-
During the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, regular sampling has been unable to keep up with the rapidly changing situation, leading to an increased focus on self-sampling. To evaluate the health and economic effects of self-sampling, we conducted a descriptive analysis of residents who used self-sampling based on data from SoundAI Health. Results revealed that self-sampling was widely accepted among residents of all ages, ranging from 22 days to 116 years old. Of the 650,452 (71.9%) residents, the time from self-sampling to result-reporting was less than one day. Self-sampling was found to save a great deal of manpower and medical resources compared to regular sampling. The practice in Fengtai showed that self-sampling could help the public effectively and economically confront the pandemic, with characteristics of general applicability, equivalent effectiveness, and low cost. In the future, self-sampling can be implemented to introduce prevention and control measures for large-scale epidemics.
Nucleic acid testing is an important measure for detecting patients, diagnosing infection, and preventing and controlling transmission. However, with the rapid spread of the Omicron variant of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), regular sampling needs to be optimized. On November 11, 2022, China introduced the Notice on Further Optimizing the Prevention and Control Measures of COVID-19 in a Scientific and Precise Manner, providing 20 detailed measures for improving prevention and control measures of COVID-19 (1). In accordance with the “20 Measures,” some places explored self-sampling to identify people with COVID-19. Fengtai, as a representative of areas conducting pilot projects on SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid self-sampling in China, provided a standardized procedure for self-sampling (2). After face-to-face or online (self-sampling videos) training, representative residents of each household obtained sampling materials from communities, completed family members and sampling information in SoundAI Health, and finished the process of self-sampling, returning the samples to communities in time (3). Samples were sent to a third-party organization for testing, and residents could get their results through SoundAI Health at any time. To ensure the quality of self-sampling, staff in communities organized various types of training for residents and checked the samples carefully, and SoundAI Health sent notifications in case of any abnormal situation occurring during an operation (4).
In this study, a total of 890,952 community residents in Fengtai underwent self-sampling from November 24 to November 30, 2022. Registered information (after anonymous processing) from SoundAI Health, a widely used WeChat program for COVID-19 related health services in China, such as booking vaccines, querying nucleic-acid testing results, and reporting antigen self-testing results, was analyzed. Descriptive analysis was used to assess the effectiveness of self-sampling, including age, region and time distribution. Age was divided into groups of 10 years, and time was divided into 5 groups (<12 hours, 12–23 hours, 24–35 hours, 36–47 hours, and ≥48 hours). Mean±standard deviation was used to describe continuous age, and frequency and percentage were applied to describe categorical variables. All data analyses were performed in R software (4.0.3; R Core Team, Vienna, Austria).
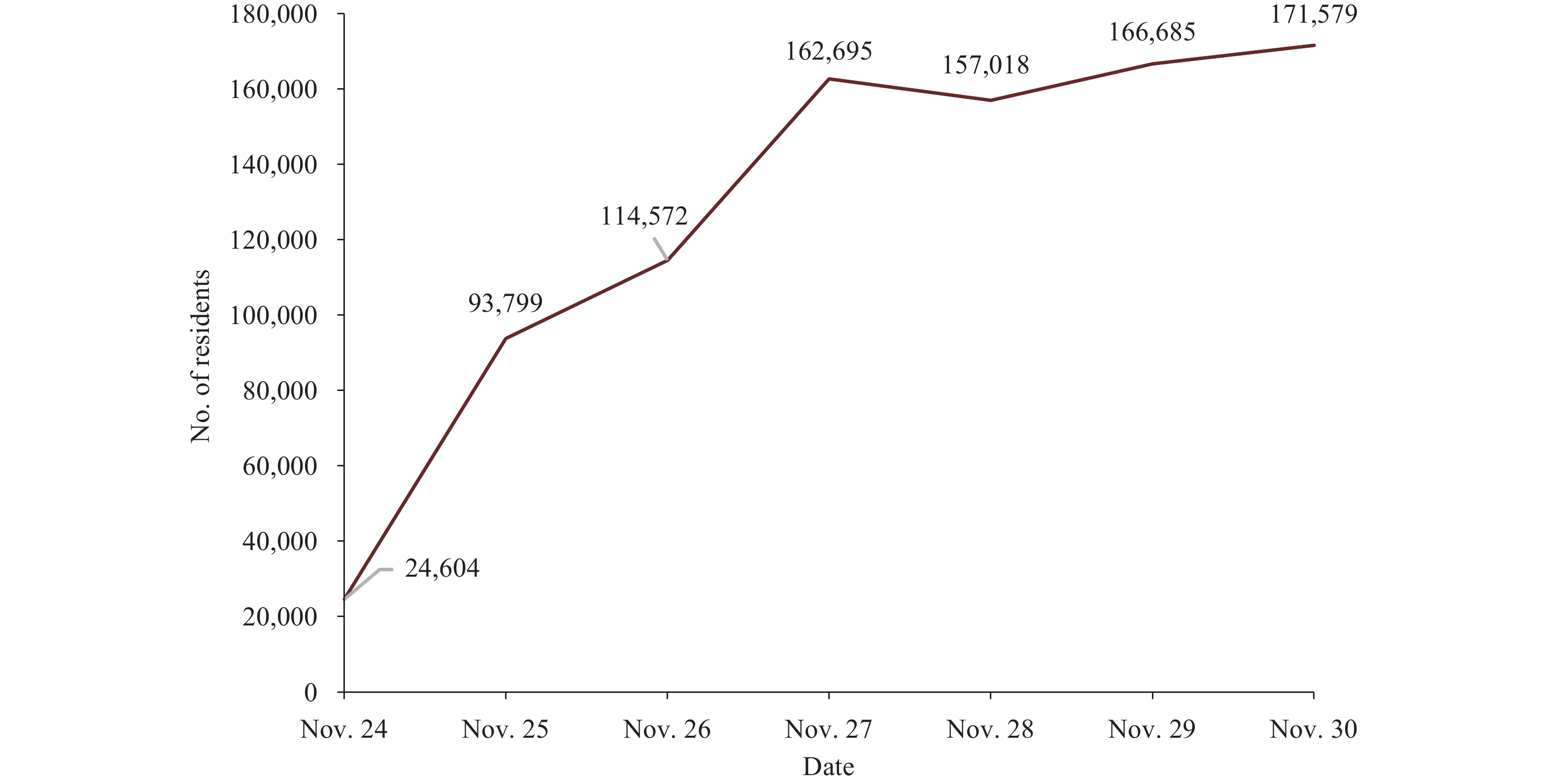
The age of 890,952 self-sampling residents ranged from 22 days to 116 years old, with a mean of 41.72±18.31 years old. The majority of residents were between 30–39 (21.2%, 188,697) and 40–49 (19.2%, 171,008) years old (Table 1). The number of self-sampling participants increased rapidly from 1,112 in Lize Financial and Business District to 100,355 in Nanyuan Street, covering all streets of Fengtai. After initiating self-sampling, the number of participants increased rapidly from 24,604 on November 24 to 114,572 on November 26, and then remained above 150,000 per day (Figure 1). The time from self-sampling to sample-collecting was mainly within 24 hours (94.9%), particularly within 12 hours (60.0%). The time from self-sampling to result-reporting was mainly <24 hours (66.6%), with residents with time over 48 hours only accounting for 3.4% (Table 1). A total of 289,017 sampling tubes were used; 94.7% of tubes contained 5 or fewer samples for each tube, i.e. “5 Mixed in 1” (Figure 2). During the same period, the daily self-sampling size was 127,279 (890,952 in a week), and the average size of regular sampling at each station was 2,568 per day (5). According to the Guidelines for Normal Nucleic Acid Testing in Beijing, there are 3–5 staff for sampling, information registering, and security at each station. Self-sampling could save numerous manpower and medical resources compared with regular sampling, as it requires fewer staff and stations. The positive rate of self-sampling was 181.49 per 100,000 population, higher than regular sampling (85.71 per 100,000 population).
Characteristic Number Percentage
(%)Age group (years) 0–9 56,891 6.4 10–19 55,132 6.2 20–29 100,172 11.2 30–39 188,697 21.2 40–49 171,008 19.2 50–59 165,294 18.6 60 and above 153,758 17.3 Street name Wangzuo Town 9,812 1.1 Shiliuzhuang 4,328 0.5 Liuliqiao 8,138 0.9 Lize Financial Business District 1,112 0.1 Xiluoyuan 17,170 1.9 Yungang 10,467 1.2 Dahongmen 11,363 1.3 Qingta 13,520 1.5 Fangzhuang 14,355 1.6 Fengtai Science and Technology Park 9,960 1.1 Donggaodi 17,735 2.0 Taipingqiao 18,451 2.1 Wanping 23,346 2.6 Wulidian 24,311 2.7 Changxindian 32,632 3.7 Heyi 33,760 3.8 Huaxiang 33,961 3.8 Yuquanying 36,082 4.0 Youanmen 37,752 4.2 Chengshousi 43,013 4.8 Lugouqiao 48,136 5.4 Majiabao 50,830 5.7 Xincun 51,750 5.8 Kandan 57,957 6.5 Dongtiejiangying 80,734 9.1 Fengtai 99,922 11.2 Nanyuan 100,355 11.3 Time from self-sampling to sample-collecting (hours) <12 534,394 60.0 12–23 311,050 34.9 24–35 24,104 2.7 36–47 13,979 1.6 ≥48 7,425 0.8 Time from self-sampling to result-reporting (hours) <12 47,355 5.3 12–23 593,097 66.6 24–35 178,810 20.1 36–47 41,574 4.7 ≥48 30,116 3.4 Table 1. Characteristics of 890,952 community residents with SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid self-sampling in Fengtai District, Beijing, November 2022.
-
This study is the first to use registered data to evaluate the effect and cost of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid self-sampling in China. Our findings suggest that self-sampling during the COVID-19 pandemic can be an effective and economical approach to responding to the spread of emerging infectious diseases.
In response to respiratory-borne diseases, which can spread rapidly, the primary point of control is early detection, diagnosis, reporting, isolation, and treatment of the source of infection. Nucleic acid testing is an extensively used screening method with high accuracy for detecting patients and is applied in various diseases. In China, nationwide regular sampling has been effective in containing the spread of COVID-19. However, with the emergence of virus variants, self-sampling appears to be more applicable to the new epidemic situation than regular sampling, with its general applicability, equivalent effectiveness, and low cost.
In our study, the age, region, and time distribution of residents with self-sampling in Fengtai revealed its general applicability. The age distribution of residents with self-sampling was wide, ranging from 22 days to 116 years old, indicating that self-sampling is suitable for all age groups and has feasibility for promotion. The number of residents with self-sampling was significantly different among streets, which may be associated with the density of permanent population in different streets. Shortly after the beginning of pilot work, participants increased rapidly, indicating that self-sampling had excellent population acceptance and operability. In addition, 71.9% of residents had results reported within 24 hours of self-sampling, conveying that self-sampling could meet the needs of daily nucleic acid testing. During the process of pilot work, Fengtai introduced two self-sampling types: “5 Mixed in 1” (i.e. 5 or fewer samples in each tube, suitable for family use) and “10 Mixed in 1” (i.e. 6–10 samples in each tube, suitable for company use). We found that the number of samples in a tube was mostly ≤5 (94.7%), reflecting that the demand for family-type self-sampling was higher than the demand for company-type, and self-sampling was convenient without worries about environment, location, and time. Moreover, the re-check work was more concentrated if the result of preliminary screening was positive.
The results of our study indicated that self-sampling was not inferior to regular sampling in terms of effectiveness and cost. A systematic review and meta-analysis reported that there was no statistical difference in sensitivity and specificity between samples collected by health-care workers and self-collected samples (6). Adequate training of community residents could ensure that self-sampling and regular sampling yielded the same results. Additionally, self-sampling could save on manpower, room space, equipment, medical materials, and other running costs once the sampling operation was assigned to individuals.
Additionally, self-sampling could strengthen individuals’ roles in the prevention and control of infectious diseases. On December 2, 2022, the Beijing Municipal Health Commission published the article “Fulfill the Responsibility of Epidemic Prevention and Be the First Line of Defense in Your Own Health,” which emphasized individual responsibility in epidemic prevention and control (7). On December 7, 2022, China further introduced the Notice on Further Optimizing and Implementing the Prevention and Control Measures of COVID-19, proposing 10 targeted measures (8). In line with the “20 Measures” and “10 Measures,” many provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) in China have announced new regulations on nucleic acid testing, such as no requirements for general testing, no requirements for a negative result when accessing public places except for several special places, and no requirements for testing mobile people (9). These policies and measures increased public awareness of self-responsibility in health and highlighted the feasibility of self-sampling in confronting emerging infectious diseases.
Our study had several limitations. First, due to the information system not collecting sufficient residents’ characteristics, such as marital status and education, we were unable to develop a more in-depth analysis on characteristics of residents with self-sampling. Second, as we were unable to obtain the gold standard testing results, the sensitivity and specificity of self-sampling and regular sampling were unknown. Third, our study focused on self-sampling under the background of the COVID-19 pandemic, which may limit the ability to extrapolate results. However, the self-sampling model has been used in other countries for primary detection of patients with COVID-19 and other infectious diseases, such as HIV infection (6,10). Therefore, our findings provide an inspiration for model innovation, a public-participation model, for responding to emerging infectious diseases.
In conclusion, self-sampling could help the public effectively and economically respond to large-scale epidemics, with characteristics of general applicability, equivalent effectiveness, and low cost. However, our study only conducted a qualitative economic evaluation of self-sampling, and the testing results may be affected by many factors, such as whether the sampling process is standard or not. Therefore, further research is needed to explore the sensitivity, specificity, and economic effect of self-sampling in the real world. In the future, self-sampling can be implemented to introduce prevention and control measures for infectious diseases.
-
No conflicts of interest.
-
Fengtai District Health Commission of Beijing Municipality. All residents and workers who participated in the process of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid self-sampling, collection, and testing.
HTML
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download:





