-
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death worldwide (1) and account for more than 40% of deaths in China (2). Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is a common and the most serious form of CVD with a high mortality rate (3). The World Health Organization (WHO) monitoring trends and determinants in CVDs MONICA project reported that AMI was the cause of approximately three-quarters of CVD deaths across 37 populations in 21 countries over the past few decades (4). The case fatality rate (CFR) of AMI patients is an important index to reflect the prognosis of AMI. It can provide information on severity of AMI and help determine the focus of secondary prevention (5). A few studies showed that in-hospital CFR of AMI patients in China had decreased in recent years, but most of them were single-city studies with limited geographical coverage or focusing on grade Ⅲ hospitals (5). No studies were carried out to address the post-discharge out-of-hospital CFR. This study used data of AMI patients from 253 chest pain centers (CPC) in China from 2019 to 2020 to estimate the CFR of AMI (6). The study found that the CFR of AMI in-hospital was significantly lower than that of post-discharge out-of-hospital, and the CRF in grade Ⅱ hospitals was higher than that in grade Ⅲ hospitals. In this study, the overall CFR of AMI post-discharge out-of-hospital was 6.0% and grade Ⅲ hospitals was 5.2%. Much more efforts should be made to promote the level of treatment of patients with AMI in grade Ⅱ hospitals.
The study linked patients’ data to China National Death Registration System by unique national identification numbers to obtain the accurate vital status for all patients within CPC. The system collected all deaths outside of hospitals and in hospitals, covering nearly 99% of the counties and districts in China. CPC data was obtained from the CPC reporting system initiated since 2015 and the data quality was improved gradually. We used patients’ data from CPC in 2019 and 2020 when China Chest Pain Center Quality Control Indicators and Assessment Measures (Second Edition) and the China Chest Pain Center Normalization Quality Control Plan were carried out to form a three-level external and internal quality control mechanism for hospitals (6). The study first selected 885 CPCs whose completeness of patients’ ID was higher than 90%. In the next step, CPCs with AMI patients less than 50 in 2019 and 2020 were excluded as some CPCs did not report data from all of their patients. A total of 36,689 AMI patients from 253 CPCs from 23 provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) (10 from east, 6 from central, and 7 from west) were included in the analysis. These patients were identified as having ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) by discharge diagnosis. The study also considered both in-hospital and post-discharge out-of-hospital deaths and calculated the 30-day, 60-day, and 90-day CFR of AMI patients by the following formula to define the proportion of patients who died within 30 days, 60 days, and 90 days in all AMI patients admitted to CPCs:
30-day/60-day/90-day CFR = the number of deaths occurring within 30/60/90 days from date of admission to date of death/the number of all AMI patients in CPC
In-hospital death and post-discharge out-of-hospital death were defined according to death’s place in the death certificate. Categorical variables were presented as counts (%). The 30-day, 60-day, and 90-day CFRs of AMI were also calculated in different age groups, sex, AMI types, risk factors, comorbidities and hospital levels. SAS software package (version 9.4; SAS Institute, Inc. Cary, NC, USA) was used for all statistical analyses.
This study included 36,689 patients with AMI, 74.0% were males, 91.4% were older than 45 years, 64.5% were STEMI, and 35.5% were NSTEMI; many AMI patients presented comorbidities, including 2,354 (6.4%) with stroke, 847 (2.3%) with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), 249 (0.7%) with cancer, and 6,785 (18.5%) with diabetes mellitus. Overall, 11,638 (31.7%) were from grade Ⅱ hospitals and 25,051 (68.3%) were from grade Ⅲ hospitals (Table 1).
Variable N Proportion (%) Total 36,689 100.0 Year 2019 10,272 28.0 2020 26,417 72.0 Age group (years) < 45 3,164 8.6 45–65 16,794 45.8 > 65 16,731 45.6 Sex Male 27,136 74.0 Female 9,553 26.0 Type of MI STEMI 23,672 64.5 NSTEMI 13,017 35.5 Risk factors Hypertension 17,737 48.3 Hyperlipidemia 8,258 22.5 Current smoking 13,285 36.2 Obesity 2,588 7.1 Family history of CVD 926 2.5 Comorbidity Stroke 2,354 6.4 COPD 847 2.3 Cancer 249 0.7 Diabetes mellitus 6,785 18.5 Hospital level Grade Ⅱ 11,638 31.7 Grade Ⅲ 25,051 68.3 Notes: Grade II hospitals are generally affiliated with medium size cities, counties, or districts and contain 100–500 beds. Grade III hospitals are generally located in major cities with more than 500 beds and offer the highest-quality care.
Abbreviations: MI=myocardial infarction; STEMI=ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction; NSTEMI=non-ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction; CVD=cardiovascular disease; COPD=chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Table 1. Baseline Characteristics of 36,689 acute myocardial infarction patients from 253 chest pain centers in China, 2019–2020.
AMI patients’ overall 30-day, 60-day, and 90-day CFRs were 5.9%, 6.9%, and 7.6%, respectively. The CFR increased with age and was higher in females than in males. The 30-day CFR of STEMI was 6.6%, higher than NSTEMI (4.7%). Patients with cancer had the highest CFR on different days. Compared with the grade Ⅱ hospitals, the CFR of AMI patients in grade Ⅲ hospitals was much lower (Table 2).
Variable Case fatality rate (%) 30-day 60-day 90-day Total 5.9 6.9 7.6 Year 2019 4.6 5.8 6.7 2020 6.4 7.4 7.8 Age group (years) < 45 1.9 2.1 2.2 45–65 3.1 3.5 3.9 > 65 9.6 11.2 12.4 Sex Male 4.7 5.5 6.1 Female 9.4 10.9 12.0 Type of MI STEMI 6.6 7.6 8.2 NSTEMI 4.7 5.8 6.6 Risk factors Hypertension 5.8 6.9 7.6 Hyperlipidemia 3.5 4.3 4.8 Current smoking 3.5 4.1 4.6 Obesity 5.3 6.1 6.8 Family history of CVD 4.8 6.0 6.7 Comorbidity Stroke 8.4 10.2 11.6 COPD 8.1 10.4 12.5 Cancer 13.7 16.9 18.5 Diabetes mellitus 6.7 7.9 8.6 Hospital level Grade Ⅱ 7.0 8.2 9.2 Grade Ⅲ 5.4 6.3 6.9 Notes: Grade II hospitals are generally affiliated with medium size cities, counties, or districts and contain 100–500 beds. Grade III hospitals are generally located in major cities with more than 500 beds and offer the highest-quality care.
Abbreviations: MI=myocardial infarction; STEMI=ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction; NSTEMI=non-ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction; CVD=cardiovascular disease; COPD=chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Table 2. Case fatality rate of patients with acute myocardial infarction in 253 chest pain centers in China, 2019–2020.
For post-discharge out-of-hospital deaths, the overall CFR was 6.0%, higher in grade Ⅱ hospitals (7.8%) than in grade Ⅲ hospitals (5.2%), and the 30-day, 60-day, and 90-day CFRs of all AMI patients in grade Ⅲ hospitals were 2.5%, 3.1%, and 3.6%, respectively, which were lower than grade Ⅱ hospitals (3.7%, 4.7%, and 5.5%, respectively) (Figure 1A). For in-hospital deaths, the overall CFR was 4.0% higher in grade Ⅱ hospitals (4.1%) than in grade Ⅲ hospitals (3.9%), and the 7-day, 14-day, and 21-day CFRs were 2.3%, 2.6%, and 2.8%, respectively, which were also lower than grade Ⅱ hospitals (2.7%, 3.1%, and 3.2%, respectively) (Figure 1B).
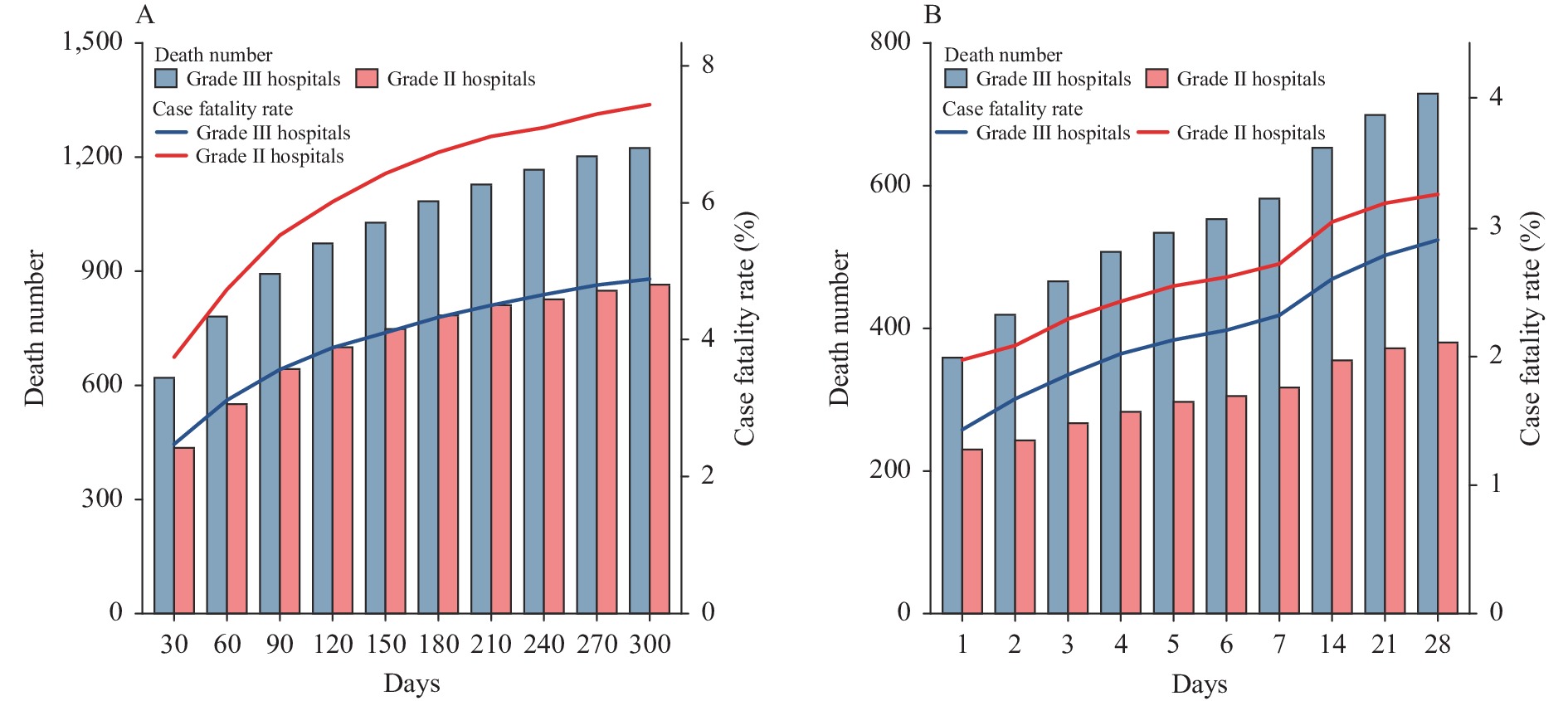 Figure 1.
Figure 1.The number of death and case fatality rate (CFR) of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in post-discharge out-of-hospital and in-hospital of Grade II and III hospitals in China, 2019–2020. (A) The number of post-discharge out-of-hospital death and CFR of AMI in Grade II and III hospitals, China, 2019–2020. (B) The number of in-hospital death and CFR of AMI in Grade II and III hospitals, China, 2019–2020. Notes: Grade II hospitals are generally affiliated with medium size cities, counties, or districts and contain 100–500 beds. Grade III hospitals are generally located in major cities with more than 500 beds and offer the highest-quality care.
-
This study provided the most recent estimates of CFR of AMI patients from CPCs in China from 2019 to 2020. First, the 30-day, 60-day, and 90-day CFR of all AMI patients were 5.9%, 6.9%, and 7.6%, respectively, 65% of the patients were STEMI patients and the CFR of STEMI patients were higher compared to that of NSTEMI patients. STEMI patients were more likely to have comorbidities (7) and NSTEMI patients lacked typical electrocardiogram changes, had a lower incidence of alarm symptoms of arrhythmia and resting chest pain, and had lower levels of blood myocardial necrosis markers, which may lead to clinical misdiagnosis and delayed treatment (8). Second, the CFR of AMI in grade Ⅱ hospitals was higher than that in grade Ⅲ hospitals, which may be related to better facilities and healthcare level of grade Ⅲ hospitals.
Compared with previous studies (5), the 30-day, 60-day, and 90-day CFRs of all AMI patients in this study were lower, which may be due to the continuous improvement of the treatment of AMI and the extensive national healthy lifestyle campaign. In addition, based on the primary purpose of “rapid diagnosis, timely treatment, reducing death, and avoiding waste,” CPCs have been gradually established in China since 2014, playing an essential first aid role. Our results also showed that three-quarters of all AMIs occurred in males. It can be explained by the fact that men are more likely to be exposed to various AMI risk factors such as smoking, alcohol abuse, unbalanced diet, and air pollution than women (9). Although there were more male patients, the CFR was much lower in men than in women. The reason may be that female patients were older than male patients, the risk of concomitant disease was higher, and the use of secondary prophylaxis drugs was significantly lower than that of males (10).
The findings of this study should be interpreted in view of several limitations. First, we only have two years of data and cannot analyze the trends of the CFR of AMI. Therefore, this study mainly describes the current situation. Second, we may underestimate the number of deaths of AMI patients due to the under-reporting in the national death registration system. The vast majority of CPCs in this study were from eastern and central PLADs, where the completeness of death registration is high and potential under-reporting from western PLADs may not have a major impact on the results. Third, we only included patients from CPC and those patients who died out-of-hospital prior to hospital admission were not covered in our study. More data from the emergency care system will be needed to address this issue. Finally, the generalization of the results is limited because the data were from hospitals with certified CPC.
-
No conflicts of interest.
HTML
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download:




