2020 Vol. 2, No. 20
What is already known on this topic?
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) is endemic in Liaoning Province. Both Seoul and Hantaan virus are circulating in rodents, and epidemic outbreaks and sporadic cases have been recorded every year since the disease was recognized.
What is added by this report?
The epidemic trend of HFRS over the past 20 years (1999–2018) in Liaoning was analyzed, which showed both regional complexity and consistence with the epidemic in China. Genetic and antigenic stability of the circulating hantavirus were demonstrated, which suggested the effectiveness of the approved inactivated vaccine currently used in China.
What are the implications for public health practice?
Precise risk-based strategic practices that are integrated and regional are required for further improvement of the prevention and control of HFRS.
What is already known about this topic?
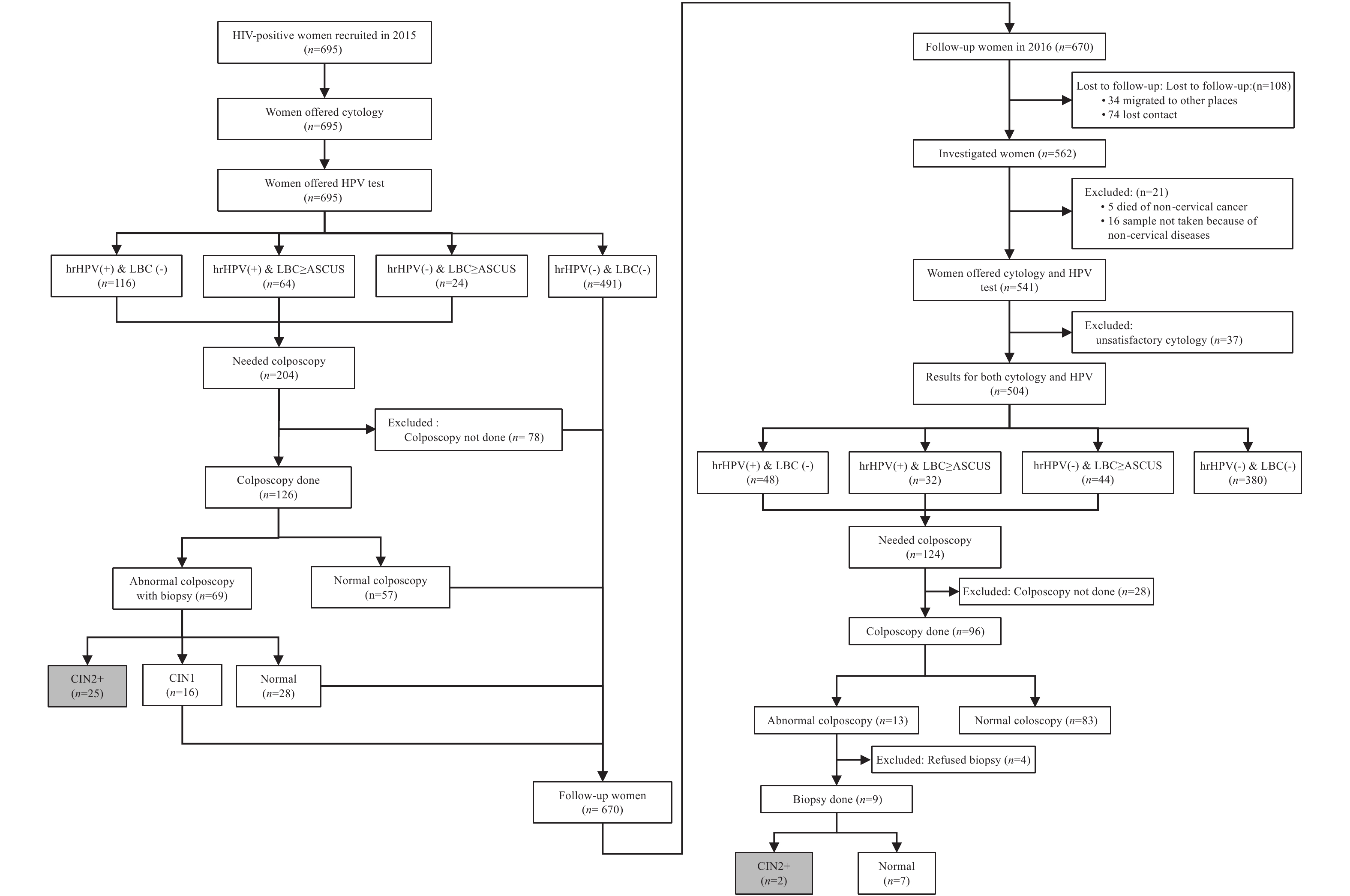
Cervical cancer is one of the most common cancers among HIV-positive women. The World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended a program of cervical cancer screening for HIV-positive women. Prospective follow-up studies and specific recommendations on cervical cancer screening for HIV-positive women in China are not currently being performed.
What is added by this report?
Among HIV-positive women from high HIV-burden areas of China, the detection rate of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or worse (CIN2+) in the baseline survey and the incidence of CIN2+ in the follow-up survey after 18 months was high. High-risk human papillomavirus (hrHPV) infection and early (< 18 years old) sexual debut was associated with CIN2+ among HIV-positive women.
What are the implications for public health practice?
HIV-positive women need cervical cancer prevention and regular screening services. These women might benefit from a cervical cancer screening program that combines hrHPV test and cytology and has short intervals between screenings.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed