2022 Vol. 4, No. 47
The number of newly diagnosed human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) cases among Chinese youth 15–24 years of age shows an upward trend between 2010 and 2019.
This survey is on a larger scale as compared to previous studies. It shows inadequate HIV knowledge — especially on HIV treatment, self-testing, and post-exposure prophylaxis — among college students. A significant gap exists between knowledge and behavior as indicated by the low condom use rate despite a high knowledge level.
Findings suggest priorities for future HIV education and awareness creation of existing services. A low condom use rate at sexual debut suggests that HIV prevention education should start early.
Little is known about Chinese American dementia caregivers’ attitudes toward tube feeding.
To address this knowledge gap, the paper seeks to characterize participants’ attitudes toward tube feeding based on a survey conducted among Chinese American dementia caregivers.
It is crucial to develop culturally tailored interventions to promote knowledge on tube feeding and advance care planning engagement in Chinese American communities.
Melioidosis, a tropical infectious disease caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei (BP)
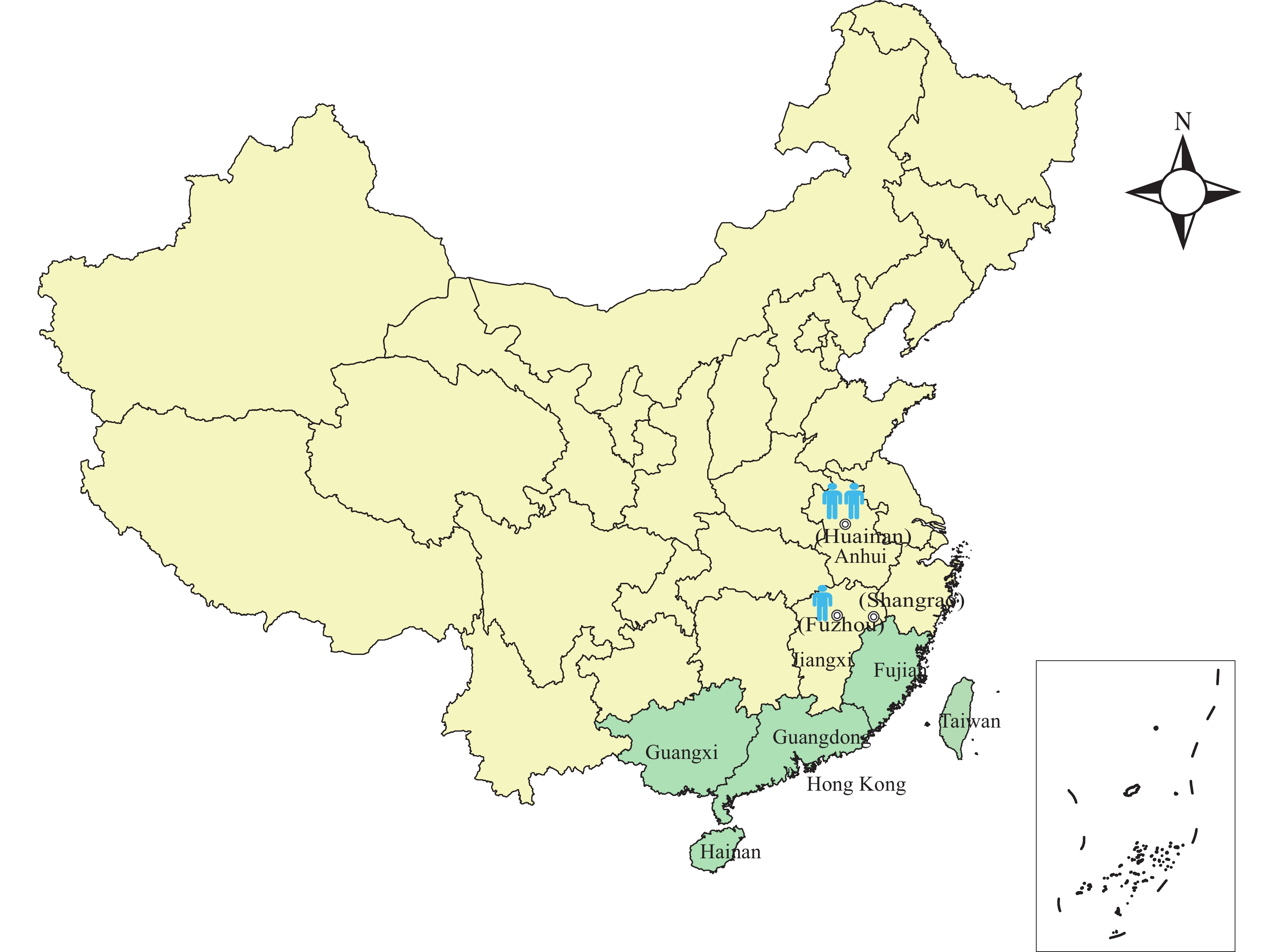
Three melioidosis cases, including two in young children and one in a 19-year-old female, were reported in Anhui and Jiangxi (two inland PLADs of China) respectively, in 2021. None of the patients had a travel history to a melioidosis-endemic area. All the BP isolates belonged to the same sequence type (ST51), which had been reported from elsewhere in Southeast Asia.
This is the first report of autochthonous melioidosis cases in inland Chinese PLADs. Surveillance and prevention and control work should be strengthened in this region.
This study seeks to explore efficient and multiple-item detection modes in new-style HIV labs, as well as access the accuracy and reliability of CD4 cell count detected by point of care (POC) to analyze POC work feasibility in district or county labs.
POC devices adopted in grassroots-level labs and flow cytometers adopted in prefecture-level labs were used to analyze the same group of blood samples. The individual results were collected and compared for parametric tests in correlation and consistency.
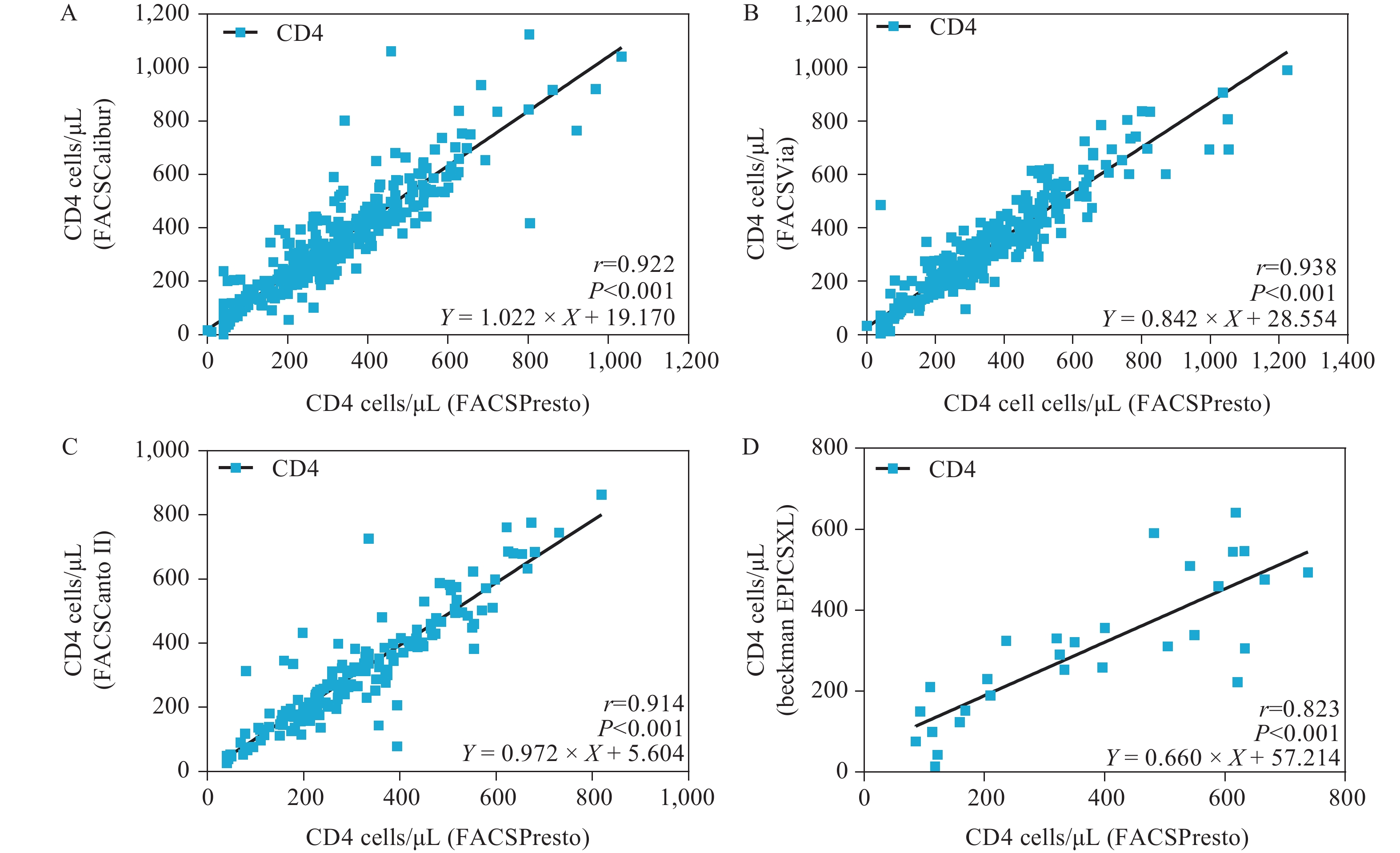
The Pearson correlation coefficients (r) between results detected by FACSPresto and those by FACSCalibur, FACSVia, FACSCantoII, and EPICSXL were 0.922, 0.938, 0.914, and 0.823, respectively; the average deviations were −25.64, 24.68, 3.05, and 70.97 cells/μL, respectively; the Pearson correlation coefficient (r) between results by Pima and FACSCalibur, FACSVia, FACSCantoII, and EPICSXL were 0.900, 0.950, 0.954, and 0.876, respectively; and the average deviations were −73.99, −40.78, −29.32, and −22.75 cells/μL, respectively.
Strong positive correlations and good consistency were observed between the CD4 count tested by POC and flow cytometers. These findings provide theoretical support for new-style HIV labs and one-stop services, which can provide shorter testing duration and simpler testing processes, so that the most comprehensive testing results can be obtained in the shortest amount of time.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed