-
Campylobacter jejuni lipooligosaccharides (LOS) possess a mimicry antigen structure with gangliosides, explaining the mechanism by which C. jejuni causes Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) (1). This study investigated 25 C. jejuni strains isolated from seagulls in southern China, 12 of which possessed class R LOSs. Notably, all 12 strains belonged to specific serotypes (HS2, HS4c, HS19, HS41) previously shown to be strongly associated with GBS (2). Further genetic dissection revealed that these 12 strains could be classified into 2 groups based on LOS sialylation: sialylated (8 strains) and non-sialylated (4 strains). Antigenicity analysis using immunized rabbit serum and serum from GBS patients demonstrated that antigen-antibody reactions occurred only in strains with sialylated LOSs, termed here as emerging C. jejuni. These results indicate that emerging C. jejuni strains, possessing both GBS-associated serotypes and sialylated class R LOSs, exhibit ganglioside mimicry antigen structures and a high potential for triggering GBS.
A total of 25 C. jejuni strains isolated from the feces of seagulls in Kunming City, Yunnan Province from 2018 to 2023, and 4 laboratory-stocked GBS-associated strains coded ICDCCJ07001 (HS:41, LOS class A, GD3-mimic), ICDCCJ07002 (HS:41, LOS class A, ganglioside mimic as GT1a, GM1, GD1a, GD1b, GT1b), HB-CJGB-QYT (HS:2, LOS class A, ganglioside mimic as GT1a, GM1, GD1a, GD1b, GT1b), and HB-CJGB-ZB (HS:19, LOS class A, ganglioside mimic as GD1a, GM1) were included in this study (Table 1). Campylobacter spp. isolation was carried out using the Campylobacter Isolation Kit and the membrane filter method (ZC-CAMPY-002, Qingdao Sinova Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China). Suspected colonies were picked and identified by Gram stain and biochemical tests. Polymerase chain reaction (Real-time PCR) tests were used to confirm and identify the species according to a previous study (3). The potential for ganglioside mimicry of these four strains was previously determined in Dr. Gilbert’s lab via mass spectrometry analysis (data not shown). All studied strains were serotyped using a set of 25 commercial antisera for the serotyping of heat-stable (Penner) antigens of C. jejuni by the passive hemagglutination method. LOSs for immunization experiments were purified from strains ICDCCJ07001, ICDCCJ07002, HB-CJGB-QYT, and HB-CJGB-ZB by the hot aqueous-phenol method. New Zealand White rabbits (2.0 to 2.5 kg) were immunized with 400 μg of LOS in complete Freund's adjuvant. Blood was collected from the immunized rabbits until the serum titer reached 1∶100,000. Seven serum samples from GBS patients in a GBS outbreak in Jilin (northern China) were stocked in the laboratory (4). Ganglioside antibodies were previously measured, and antibodies against gangliosides GT1a and GM1 were positive. The antigenicity of the LOSs was analyzed using Western blotting.
Strain LOS locus class CPS genotypes Penner serotype ICDCCJ07001 A HS41 HS41 ICDCCJ07002 A HS41 HS41 HB-CJGB-QYT A HS2 HS2 HB-CJGB-ZB A HS19 HS19 KW_CHFB_005 R1 HS2 HS2 KW_CHFB_014 R1 HS2 HS2 KW_CHFB_028 R1 HS2 HS2 KW_CHFB_017 R2 HS4c HS4c KW_CHFB_022 R2 HS4c HS4c KW_CHFB_024 R2 HS4c HS4c KW_CHFB_029 R2 HS4c HS4c KW_DBFB_008 R1 HS19 HS19 KW_CHFB_006 R1 HS41 HS41 KW_CHFB_009 R1 HS41 HS41 KW_CHFB_011 R1 HS41 HS41 KW_CHFB_020 R1 HS41 HS41 KW_CHFB_008 W HS21 HS21 KW_CHFB_026 W HS23_36 HS23_36_53 KW_CHFB_027 C HS4c HS4c KW_DBFB_007 F HS44 HS44 KW_CHFB_023 K HS44 HS44 KW_DBFB_009 D HS5_31 HS5 KW_DBFB_004 M HS40 UT KW_CHFB_001 CDC13 HS8_17 HS8 KW_CHFB_007 CDC14 UT UT KW_CHFB_010 CDC16 UT UT KW_DBFB_005 CDC17 HS18 HS18 KW_CHFB_021 CDC18 HS8_17 HS8 KW_DBFB_002 CDC19 HS60 UT Abbreviation: UT=untypeable; LOS=lipooligosaccharides; CPS=capsular polysaccharides. Table 1. Campylobacter jejuni strains used in this study.
A total of 13 LOS classes and 12 capsular genotypes were identified in 25 C. jejuni strains (5) (Table 1). GBS-associated capsular serotypes (HS2, HS4c, HS19, HS41, HS1_44, HS23_36) accounted for 64% (16/25) of strains. Besides, 12 of 25 (48%) strains displayed class R LOS. All 12 class R LOS strains possessed GBS-associated capsular genotypes, including HS2 (3/12, 25%), HS4 (4/12, 33.3%), HS19 (1/12, 8.3%), and HS41 (4/12, 33.3%). The phenotypic serotypes were consistent with the CPS genotypes listed in Table 1. The class R locus contains a large portion of the LOS class A locus; the first 9,700 nt showed 97% sequence identity to LOS class A, including orf3r (encoding a two-domain glucosyltransferase, Cj1135), orf4r (Cj1136), orf5r (CgtA), orf6r (CgtB), orf7r (CstII), orf8r (NeuB), orf9r (NeuC), and orf10r (NeuA). However, orf14r is specific to class R and distinguishes class A from class R (Figure 1A). The orf5a1 of strain ATCC43446 encodes CgtA, whose acceptor is a sialylated galactosyl residue, while the CgtA of strain ATCC43438 utilizes a non-sialylated acceptor. These alternative alleles are also present in class R. Based on gene content and organization of the LOS biosynthesis loci from C. jejuni class R strains, the loci were grouped into two major groups: group R1 strains with sialylated LOS (8 strains) and group R2 with non-sialylated LOS (4 strains). Amino acid sequences of CgtA and CgtB are nearly identical (98% identity) between ATCC 43446 and class R1 strains and 99% identical between ATCC 43438 and class R2 strains (Figure 1B and 1C).
 Figure 1.
Figure 1.LOS class R related to class A. (A) Genetic organization of LOS biosynthesis locus of class A and R strains. (B) Alignment of the cgtA and (C) cgtB educed amino acid sequences.
Note: Four genes (orf 1, orf 2, orf 12, orf 13) were previously recognized as responsible for LOS inner core biosynthesis. Eight genes (orf 3 to orf 10, shown in red) have a high identity to LOS class A. There is a gene (orf 14r, shown in blue), unique to class R. Alignment of the cgtA (orf 5) (1B) and cgtB (orf 6) (1C) deduced amino acid sequences showed that cgtA (orf 5) and cgtB (orf 6) of LOS class R strains use either sialylated (99% identity with class A1 strain ATCC43446) or non-sialylated (99% identity with class A2 strain ATCC43438) acceptors, and class R strains were classified into class R1 and class R2.
Abbreviation: LOS=lipooligosaccharides.
Based on the genetic characteristics and previous investigations, the mimic antigen structures of GBS-associated C. jejuni strains ICDCCJ07002, HB-CJGB-QYT,HB-CJGB-ZB, and ICDCCJ07001 were demonstrated in Figure 2A. LOSs from six strains from two groups of class R (group R1 and group R2) were purified and verified with silver staining for PAGE (Figure 2B). The reactions between different class R LOS antigens from different strains and the serum of rabbits immunized with GBS-associated strains were presented in Figure 2C. Serum immunized with LOS of strain ICDCCJ07001 did not react with any of the purified class R LOSs (Figure 2C). LOSs from three class R1 strains showed a strong reaction with the serum from seven antiganglioside-positive GBS patients. None of the R2 LOSs reacted with the patients’ serum. Sera of healthy controls did not react with any of the class R LOSs tested.
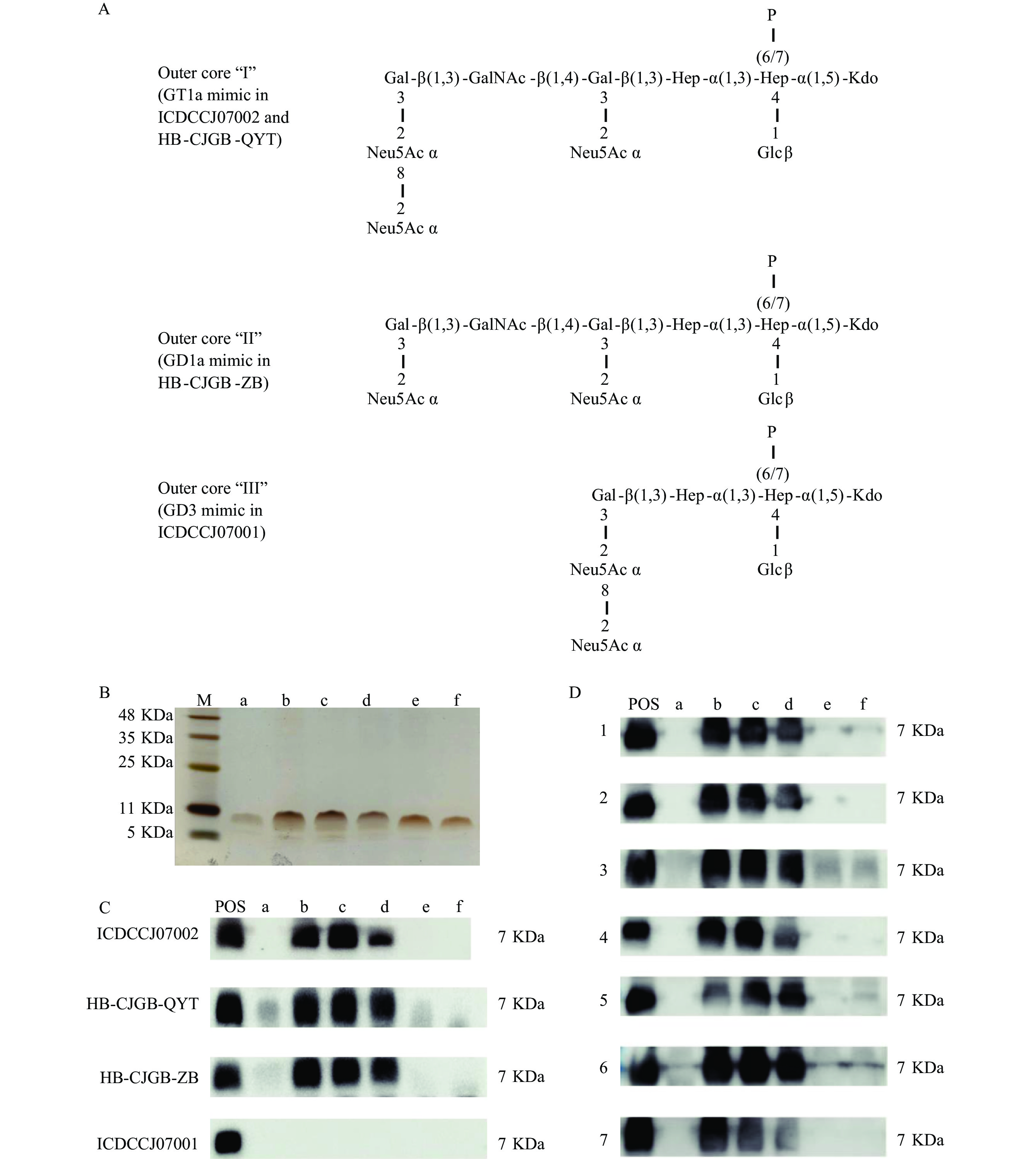 Figure 2.
Figure 2.Reaction of class R LOS with sera of either immunized rabbit or GBS patient. (A) Structures of various C. jejuni LOS used for immunization of rabbits and corresponding ganglioside mimics. (B) Silver staining of the purified class R LOS (three strains from group R1 LOS and group R2 LOS were selected in this figure, respectively). (C) Western blot analysis of class R LOS with sera from LOS-immunized rabbits. (D) Western blot analysis of class R LOS with GBS patient serum.
Note: M, marker. POS, positive control, purified LOS from different strains to immunize rabbits. a LOS from strain KW_CHFB_024 (group R2); b LOS from strain KW_CHFB_009 (group R1); c LOS from strain KW_CHFB_011 (group R1); d LOS from strain KW_CHFB_014 (group R1); e LOS from strain KW_CHFB_017 (group R2); f LOS from strain KW_CHFB_022 (group R2).
Abbreviation: LOS=lipooligosaccharides.
-
Molecular mimicry between C. jejuni LOS and host gangliosides leads to the production of cross-reactive antibodies directed against the peripheral nerves of the host to trigger GBS (6–7). Genes involved in the synthesis of sialylated LOS and ganglioside mimics are present in the LOS classes A, B, C, M, and R (8). Numerous reports indicate that C. jejuni strains with classes A, B, and C LOS are frequently isolated from the stools of patients with GBS, and classes A and B are associated with GBS and MFS, respectively. Penner serotyping showed that the combination of LOS loci that contain genes involved in LOS sialylation with the capsular types HS1/44c, HS2, HS4c, HS19, HS23/36c, and HS41 are associated with the development of GBS and MFS and are therefore markers for these neurological diseases (2). In the present study, 16 (64%, 16/25) of these seagulls isolates had GBS-associated serotypes, and 75% (12/16) of them displayed class R LOS. These results raise significant concern about the risk of these strains inducing GBS around coastal or lakeside areas.
Further pathogenicity analysis revealed that class R LOS strains could be classified into two groups: strains with sialylated LOS (group R1) and strains with non-sialylated LOS (group R2). Group R2 strains showed no reactivity with GBS patient sera and failed to induce anti-LOS antibody responses in immune serum from animals immunized with LOS from ganglioside-mimic strains. These results confirmed this study’s hypothesis that emerging C. jejuni strains isolated from seagulls — which possess specific serotypes (HS2, HS4c, HS19, HS41) and sialylated class R LOS — have ganglioside-mimicking antigen structures and a high potential risk for triggering GBS.
C. jejuni requires specific gene combinations to express ganglioside mimics. An important feature in ganglioside mimicry is the presence of sialic acid (N-acetylneuraminic acid, NANA) in both LOS and gangliosides. Sialic acid is a rare constituent of bacterial surface polysaccharides, and sialylation of bacterial proteins has thus far been found only in Campylobacter species (9). Sialylated LOS is also involved in other aspects of C. jejuni pathogenesis. C. jejuni strains expressing sialylated LOS invade human intestinal epithelial cells significantly more frequently than strains expressing non-sialylated LOS (10). Sera from seven GBS patients in this study were previously identified as being infected with C. jejuni strains bearing a GT1a-like LOS (7). Moreover, antigenicity reactions only occurred in class R1 LOS strains with four immunized sera, which were raised against LOS from the GBS-associated C. jejuni strains. This indicates the presence of additional epitopes in class R1 LOS that mimic the ganglioside structures in GT1a or GM1, GD1a, GD1b, and GT1b.
In this study, only the pathogenic characteristics of the C. jejuni strains were investigated. There was no data about the GBS patients. In the future, enhanced surveillance for both the C. jejuni infection and the GBS patients in this region will be needed for the prevention and control of GBS caused by C. jejuni infection.
In conclusion, this study indicated that these emerging C. jejuni strains, which had both GBS-associated serotypes and sialylated class R LOSs, had gangliosides mimicry antigen structures and possessed high potential for triggering GBS. The results highlight the risk of C. jejuni-induced GBS around coastal or lakeside areas which reminds us that we should strengthen the surveillance and prevention of C. jejuni infection in these areas.
HTML
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download:




