2022 Vol. 4, No. 24
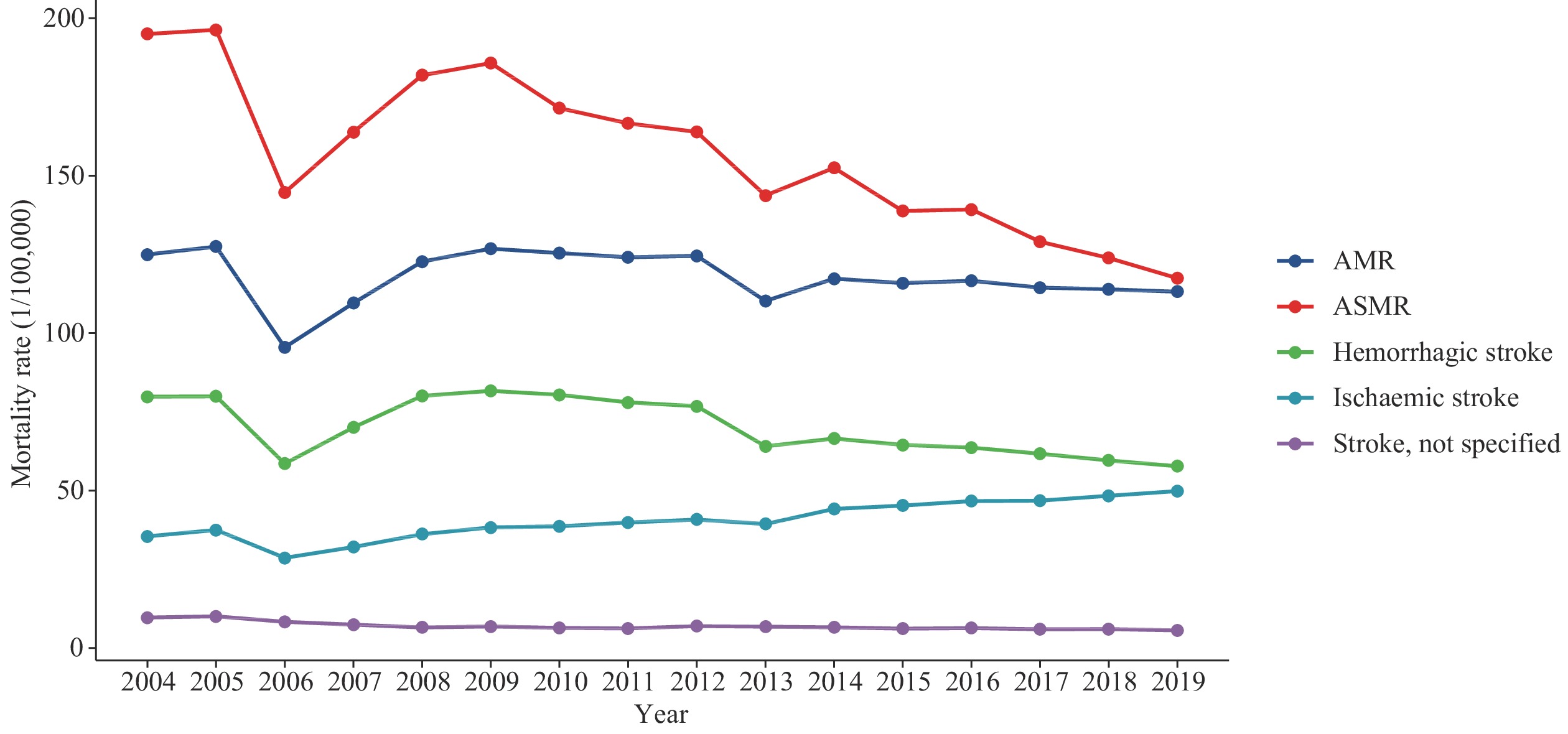
Stroke has been the leading cause of death in China for decades. This study described the trends in stroke mortality in China from 2004 to 2019.
Data was obtained from the National Disease Surveillance Point (DSP) system. A descriptive analysis was conducted. The adjusted mortality rate (AMR) and age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) of stroke were calculated.
From 2004 to 2019, the ASMR substantially decreased, with a reduction of 39.8%, but the AMR stayed relatively stable. The mortality rate of stroke in rural areas was consistently higher than in urban areas. A geographical gradient in mortality of stroke was also apparent, with an increased rate in the western part of China and a decreased rate in the eastern part of China. In central China, the rate remained relatively stable.
Although the ASMR of stroke continued to decline in China, the stagnant crude mortality rates suggested that China had not achieved sufficient decline to offset the demographic forces of population growth and ageing. More vigorous and effective prevention and treatment strategies are urgently needed to mitigate the disease burden of stroke in China, especially in areas with high stroke burden and limited resources.
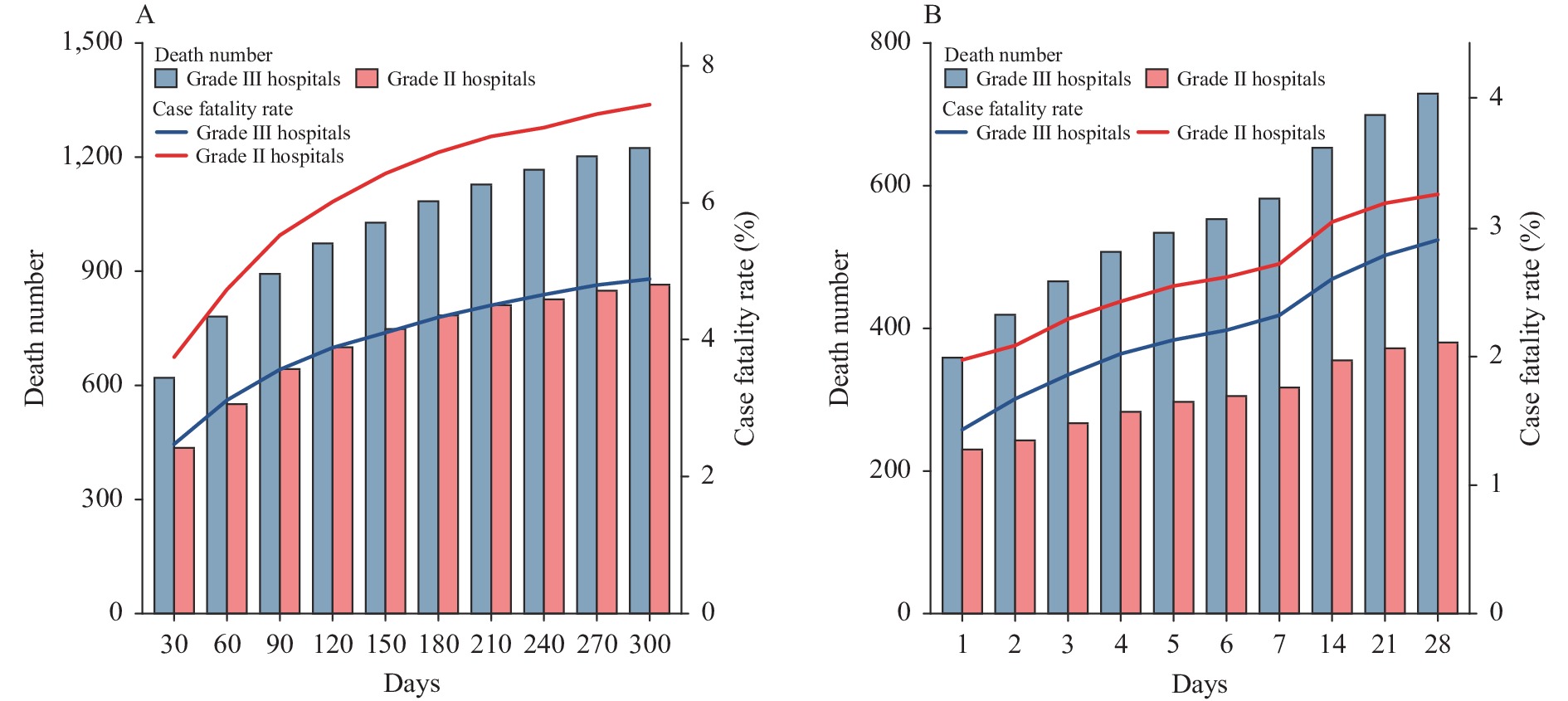
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is the most serious form of cardiovascular diseases. The case fatality rate (CFR) of AMI patients is an important index to reflect the prognosis of AMI.
During the study period, the overall 30-day, 60-day, and 90-day CFR of AMI was 5.9%, 6.9%, and 7.6%, respectively. The CFRs in grade Ⅲ hospitals were lower than in grade Ⅱ hospitals, and the in-hospital CFR was significantly lower than that in post-discharge out-of-hospital.
This study can provide evidence for targeted prevention and highlight the need to strengthen the level of treatment of patients with AMI in grade Ⅱ hospitals.
High sodium and low potassium in 24 h urinary excretion were associated with elevated blood pressure.
With increasing body mass index levels, decreasing unit urinary sodium excretion was more effective in reducing systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and increasing unit urinary potassium excretion was more effective in reducing diastolic blood pressure.
Reducing sodium and increasing potassium intake was more effective in reducing blood pressure in overweight and obese non-hypertensive adults compared to underweight and normal weight adults.
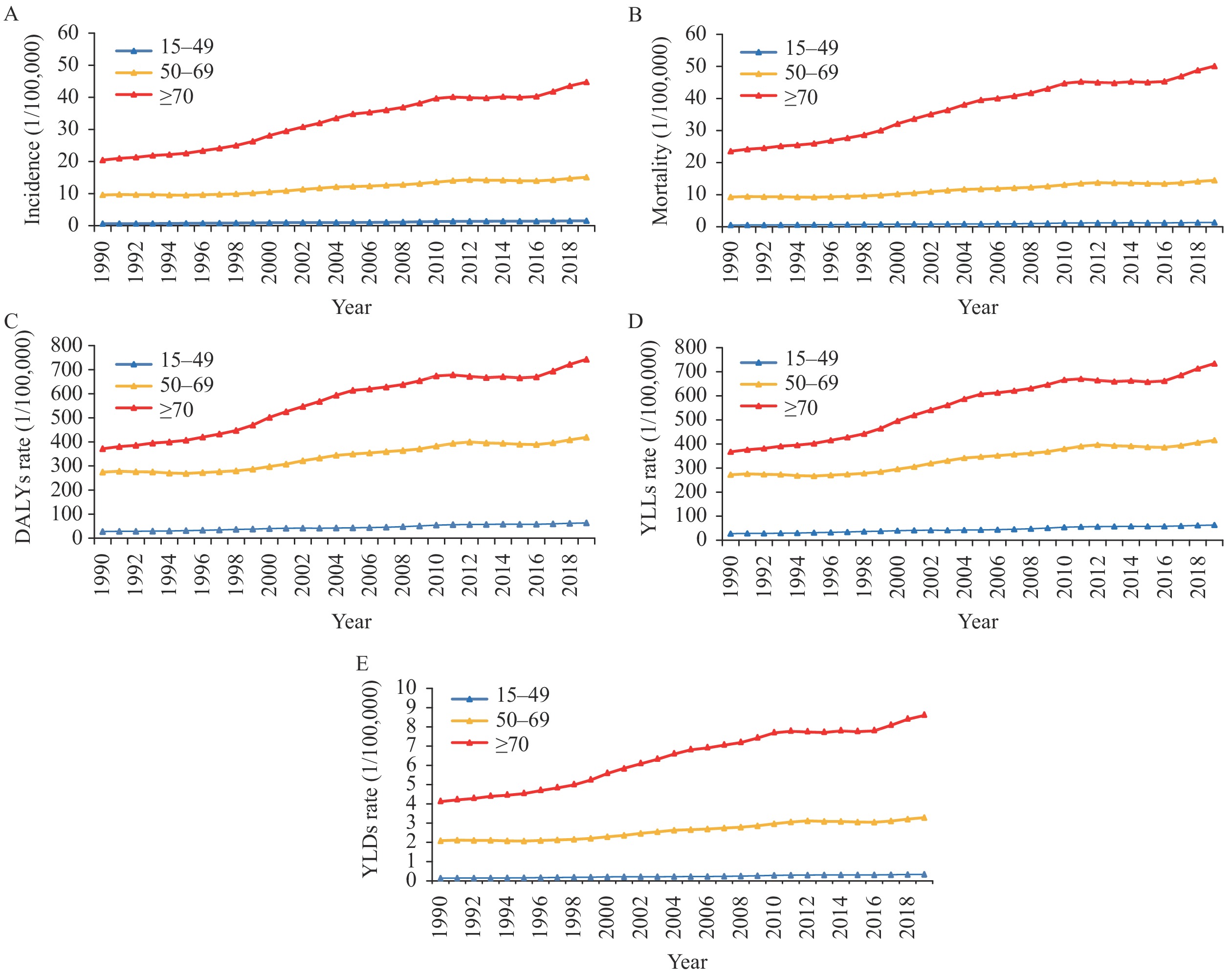
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most malignant tumors of the digestive tract, and the etiology is not clear. Pancreatic cancer has a poor prognosis and high mortality.
Compared with 1990, the burden of pancreatic cancer in China increased significantly in 2019. In 1990 and 2019, the disease burden indicator of male pancreatic cancer was higher than that of females, and pancreatic cancer became more common as age increased, especially above 50 years old.
This study mainly provided scientific data and references for the prevention and control of pancreatic cancer in people aged 50 and above.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed