2022 Vol. 4, No. 46
The first imported case of monkeypox (MPX) from the mainland of China was reported in September 2022. Herein, the study reports the isolation and characterization of MPX virus (MPXV) in this case.
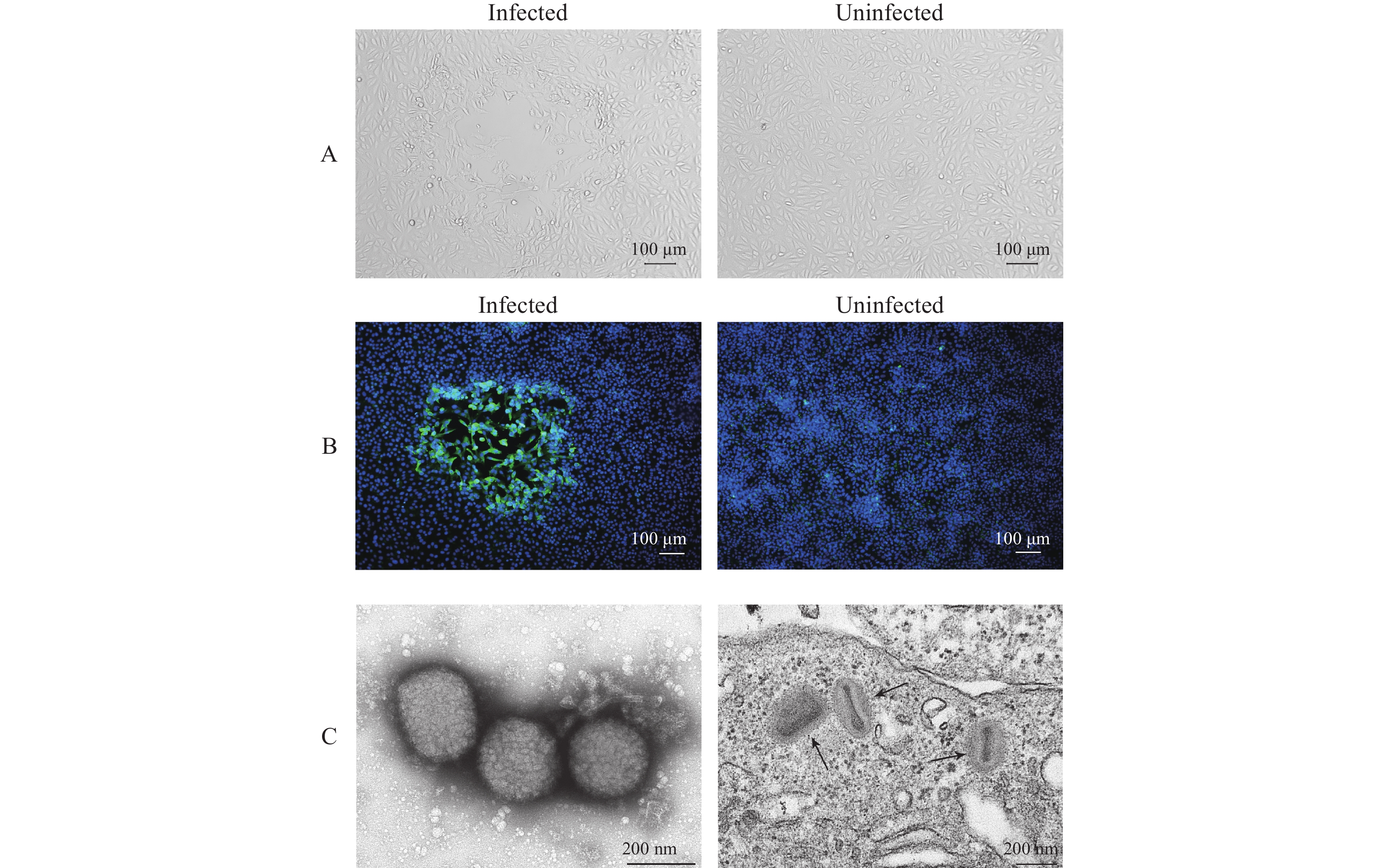
Clinical specimens including skin blister fluid, oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal swabs, and blood were collected and inoculated onto Vero cells. The isolated virus was identified as MPXV using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), cytopathic effects (CPEs), immunofluorescence assay (IFA) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Plaque assays were employed to quantify infectious plaque-forming units (PFUs). The plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT) was developed to determine the neutralizing antibody (nAb) against MPXV.
MPXV replication was confirmed with qPCR. Typical CPEs were observed 48 h post-incubation. The isolated virus was named MPXV-B.1-China-C-Tan-CQ01. IFA showed that MPXV reacted with serum of MPX case. Orthopoxvirus morphology was observed using TEM. The virus titer increased to >106 PFU/mL after three passages. The serum PRNT 50% neutralization titer (NT50) was 35 for the MPX patient 6 days after symptom onset.
The study successfully isolated the first MPXV strain in the mainland of China, MPXV-B.1-China-C-Tan-CQ01. Infectious titration and PRNT methods have been developed. The study provides key resources and technical platforms for further research as well as anti-viral drug and vaccine development against MPX.
The ease of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) non-pharmacological interventions and the increased susceptibility during the past COVID-19 pandemic could be a precursor for the resurgence of influenza, potentially leading to a severe outbreak in the winter of 2022 and future seasons. The recent increased availability of data on Electronic Health Records (EHR) in public health systems, offers new opportunities to monitor individuals to mitigate outbreaks.
We introduced a new methodology to rank individuals for surveillance in temporal networks, which was more practical than the static networks. By targeting previously infected nodes, this method used readily available EHR data instead of the contact-network structure.
We validated this method qualitatively in a real-world cohort study and evaluated our approach quantitatively by comparing it to other surveillance methods on three temporal and empirical networks. We found that, despite not explicitly exploiting the contacts’ network structure, it remained the best or close to the best strategy. We related the performance of the method to the public health goals, the reproduction number of the disease, and the underlying temporal-network structure (e.g., burstiness).
The proposed strategy of using historical records for sentinel surveillance selection can be taken as a practical and robust alternative without the knowledge of individual contact behaviors for public health policymakers.
The implementation of public health and social measures (PHSMs) was an effective option for controlling coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, evidence is needed to evaluate these PHSMs’ effects on the recently emerged variant Omicron.
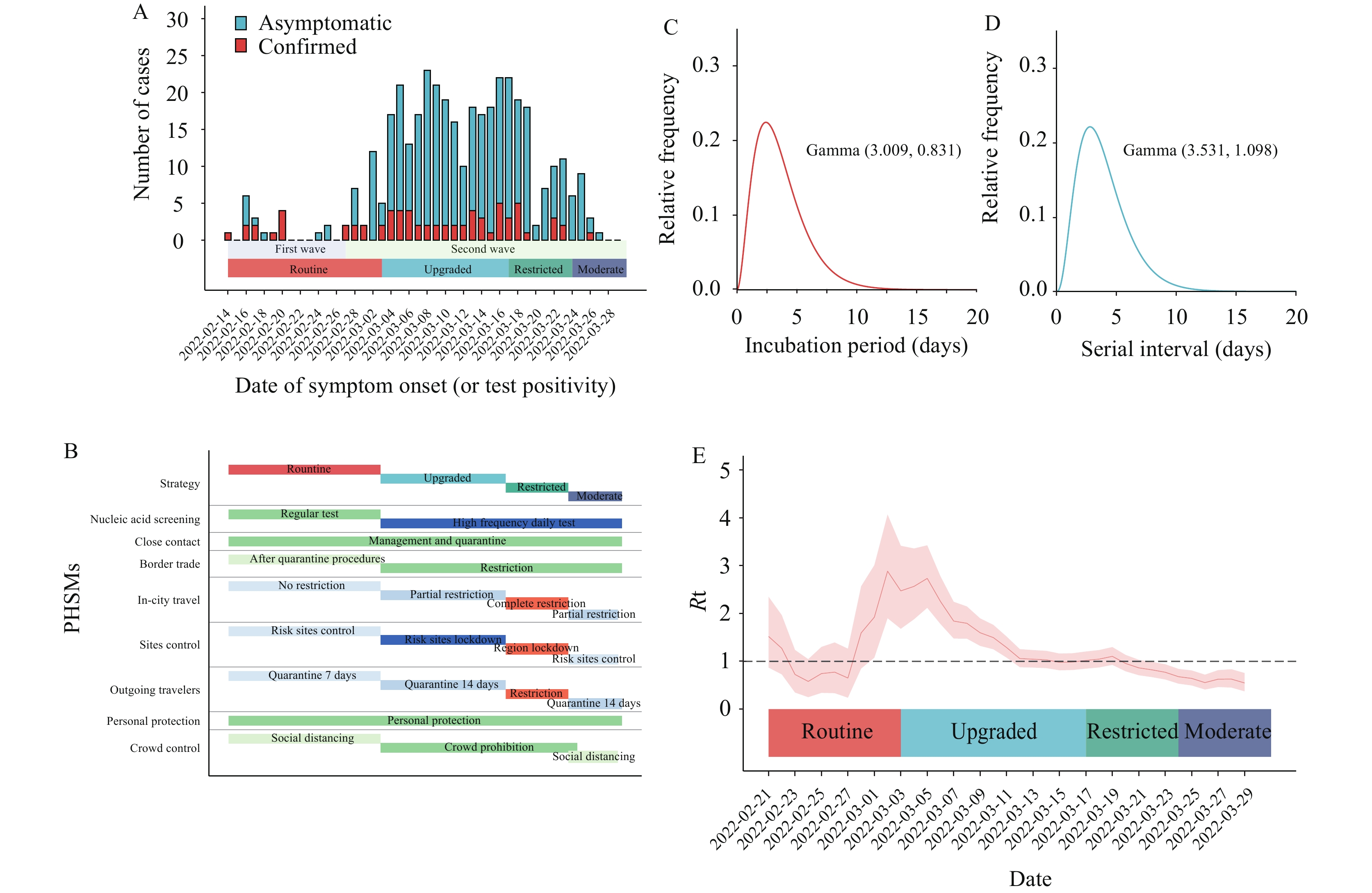
This study investigated variant Omicron BA.2’s outbreak in Ruili City, Yunnan Province, China. The disease transmission dynamics, spatiotemporal interactions, and transmission networks were analyzed to illustrate the effect of PHSM strategies on Omicron spread.
A total of 387 cases were related to the outbreak. The time-varying reproduction number was synchronized with PHSM strategies. Spatiotemporal clustering strength presented heterogeneity and hotspots. Restricted strategies suppressed temporal and spatial relative risk compared with routine and upgraded strategies. The transmission network presented a steeper degree distribution and a heavier tail under upgraded strategies. Phase transformation and distinctive transmission patterns were observed from strategy-stratified subnetworks.
The tightened response strategy contained reproduction of the virus, suppressed spatiotemporal clustering, and reshaped the networks of COVID-19 Omicron variant transmission. As such, PHSMs against Omicron are likely to benefit future responses as well.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron subvariant has a stronger transmission capacity and faster transmission speed than the previous strain.
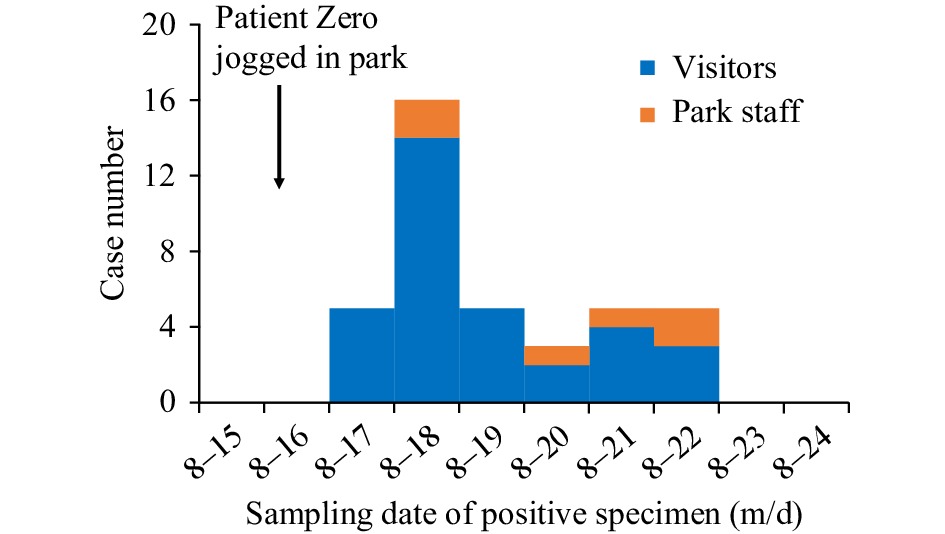
The first coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) case infected with the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariant BA.2.76 who caused local transmission was reported in Chongqing Municipality on August 16, 2022. For 35 minutes, the Patient Zero jogged along a lake at a local park without wearing a mask. Among the 2,836 people potentially exposed at the time, 39 tested positive. Overall, 38 out of 39 cases did not wear a mask on the morning of August 16. All 39 cases lacked any previous exposure to the variant before testing positive on their nucleic acid test.
It is essential to maintain personal wellbeing by ensuring one maintains personal protection and follows regulated guidelines such as maintaining safe distances from others both indoors and outdoors.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed