2020 Vol. 2, No. 21
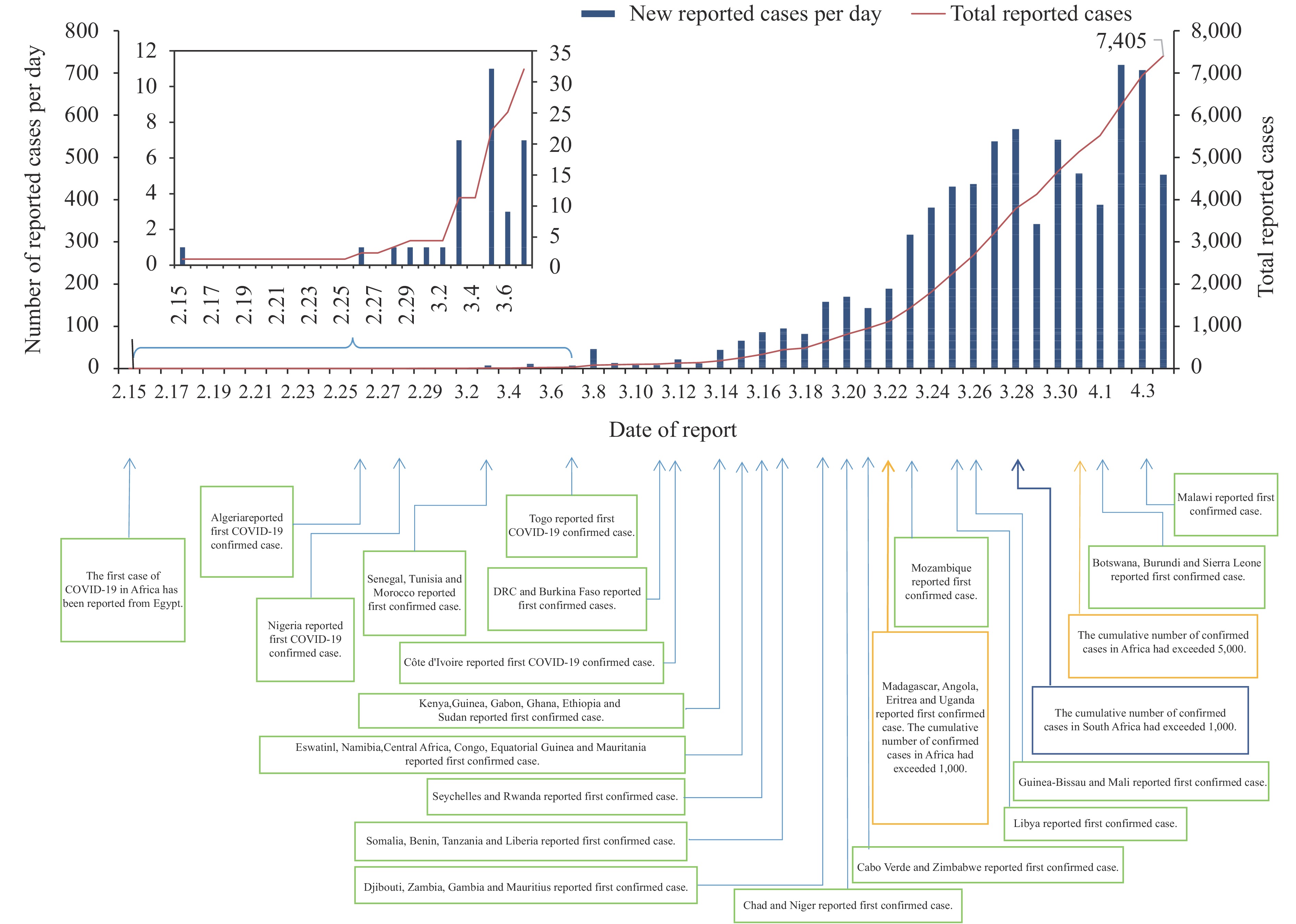
Since the first COVID-19 confirmed case was reported, the current epidemic in Africa has rapidly increased.
As of April 4, 2020, a total of 7,405 confirmed cases and 305 deaths had been reported from 51 countries across Africa. The cumulative number of reported COVID-19 cases varied among the five regions of Africa, of which northern Africa reported the largest number of confirmed cases. The five countries with the highest number of cases are South Africa, Algeria, Egypt, Morocco, and Tunisia.
Early detection, early isolation, early reporting, and early treatment of the COVID-19 are important and critical measures for the successful control of further transmission of COVID-19. Now more stringent prevention and control measures have been implemented in Africa, but due to often insufficient basic medical facilities and medical services, Africa is still facing challenges to the pandemic and needs to strengthen national health systems and develop immediate and future health plans.
What is already known about this topic?
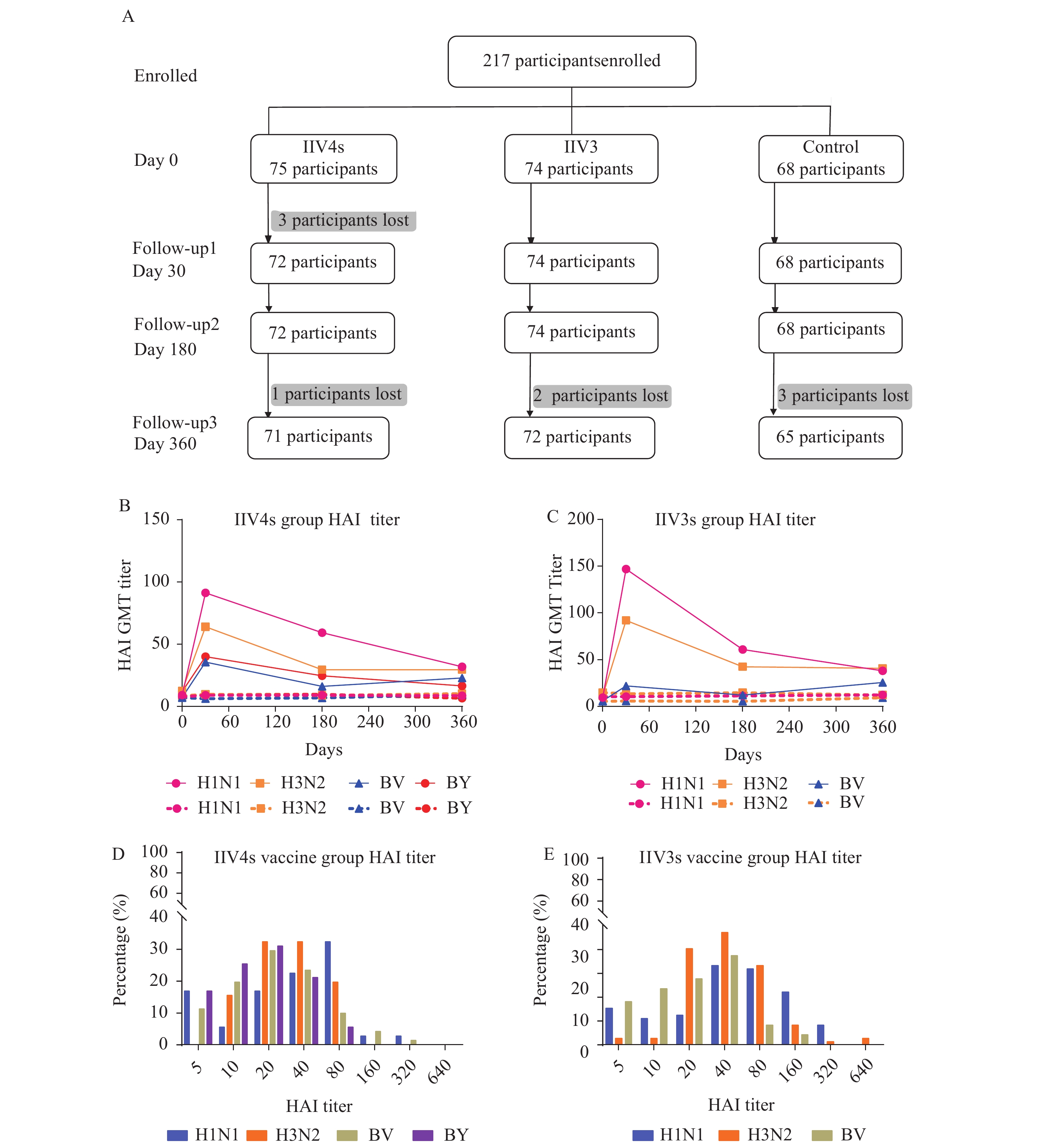
Vaccinations are the most effective way to prevent influenza virus infections and severe outcomes. Influenza vaccine effectiveness can vary by seasons.
What is added by this report?
This report monitors the antibody level among the population over time after administration of the quadrivalent or trivalent split influenza vaccine.
What are the implications for public health practice?
Real-time monitoring of serum antibody changes after vaccination provides important data for the development of reasonable and effective strategies for influenza prevention and control.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed