2022 Vol. 4, No. 41
Multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is a critical global public health problem.
Sputum cultures and lung images show a strong association with treatment outcomes, serving as a multi-dimensional approach to identify MDR-TB patients with poor outcomes.
The results imply that funds and policy investments should be increased by early monitoring of MDR-TB patients, especially regarding imaging and sputum bacterium. By informing physicians on changes to the therapeutic schedule, treatment outcomes can be improved.
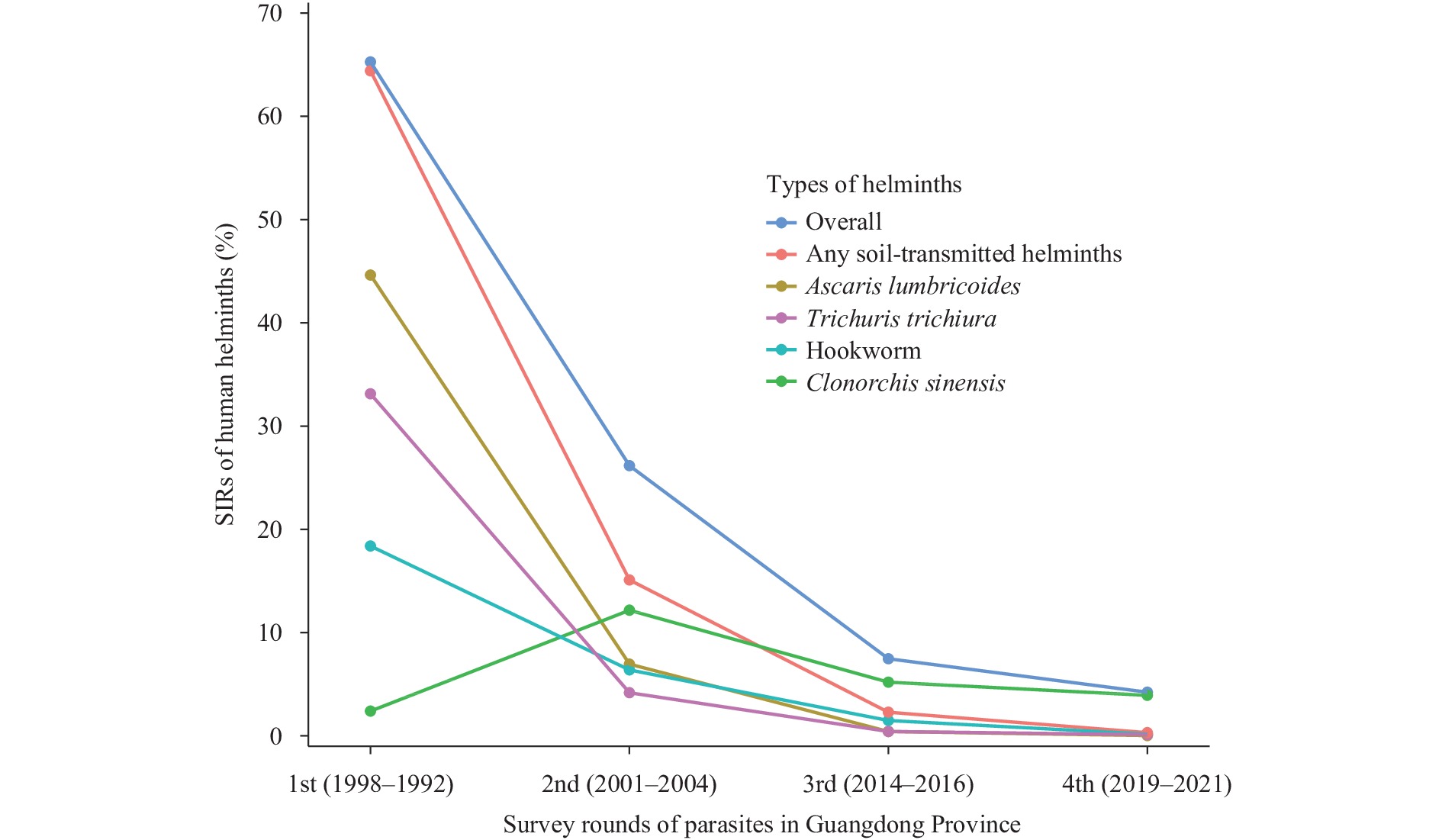
Although helminth infections threaten millions of people worldwide, the spatiotemporal characteristics remain unclear across China. This study systematically describes the spatiotemporal changes of major human helminth infections and their epidemiological characteristics from 1988 to 2021 in Guangdong Province, China.
The survey data in Guangdong Province were primarily obtained from 3 national surveys implemented during 1988–1992, 2001–2004, and 2014–2016, respectively, and from the China Information System for Disease Control and Prevention during 2019–2021. A modified Kato-Katz technique was used to detect parasite eggs in collected fecal samples.
The overall standardized infection rates (SIRs) of any soil-transmitted helminths (STH) and Clonorchis sinensis decreased from 65.27% during 1988–1992 to 4.23% during 2019–2021. In particular, the SIRs of STH had even more of a decrease, from 64.41% during 1988–1992 to 0.31% during 2019–2021. The SIRs of Clonorchis sinensis in the 4 surveys were 2.40%, 12.17%, 5.20%, and 3.93%, respectively. This study observed different permutations of gender, age, occupation, and education level on the SIRs of helminths.
The infection rate of STH has substantially decreased. However, the infection rate of Clonorchis sinensis has had fewer changes, and it has become the dominant helminth.
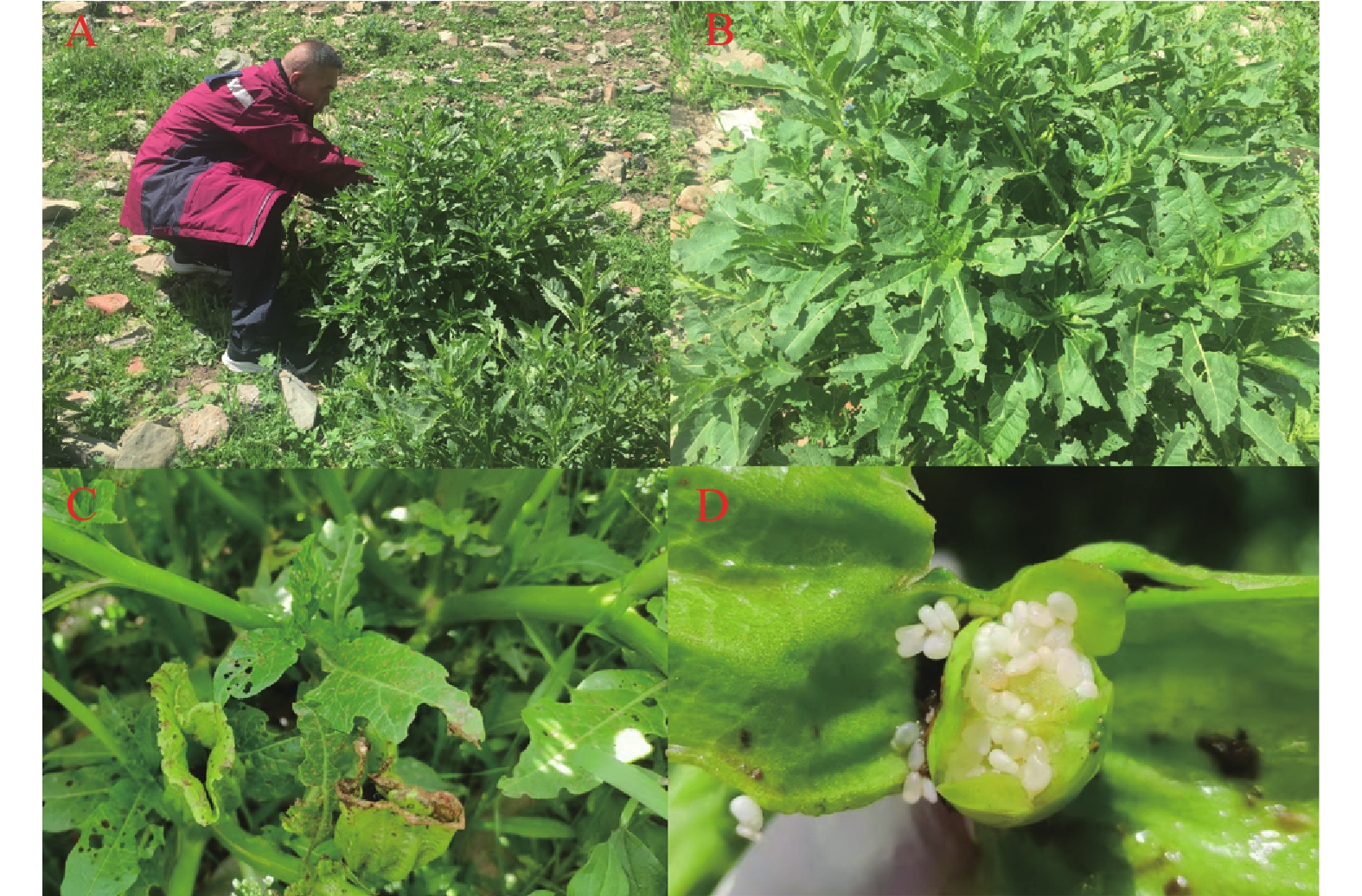
Anisodus tanguticus belongs to the Solanaceae family. The plant is toxic due to the tropane alkaloids it contains and can cause poisoning when it is ingested or used inappropriately.
A poisoning outbreak involved 10 patients, and one death was caused by Anisodus tanguticus. The etiological association of plant exposure and poisoning was confirmed with evidence from an epidemiological investigation, clinical manifestations, plant identification and a toxin analysis.
The risk of poisoning caused by mistakenly collecting and ingesting tropane alkaloid-containing plants should be highlighted, and public health practitioners should be on alert.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed