-
Introduction: Myopia has emerged as a major public health challenge affecting the visual health of children and adolescents in China. While evidence confirms the effectiveness of outdoor activity in preventing myopia, comprehensive economic analyses of its role in mitigating myopia-related diseases remain limited.
Methods: This study employed a microsimulation model to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of increasing outdoor activity across different educational stages — primary, middle, and high school — for myopia prevention in China. The model simulated myopia progression among individuals aged 6 to 18 years, with the intervention defined as an additional 40 minutes of daily outdoor activity. Outcomes measured included changes in myopia prevalence, quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), and associated medical costs.
Results: All intervention scenarios proved cost-effective, except for those targeting only the high school stage. Interventions focused on primary schools and combined primary–middle school stages not only improved health outcomes but also reduced medical costs. While the all-stages intervention yielded the greatest health benefits, its higher implementation costs make it more suitable for regions with greater resources.
Conclusion: These findings highlight the critical importance of early intervention in myopia prevention. Policymakers should prioritize outdoor activity programs at the primary school level and develop tailored prevention strategies based on local resource availability. This study provides empirical evidence for developing scientifically sound, cost-effective myopia prevention strategies for children and adolescents, with relevant implications for other developing countries facing a high myopia burden.
-
Myopia poses a significant public health challenge in China, with a prevalence of 51.9% among children and adolescents and 81.2% among high school students (1). If left uncontrolled, myopia can progress to severe visual impairments and impose substantial societal costs. While existing evidence demonstrates that outdoor activity is an effective intervention for preventing myopia, there remains a critical gap in economic analyses regarding its role in preventing myopia-related diseases. This study evaluates the cost-effectiveness of increasing outdoor activity across various educational stages in preventing myopia and its complications among children and adolescents in China. The results indicate that interventions implemented at all educational stages, with the exception of high school, are cost-effective strategies for reducing the burden of myopia.
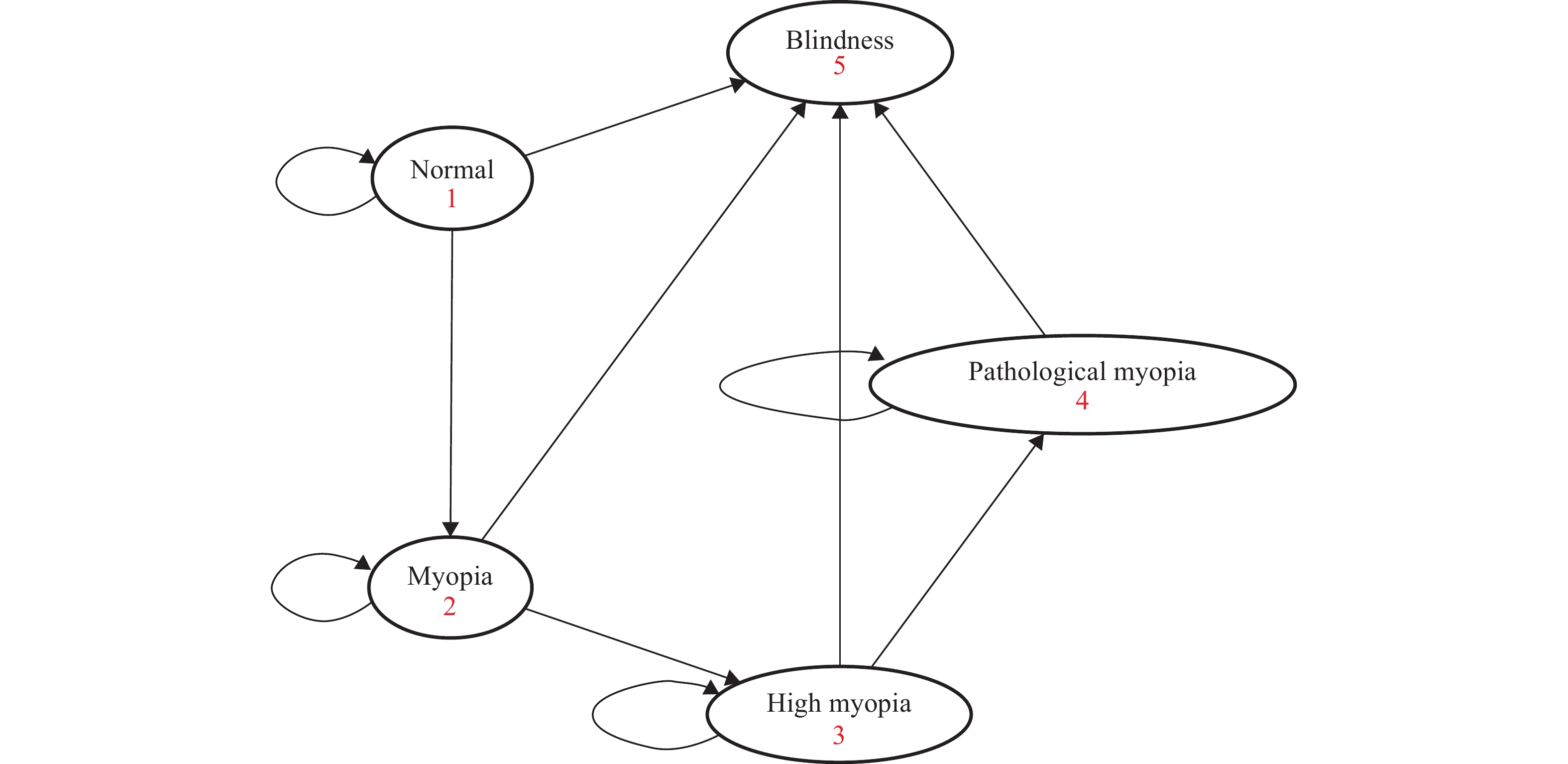
This study developed a microsimulation model to simulate myopia progression among children and adolescents aged 6 to 18 years in China. The model was validated by comparing simulated myopia prevalence with data from the 2020 national survey (Table 1) (2). Specifically, the projected myopia prevalence rates closely aligned with those observed in the 2020 national survey, indicating reasonable model validity (Figure 1). Figure 2 shows the model schematic. Briefly, the model comprised five health states: “normal,” “myopia,” “high myopia,” “pathological myopia,” and “blindness.” In each simulated year, individuals can remain in their current state, progress to a more severe state, or become blind. Interventions that reduce the risk of progression from one state to another could potentially alter the healthcare costs and quality-adjusted life years (QALYs).
Educational stage 2018 input value (%) 2020 predictive value (%) 2020 true value (%) 6 years old 14.5 14.5 14.3 Lower grades of primary school 22.3 25.7 20.7 Upper grades of primary school 49.7 47.2 50.5 Middle school 71.6 70.2 71.1 High school – 83.1 80.5 Note: “–” means that no input value was required for this stage. Table 1. Model validation against real-world data.
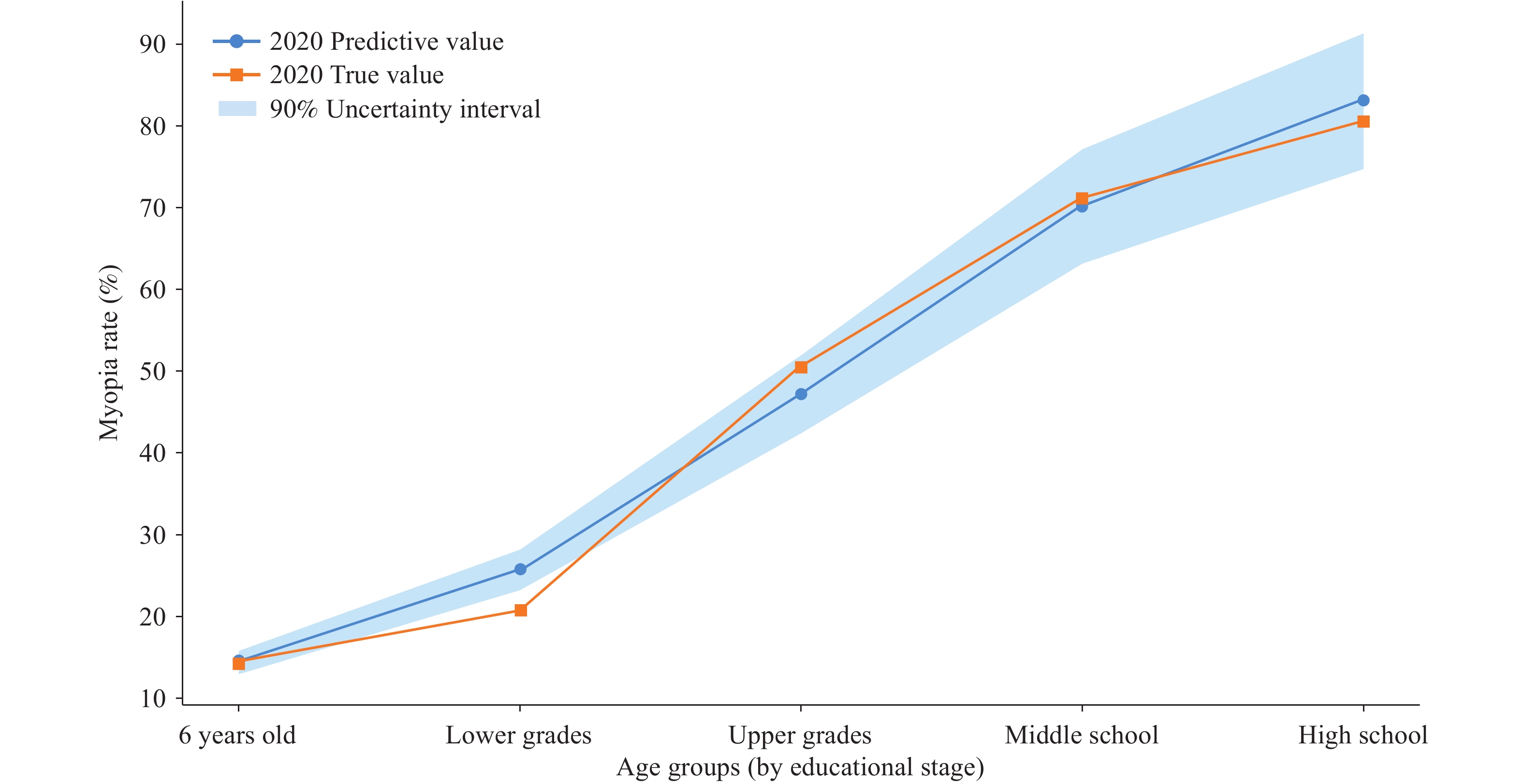 Figure 1.
Figure 1.Model validation against real-world data.
Note: “Lower grades” and “Upper grades” means the lower and upper grades in primary school.This study estimated myopia prevalence from a 2022 government report (1). Age-specific transition probabilities between health states were derived from published literature, data from the National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, and reports from the National Expert Advisory Committee on Vision Health Management for Children and Adolescents. In this study’s model, it was assumed that simulated individuals had no other conditions affecting eyesight (e.g., glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, and cataracts) and did not receive myopia treatment (e.g., surgery). The model tracked myopia onset, QALYs, and associated healthcare costs through age 18 under different intervention scenarios. This study developed the model using TreeAge Pro (version 2022, TreeAge Software, LLC, Williamstown, MA, USA), and the study was exempt from ethics approval as all data were publicly available.
The intervention in this study consisted of adding 40 minutes of outdoor activity each school day for three years. It based intervention effectiveness on a cluster randomized trial conducted in Guangzhou, China, which demonstrated a 30.4% cumulative incidence rate of myopia in the intervention group compared to 39.5% in the control group over three years (3). This study defined compliance rate as the proportion of children and adolescents who engaged in 40 minutes or more additional outdoor time following intervention implementation. The baseline analysis used an 83.5% compliance rate, as reported in this trial.
This study then modeled the impact of increasing outdoor activity across different educational stages: 1) primary school, 2) middle school, 3) high school, 4) primary and middle school, 5) middle and high school, and 6) all-stages (primary, middle, and high school). It compared these intervention strategies against a no-intervention scenario.
This study also collected cost data from a societal perspective, incorporating both direct and indirect costs, with estimates derived from previously published studies (4-5). Intervention and labor costs were estimated at 10.85 USD per person (6). Utility values for each health state were obtained from published literature (7), and QALYs were calculated by multiplying the duration spent in each health state by its corresponding utility value. Both costs and QALYs were discounted at 3.5% annually (8).
Table 2 presents the projected health and economic outcomes for 100,000 simulated children, comparing the status quo to the outdoor activity intervention. The primary school intervention was projected to increase QALYs by 0.069 years, while the middle school intervention was expected to increase QALYs by 0.011 years, and the high school intervention showed virtually no impact. The primary and middle school intervention was expected to increase QALYs by 0.083 years, while the middle and high school intervention showed an increase of 0.012 years. The all-stages intervention was projected to increase QALYs by 0.084 years. All interventions, except those limited to high school, were associated with reduced healthcare costs, with the largest savings observed in the all-stages intervention (168 USD), although it also incurred the highest implementation costs (130 USD per individual).
Intervention strategy Mean estimate QALYs Incremental QALYs Costs (USD) Incremental costs(USD) ICER (USD/QALYs) Status quo 9.279 – 1,228.95 – – Primary school 9.348 0.069 1,175.02 −53.93 Cost-saving Middle school 9.290 0.011 1,235.70 6.75 608.03 High school 9.279 0 1,243.26 14.31 28,901.72 Primary & middle school 9.362 0.083 1,177.10 −51.84 Cost-saving Middle & high school 9.290 0.012 1,249.86 20.91 1,787.32 All-stages 9.362 0.084 1,191.01 −37.94 Cost-saving Note: “–” indicates not applicable; the status quo serves as the reference and thus has no incremental or ICER values. Incremental QALYs and Incremental costs are both compared to the status quo.
Abbreviation: QALYs=quality-adjusted life-years; USD=United States dollar; ICERs=incremental cost-effectiveness ratios.Table 2. Projected health and economic outcomes under different interventions.
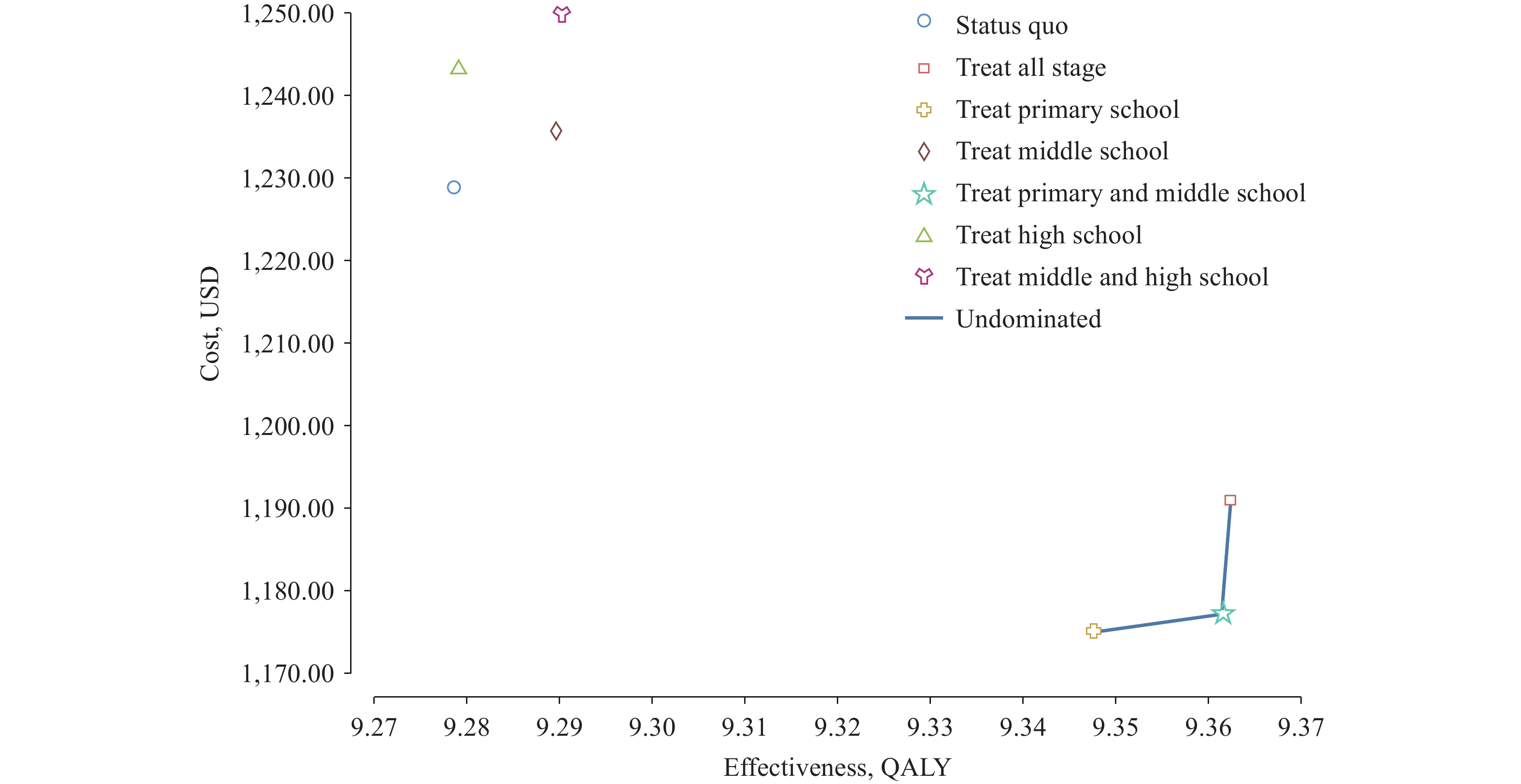
The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) for the primary school, primary and middle school, and all-stages intervention was cost-saving. The middle school, middle and high school, and high school intervention had ICERs of 608 USD/QALY, 1,851 USD/QALY, and 28,902 USD/QALY, respectively. Compared to the status quo, all interventions except the high school-only intervention were cost-effective. Figure 3 presents the cost-effectiveness outcomes for all strategies, highlighting the “undominated strategies” — the primary school, primary and middle school, and all-stages interventions. These are considered optimal as they offer greater effectiveness at the same cost or lower costs for the same effectiveness. From a cost-effectiveness perspective, the primary school intervention is the favorable choice for scenarios with limited budgets. Meanwhile, the primary and middle school or all-stages interventions are more suitable for achieving higher effectiveness when resources permit.
-
This study, utilizing a microsimulation model of myopia progression, provides valuable insights for guiding resource allocation in myopia prevention. To the best of this study’s knowledge, it is the first health economic evaluation to assess the impact of increasing outdoor activity on preventing myopia among children and adolescents in China. The results demonstrate that outdoor activity interventions can substantially reduce the incidence of myopia-related diseases, with interventions in primary and middle school proving most cost-effective.
This study’s findings emphasize that early intervention — particularly in primary school — yields the greatest benefits in preventing myopia. This supports previous research showing that myopia progression can be most effectively controlled when interventions are introduced early in life (9). Furthermore, while the all-stages intervention produces the largest reduction in healthcare costs, its higher implementation cost makes it less feasible for regions with limited economic resources. Interventions at the primary and middle school levels, though cost-saving, incur lower implementation costs and may be more appropriate for such regions.
The findings also underscore the importance of supportive public health policies tailored to the needs of different regions. Global initiatives, including those from the World Health Organization and the American Academy of Ophthalmology, have emphasized the importance of outdoor activity in myopia prevention (10). In China, national efforts, such as the “National Key Work Plan for Comprehensive Prevention of Myopia in Children and Adolescents,” have recently been introduced to address myopia, including strategies to extend break times for students and promote outdoor activities. However, these policies often lack the specificity needed for effective implementation. For instance, they typically do not define the optimal duration of outdoor activity or outline structured intervention programs designed to maximize the benefits of outdoor exposure.
This study offers several strengths: it validated its microsimulation model of myopia progression against real-world data on the prevalence and incidence of myopia in Chinese children and adolescents, which enhances the reliability of the resultant cost-effectiveness results. Additionally, by simulating various intervention strategies, it provides robust evidence that can inform the development of practical, cost-effective myopia prevention policies. Furthermore, this study demonstrates how interventions should be tailored to accommodate the economic and healthcare constraints of different regions.
Despite these strengths, this study has several limitations. First, it focuses exclusively on the health and economic outcomes of myopia-related diseases, potentially overlooking the broader benefits of outdoor activity. Second, it assumes that outdoor activity only influences the transition from “normal” to “myopia” due to insufficient evidence regarding the effect of outdoor activity on myopia progression after onset. Future research should investigate the effects of outdoor activity on individuals with more severe myopia-related diseases and examine the optimal duration and timing of interventions.
In conclusion, this study is the first to assess the health and economic impacts of increasing outdoor activity for myopia prevention among children and adolescents in China. The results provide valuable evidence for policymakers developing cost-effective myopia prevention strategies. Furthermore, these findings can serve as a reference for other developing countries facing a high burden of myopia.
HTML
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download: