2022 Vol. 4, No. 43
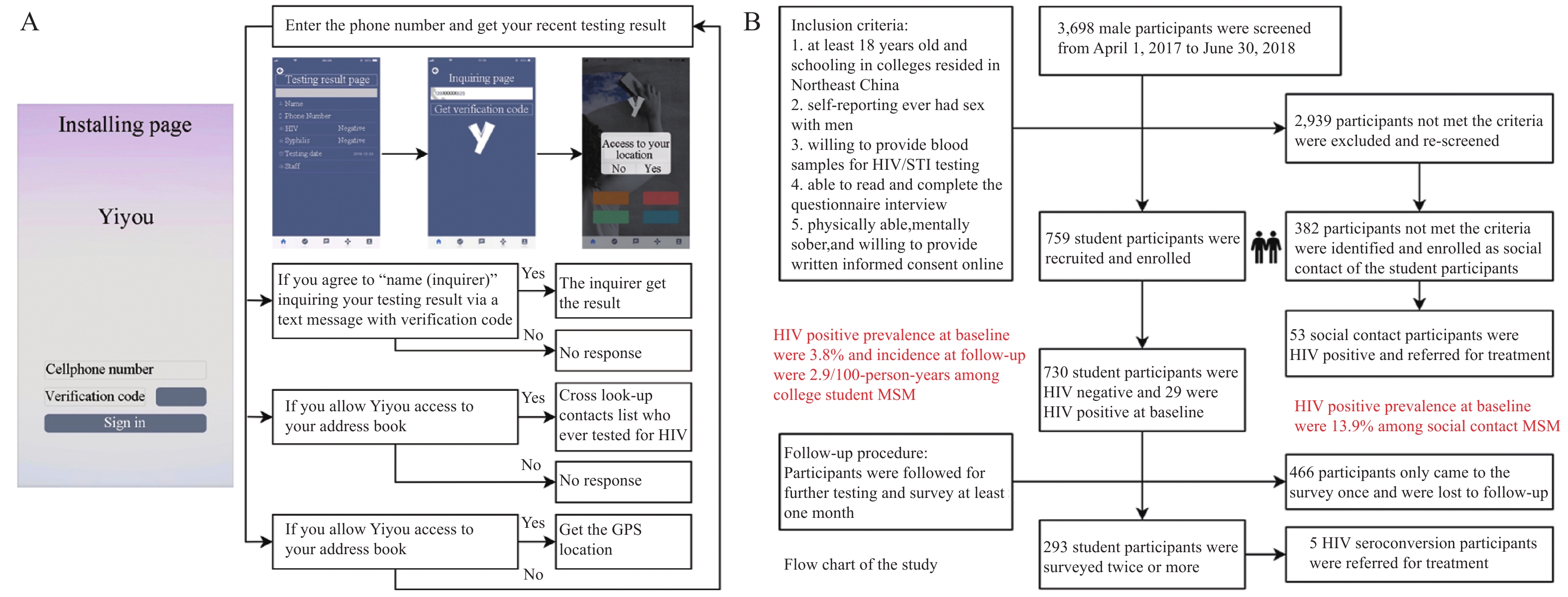
Men who have sex with men (MSM) bear a disproportionate burden of new human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infections and young MSM demonstrate parallel internet-driven HIV incident infection and dynamic social network.
The HIV positive prevalence and incidence among college MSM were 3.8% and 2.9 per 100 person-years, respectively, while these rates were 13.9% and 10.5 per 100 person-years, respectively, among their social contacts. The overall HIV positive prevalence was 7.2% in Northeast China. HIV-positive MSM have comparatively more social contacts than HIV-seronegative MSM.
Hyper-linkages found in app-based social networks play an important role in HIV transmission via risky sexual behavior and suggest options for online intervention to promote HIV prevention.
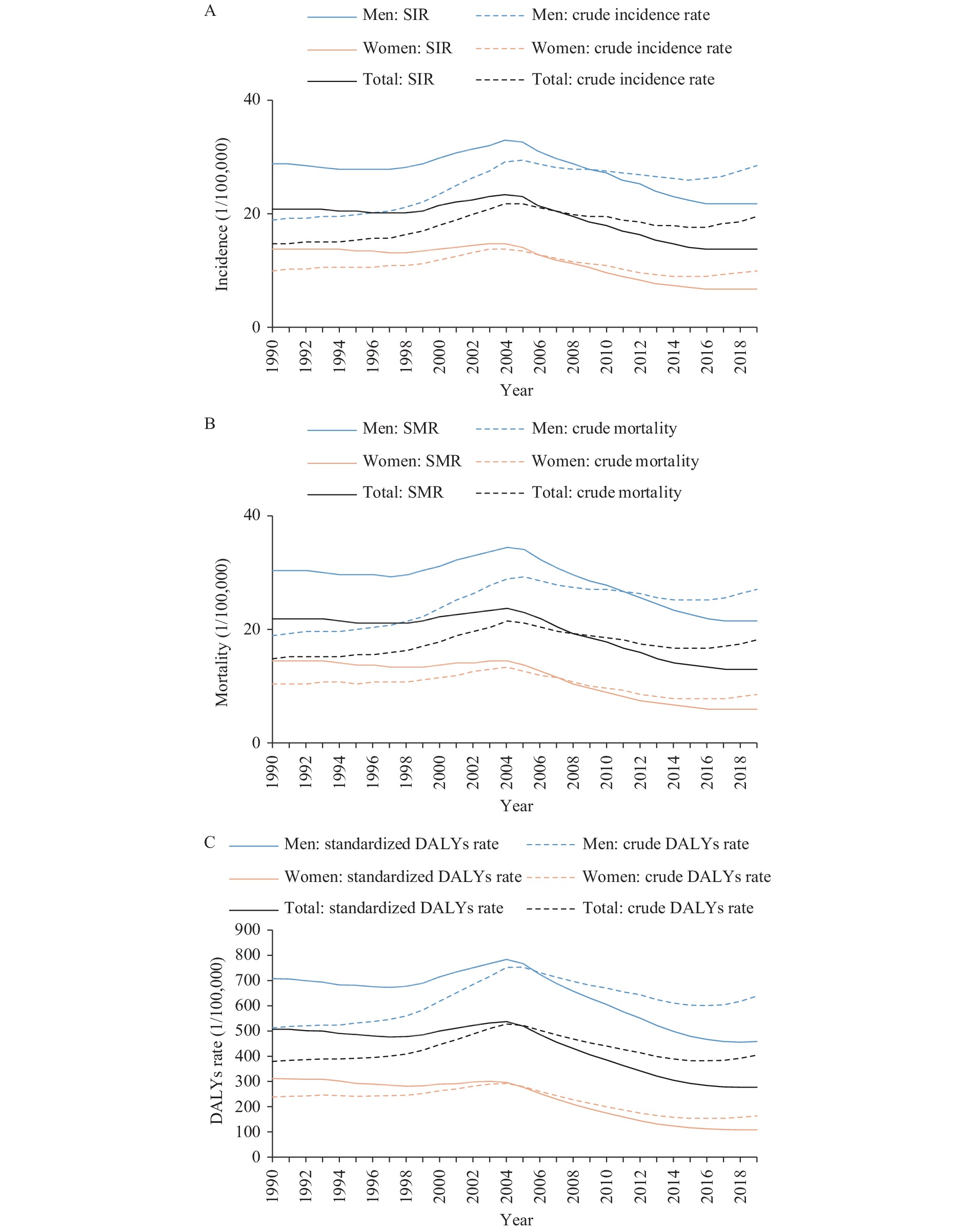
Esophageal cancer (EC) is one of the most common malignant tumors in China. The new cases and deaths in China account for more than half of the world, and the disease burden of esophageal cancer is serious.
From 1990 to 2019, the disease burden of EC in China showed a decrease overall; it first increased between 1990 and 2004, but then decreased between 2004 and 2019. The burden of EC in men was much higher than that in women. Age was an important factor affecting the burden of EC, with disease burden rising rapidly after 40 years old.
The screening, early diagnosis, and treatment for EC should continue to be strengthened in China. Middle-aged and elderly men are high-risk groups of EC and should be a key population for EC prevention and control.
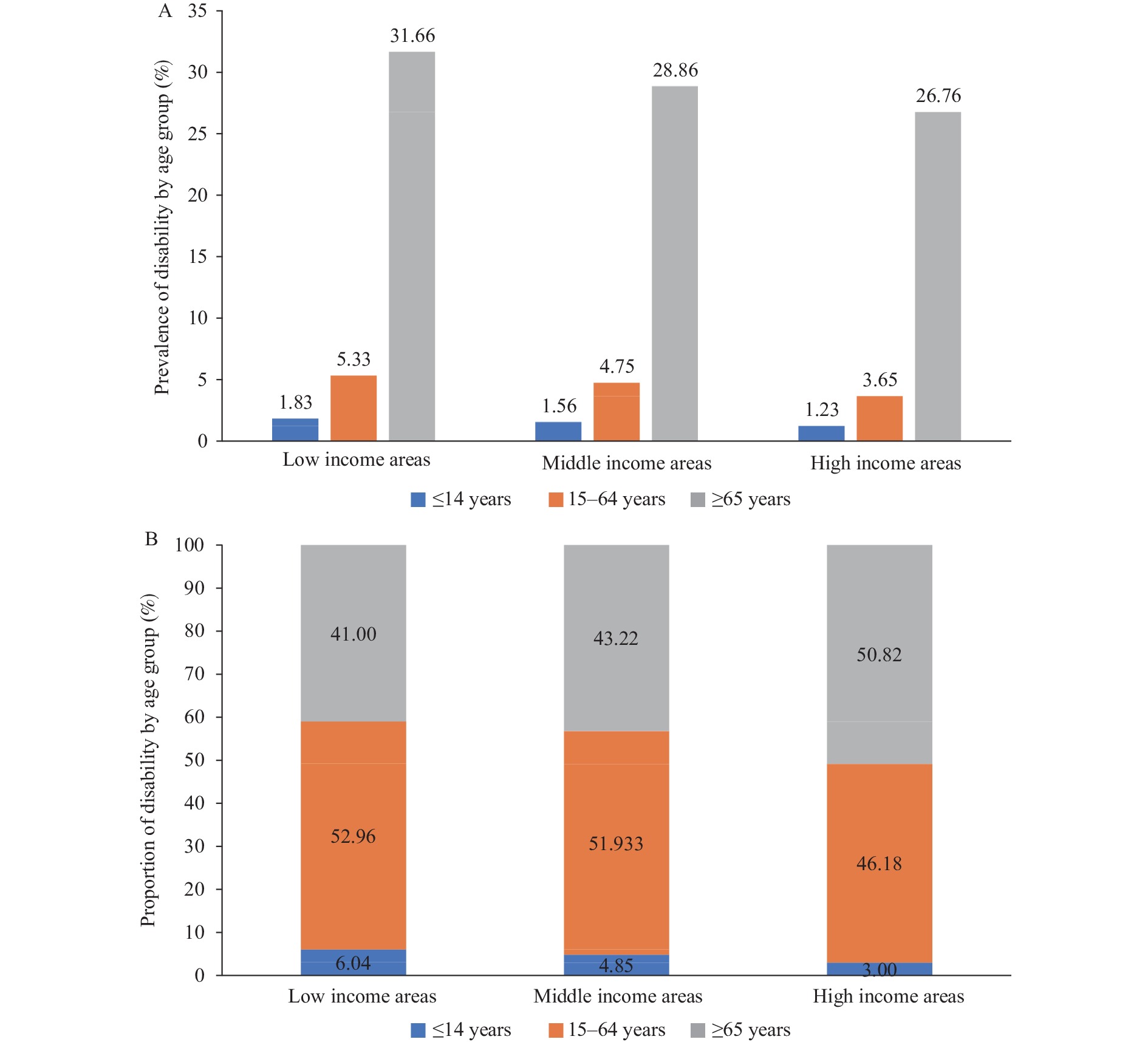
Understanding the regional distributions of disability is helpful for policymaking in precise disability prevention and control, especially in China. However, only a few studies have focused on the regional distributions of disability and their relationships with socioeconomic conditions, and almost all of them have ignored the variances of disability within provinces in China.
This research found that with the increase in the regional income level, the prevalence of disability showed a decreasing trend. The aging process of disability in high-income regions is more serious than that in other income level regions, and with the improvement of income level, the prevalence of disability in males declines rapidly.
The study analyzed the county-level distribution patterns of disability and their relationship with socioeconomic factors to provide a basis for implementing regional policies on disability prevention and control.
The prevalence of birth defects (BDs) at ≥28 gestational weeks in China has declined significantly in recent years. However, a few studies have implied that the prevalence is underestimated due to pregnancies with severe BDs often being terminated before 28 weeks of gestation. This study sought to contribute to this data conflict by determining the total prevalence of BDs throughout the entirety of pregnancies, depicting the epidemiological distribution of BDs in Shaanxi Province, and examining the impact of pregnancy termination before 28 weeks of gestation on overall BD prevalence.
Based on data extracted from the provincial Birth Defects Surveillance Network in Shaanxi Province, from 2014 to 2020, the trends of 18 frequent, major BDs at any gestational age were analysed.
The total prevalence of BDs throughout pregnancy in Shaanxi Province increased significantly from 2014 to 2020, partly due to the inclusion of slight congenital heart diseases. It was also shown that the prevalence of all major types of BD had been previously underestimated, particularly severe external BDs, anywhere from 10% to 100% due to the previous sole measurement of terminations after 28 gestational weeks. Neural tube defects, however, remained one of the top five BDs with the highest total prevalence.
The exclusion of pregnancy terminations <28 weeks of gestation resulted in a severe underestimation of the total birth prevalence of BDs, particularly severe external defects. To estimate the true population-level prevalence of BD better, the current BD surveillance system should include pregnancy terminations before 28 weeks of gestation.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed