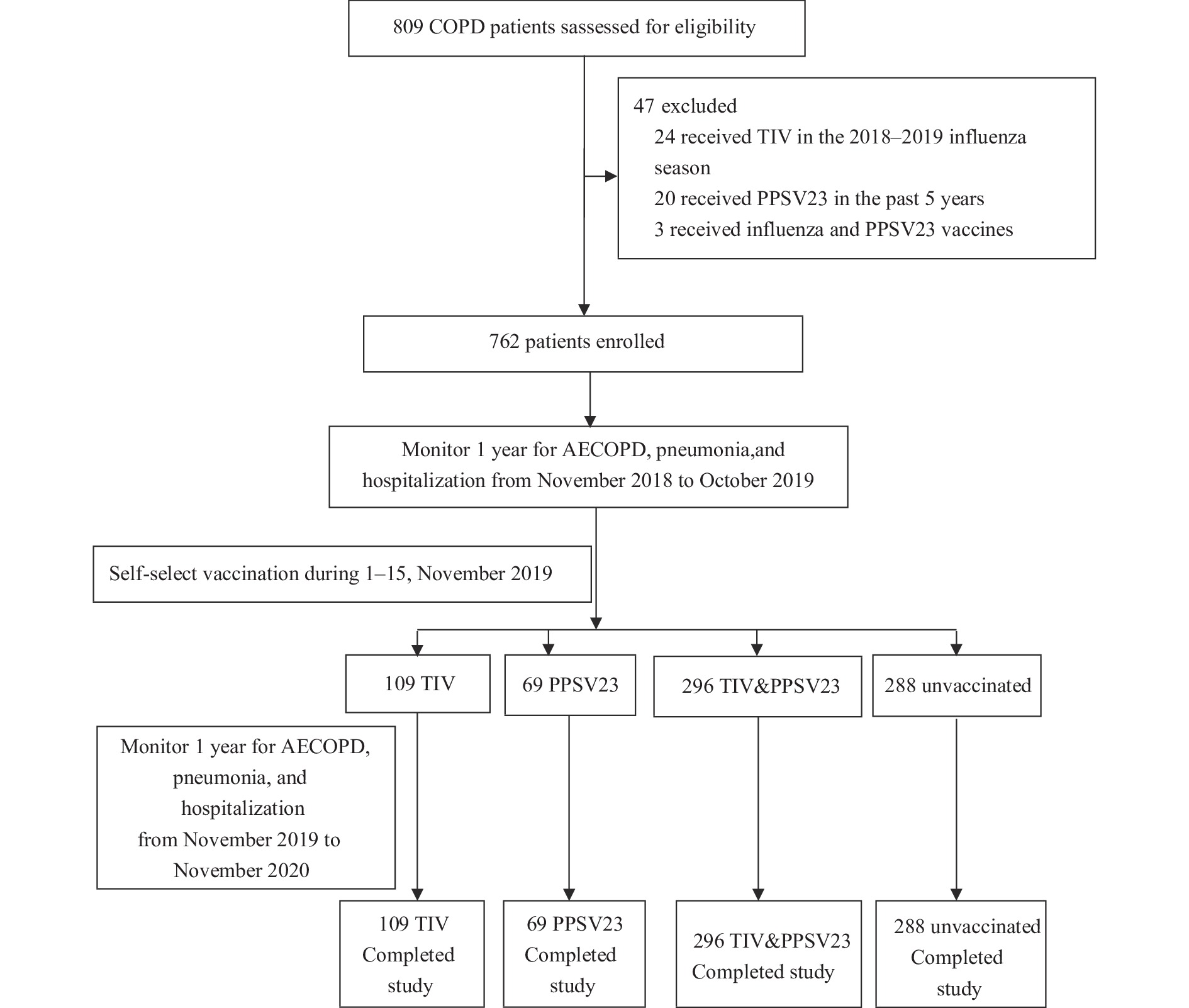
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations increase household economic burden, but there is limited evidence from prospective cohort studies in China about the impact of vaccination on economic burden.
This study demonstrated the economic burden of COPD exacerbations, pneumonia, and hospitalization in COPD patients in China is substantial. Influenza vaccine and 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23), separately or together, were significantly associated with decreased economic burden.
Our study supports evidence on recommendations that COPD patients in China are offered both influenza vaccine and PPSV23.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed