-
Healthy life expectancy (HLE) is an instrumental gauge that accounts for mortalities and morbidity conditions resulting from diseases or disabilities. This measure estimates the average number of years an individual can anticipate living in optimal health. Consequently, HLE serves as a fundamental tool in developing health objectives and customizing health strategies, as evidenced in national health schemes.
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines health as a condition of complete physical, mental, and social well-being rather than merely being devoid of disease or affliction (1). This inclusive definition acknowledges the multifaceted nature of health. Researchers have crafted various indicators related to health-related quality of life (HRQoL) (2). These indicators concentrate on diverse facets, such as physical function, disease impact, and self-perception (3). Nonetheless, the current set of indicators lacks the capacity to evaluate population health across these diverse dimensions comprehensively. Nations worldwide are increasingly adopting their bespoke systems to evaluate HLE, highlighting a critical absence of a globally recognized concept, methodology, or theoretical framework for HLE. In this context, recent HLE research within China has primarily focused on regional dimensions, revealing a significant shortfall — the lack of a universally endorsed approach for empirical analysis. This gap necessitates an urgent integration of international HLE learnings, tailored specifically to China’s unique socio-cultural landscape, a need further catalyzed by the vigorous advancement of the “Healthy China” and “Healthy Aging” campaigns. Consequently, this project is principally dedicated to mitigating this empirical deficit by developing comprehensive tools for health assessment and establishing a coherent HLE indicator framework, distinctly aligned with China’s national prerequisites.
-
A scoping review encapsulates the synthesis of evidence intending to identify and chart relevant pointers on a specific theme, framework, idea, or issue, adhering to pre-set inclusion criteria. Unlike traditional systematic reviews, its core objective is to provide an extensive overview of the accessible evidence without emphasizing quantitative or qualitative data synthesis. Consequently, the guiding research questions in a scoping review are generally broader in scope (4). The most updated advice on executing scoping reviews is incorporated in the guidelines put forth by Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) in 2020 (5), and the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) (6). Both the JBI guidelines and the PRISMA-ScR offer contemporary and comprehensive guidance for authors embarking on scoping reviews. They further provide a structured layout for reporting the scoping review process. Due to the unique features of the JBI and PRISMA-ScR frameworks when juxtaposed against other review methodological frameworks, we have chosen them to conduct our scoping review to guarantee more suitable and insightful outcomes.
-
This study adheres to the population, concept, and context (PCC) paradigm, as suggested by the JBI, for establishing research questions and objectives (5). The dual purpose of this scoping review is to: 1) examine measurement devices for evaluating the health status of populations and metrics for determining HLE; 2) characterize the properties and structure of current tools and indicators. The research objectives steering this review include: 1) Identifying indicators that are utilized for evaluating population health statuses; 2) Determining measurement tools that are associated with these identified indicators; 3) Documenting the characteristics of these tools and indicators.
-
A comprehensive search was conducted across two literature databases, namely, PubMed and Web of Science, encompassing articles published from January 2020 to March 2023. The search strategy followed the guidelines provided by JBI and PRISMA-ScR, adhering to the specific search criteria and syntax for PubMed and Web of Science. A blend of subject headings and words was utilized, primarily focusing on terms correlated with healthy life expectancy, the state of health, and respective measurement instruments. The search encompassed the following MeSH terms: “Healthy Life Expectancy” [Mesh] OR “Healthy State Life Expectancy” [title or abstract] OR “Health Adjusted Life Year” [Mesh]”.
-
The initial analysis entailed implementing a duplication elimination process via Endnote X9. The subsequent step consisted of conducting a manual review of the remaining articles. This evaluation involved an inspection of the abstracts and the titles, followed by a full-text feasibility assessment. This study was steered by multiple health interpretations, including physical, mental, and social well-being. Special emphasis was placed on the assessment of healthy states across these parameters and pinpointing the corresponding indicators for HLE.
During the review stage of titles and abstracts, the criteria for article inclusion hinged upon incorporating the keyword “HLE” in either the title or abstract, regardless of whether the paper’s primary focus was HLE. Consequently, articles that did not pertain to HLE or were not peer-reviewed were omitted from the study.
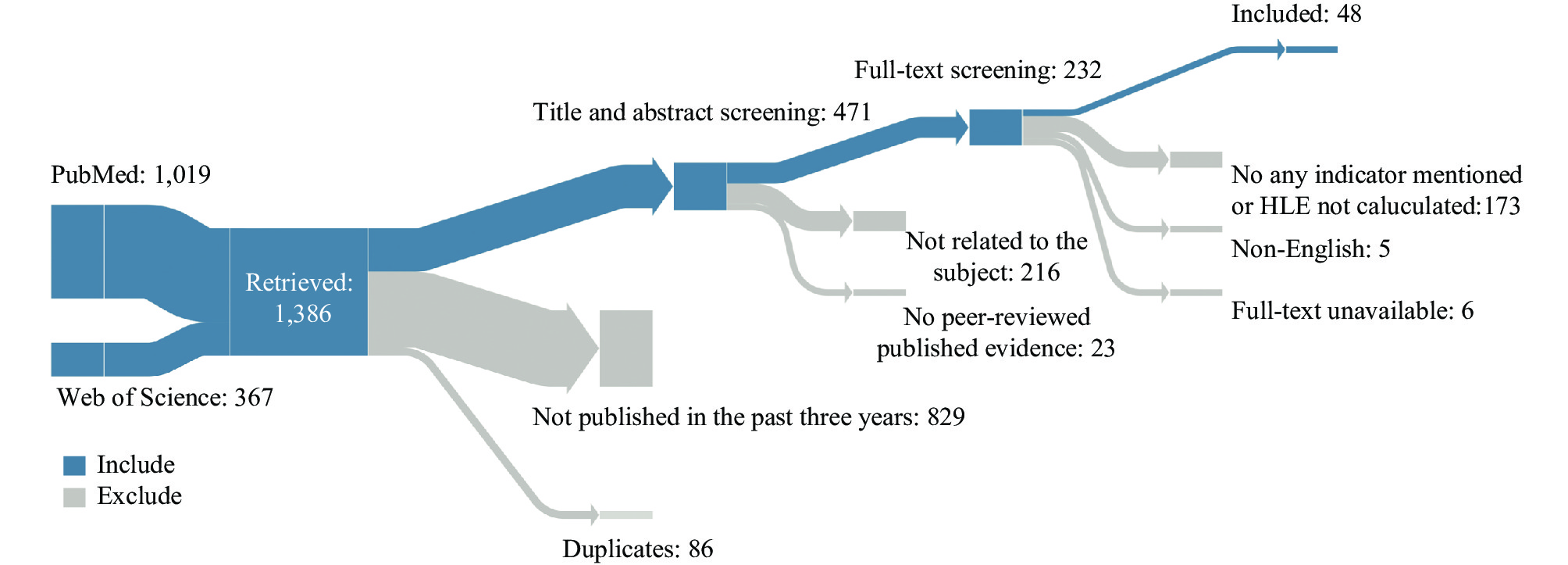
In the prior phase, unresolved consensus regarding an article automatically progressed to the full-text feasibility assessment. In the event of any disagreement during this phase, the team carefully reassessed the inclusion/exclusion criteria to achieve consensus. Our study selection criteria required at least one appraisal of health state dimensions and an evaluation of the corresponding HLE. Studies that merely mentioned HLE without conducting a health state assessment or HLE measurement, or those unavailable in full text, or not in written English, were excluded (Figure 1).
-
The process of graphing data is a valuable analytical tool enabling comprehensive literature analysis, identifying key concepts, and establishing underlying themes. In our study, we utilized a standardized Microsoft Excel sheet for data collection. One researcher initially retrieved the information, while another independently verified the data for accuracy. We then summarized the extracted data based on various study features such as national origin, publication date, and authorship. Moreover, we detailed the study design and sample information, including methodology, sample size, and the specific demographics and geographic regions targeted. Additionally, we gathered data on the tools employed to evaluate health status and healthy life expectancy indicators. Our findings are reported descriptively, and we have synthesized associations and made comparisons of indicators where relevant.
-
In an evaluation of 1,386 articles assembled from database searches, with 1,019 sourced from PubMed and 367 from the Web of Science, only 48 studies met the defined inclusion criteria and were subsequently included in the final synthesis (Figure 1).
-
This research encompassed 48 studies from 22 countries, utilzing 19 distinct measurement tools to assess the general health status of populations in 37 nations or regions and calculate 11 relevant HLE indicators. The employed methodologies were predominantly cross-sectional (n=26) or longitudinal (n=22). A significant focus was on participants aged 60 and over, as depicted in Figure 2.
-
The classification of indicators is shown in Table 1. The HLE indicators were classified into healthy state life expectancy (HSE) indicators and healthy adjusted life expectancy (HALE) indicators according to the Réseau Espérance de Vie en Santé (REVES) classification. Out of the 48 studies included in our analysis, 9 HSE indicators were measured. This study further classified these HSE indicators into disability-ree life expectancy (DFLE), disease-free life expectancy (DisFLE), self-rated healthy life expectancy (SRH), and other customized HSE indicators.
Category Dimension Indicator Count Percentage (%) Healthy state expectancy 91 96.81 Disability Disability-free life expectancy 62 65.96 Disease Cognitive-impairment-free life expectancy 1 1.06 Depression-free life expectancy 1 1.06 Anxiety-free life expectancy 1 1.06 Chronic disease-free life expectancy 3 3.19 Depression and anxiety-free life expectancy 1 1.06 Perceived health Self-rated healthy life expectancy 4 4.26 Others Frailty-free life expectancy 10 10.64 Dependence-free life expectancy 8 8.51 Health adjusted life expectancy 3 3.19 Disability-adjusted Disability-adjusted life expectancy 2 2.13 Quality-adjusted Quality-adjusted life expectancy 1 1.06 Abbreviation: REVES=Réseau Espérance de Vie en Santé. Table 1. Summary of HLE indicators of included studies from recent three years, globally, classified by REVES.
In the surveyed literature involved in this study, DFLE emerged as the most frequently assessed HSE, with a total of 62 occurrences across various studies. Furthermore, DisFLE was evaluated through five indicators, constituting seven measurements. SRH, also known as healthy life expectancy, comprised another considerable focus of this research, observed in four countries or regions.
HLE represents a category within the REVES network, specifically highlighted by HALE. Two key indicators within HALE are utilized: disability-adjusted life expectancy (DALE) and quality-adjusted life expectancy (QALE). These indicators have been incorporated in the studies under review, with DALE twice and QALE included once.
-
Figure 2 indicates eight different tools that were utilized to assess disability status. The Activities of Daily Living/Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (ADL/IADL) and Groningen Activity Restriction Scale (GARS) were recorded as the predominant tools, with usage frequencies of 26 and 18 times, respectively.
To gauge the manifestation of disease, we utilized the mini-mental state examination, Patient Health Questionnaire-2, and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-2 as evaluative metrics to determine the health status in Cognitive-Impairment-Free Life Expectancy (CIMFLE), Depression-Free Life Expectancy (DeprFLE), and Anxiety-Free Life Expectancy (AFLE) respectively. Furthermore, we employed self-reported measures to appraise the presence of chronic disease, depression, and anxiety in the Chronic Disease-Free Life Expectancy (CDFLE) and Depression and Anxiety-Free Life Expectancy (DAFLE) cohorts..
Four studies included in this analysis utilized self-assessed measures to evaluate the comprehensive health status of the subject pool, covering diverse facets of individual physical, psychological, and social adaptation.
Two studies independently gauged health status using distinct methodologies. The initial study employed the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe-Frailty Instrument (SHARE-FI) questionnaire for its assessment, while the subsequent study leveraged open-ended questions. Upon completion, researchers derived two indicators of health state evaluations, namely; Frailty-Free Life Expectancy (FFLE) and Dependence-Free Life Expectancy (DepFLE).
In regard to HALE, two studies leveraged disability-adjusted life years (DALY) as a measure, whereas another study deployed the European Quality of Life Five-dimension Five-level Questionnaire (EQ-5D-5L) instrument to evaluate the subjects’ quality of life.
-
HLE has become a key component of current population health research and frameworks, with a broad spectrum of countries and regions adopting it as a crucial metric for assessing their populations’ overall health status. Nonetheless, calculating and comparing HLE often poses challenges due to variations in health dimensions and the absence of consensus on validated assessment tools.
-
HSE quantifies the anticipated duration of an individual’s life in a healthy condition. The designated endpoint for HSE calculations can differ between studies, potentially encompassing aspects such as disability, distinct diseases, or self-perceived health.
Indicators of HSE bear limitations in their capacity to fully represent the health spectrum of a population. These markers typically concentrate on one aspect, such as disability, to the exclusion of equally crucial factors like disease prevalence. For instance, employing the DFLE parameter discounts the presence of diseases or conditions. In contrast, the DisFLE combines disease prevalence and mortality data to delineate a healthy state but overlooks certain unrecognized factors contributing to poor health. Fluctuations in the calculated DFLE values can stem from disparities in the assessment tools implemented to quantify disability. Adding to the complexity, the definition of a healthy state can differ across studies due to inconsistent operational parameters. For example, categorizing all individuals with severe disabilities as equally disabled overlooks the nuances between mild, moderate, and severe disabilities.
The self-rated health instrument is often perceived as a more subjective evaluative method for gauging an individual’s overall health status in contrast with other measures. While self-rated health is widely used for its simplicity, interpreting its results requires caution. This stems from its reliance on individuals to gauge their own physiological and psychological wellness. However, factors such as geographical locale, ethnicity, and cultural heritage can shape how respondents perceive their health, leading more toward a generalized health assessment rather than a specific one (7). This presents a potential hazard of underestimating the true condition of health.
In closing, the varying definitions of a healthy state and the assessment tools employed can yield different HSEs (3). Establishing a standard definition of a healthy state and adopting universal health state metrics is essential to enhance consistency and facilitate the comparison of study outcomes.
-
Compared to HSE indices, the HALE indicator is more attuned to population mortality rates and the fluctuating prevalence and severity of diseases, thereby affording a more all-encompassing evaluation of population health. The HALE indicator cluster incorporates health statuses from many dimensions in a weighted manner, yielding a more comprehensive and logical appraisal than single-dimensional assessments. However, collecting comprehensive data on each health dimension is challenging, especially given the absence of a standardized approach to weights adjustment. The HALE indicators that are most frequently utilized are the DALE and the QALE (8-9).
The comparability of HSE indicators, derived from self-reported health, is hindered by discrepancies across countries in survey methodologies and cultural differences in health reporting. Nonetheless, this challenge is significantly mitigated by the implementation of the DALYs measure (10). The DALY approach enables the computation of the HALE, otherwise recognized as the DALE. This method determines the estimated number of years an individual is projected to live in optimal health (10).
Utilizing the QALE has a distinct advantage as it can readily calculate the HALE for small-scale regions such as districts, cities, or provinces (3). This particular attribute enhances the value of QALE in evaluating the burden associated with behavioral risk factors, health determinants, diseases, and injuries (9). QALE achieves this by designating varying weighting factors to diverse disability states, effectively translating the survival time of these states into an equivalent survival time in an ideal healthy state, contingent on their corresponding weighting factors. As such, by measuring both the duration and quality of life expectancy, QALE offers a more holistic representation of the population’s overall health status.
This study acknowledges two significant limitations. First, health is a multidimensional concept encompassing a broad spectrum of terms to characterize its varying dimensions. Consequently, our search strategy might not have encapsulated all pertinent studies. Second, our review is confined to studies published in English, thus potentially precluding valuable research available in other languages.
-
Our review has determined that a wealth of research exists on multiple aspects of HLE. Scholars have intensively examined and implemented related concepts, theoretical frameworks, and measurement procedures. Studies concentrating on older populations commonly use HSE indicators, whereas those incorporating the entire or adult population frequently employ HALE indicators. The majority of these studies adopt self-report questionnaires to evaluate a single domain. The DFLE has garnered significant attention among the HSE indicators, with ADL and IADL emerging as favored instruments for health state evaluation. The insights gleaned from this review can guide the creation of an all-encompassing healthy life expectancy system that includes multiple dimensions.
-
No conflicts of interest.
HTML
Research Objectives and Questions
Search Strategy
Evidence Selection and Appraisal
Data Extraction and Synthesis
Literature Screening
Summary of Empirical Studies on HLE
Indicators Classification and Measurement Tools
Indicators classification:
Measurement tools:
Healthy State Expectancy
Health-Adjusted Life Expectancy
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download:





