-
Recently, local cluster COVID-19 epidemics have occurred in rural areas and the urban-rural border regions in Shijiazhuang City, Hebei Province. Rural medical institutions were not able to detect new cases promptly, resulting in rapid spread of the epidemic (1).
Reverse transcriptase real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) is considered the gold standard of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA detection. However, it is difficult to be used at the grass roots level due to being relatively time-consuming and requiring skillful technicians, specialized equipment, and biosafety labs (2-3). In our previous study, we reported an ultrafast single-tube assay for SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection using a reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification (RT-RAA) kit, which revealed the distinctive advantages of simplicity and rapidity in terms of operation and turnaround time (4). We then upgraded this kit and developed a duplex single-tube assay for SARS-CoV-2 RNA targeting both the ORF1ab gene and GAPDH gene (endogenous internal control). The RT-RAA kit passed the quality assessment of National Institutes for Food and Drug Control and showed the lowest detection sensitivity in the range of 45 copies/mL to 137 copies/mL on November 30, 2020. Afterwards, the kit obtained the CE certification of the European Union and was officially approved by National Medical Products Administration (NMPA). Here we presented the onsite evaluation results of the RT-RAA kit, completed in Hebei CDC from January 17, 2021 to January 27, 2021.
-
The specificity evaluation panel was preserved in China CDC consisting of inactivated cultures or nucleic acids of SARS-CoV-2, human coronavirus (HKU1, OC43, NL63, and 229E), influenza virus types A (Flu A), FluA-H1N1, FluA-H3N2, FluA-H5N1, FluA-H7N9, influenza virus types B, respiratory syncytial virus type A and B, parainfluenza virus, human rhinovirus type A, type B, and type C, human adenovirus, enteroviruses, human metapneumovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, measles virus, human cytomegalo virus, Boca virus, rotavirus, norovirus, mumps virus, varicella zoster virus, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophilia, Bordetella pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Aspergillus fumigatus, Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Cryptococcus neoformans and human genome DNA.
A total of 808 throat swab samples were collected in Hebei from January 17 to 27, 2021. National Reference Panel for 2019-nCoV Nucleic Acids Detection Kit was from NMPA. All aspects of the study were performed as per the National Code of Ethics and approved by the Institutional Review Boards of local CDCs and hospitals mentioned above.
-
The schematic diagram of the endogenous internal controlled RT-RAA was shown in Figure 1. All of the primers and probes for the ORF1ab gene and GAPDH gene (5) were lyophilized in the reaction unit. The specificity evaluation panel as described above was used to evaluate the specificity of RT-RAA assay. The original concentration of National Reference S solution was 3×105 copies/mL. The sensitivity of RT-RAA assay was assessed using 3-fold serially diluted S solution (1∶9, 1∶27, 1∶81, 1∶243, 1∶729, and 1∶2,187, labeled as S1–S6, respectively). Nucleic acid extraction of each S concentration was then carried out for eight replicates by RT-RAA detection.
-
Total RNA was extracted from 200 μL of sample preservation solution using automatic extraction kits (BioPerfectus, China) according to the instructions recommended by the manufacturer. The nucleic acid was eluted in 50 μL of nuclease-free water and stored at -80 °C until use.
-
RNA was obtained from 58 clinical samples using nucleic acid lysis solution (Qi Tian, Jiangsu Province, China) under the following dilution: 95 μL of clinical samples mixed with 5 μL of lysis solution. The mixtures were then briefly vortexed and incubated at room temperature for 2 min, followed by centrifugation (10,000 rpm) prior to use. Among them, 10 samples were collected in sampling tubes from Changchun Zhihe Co., Ltd, China and the other 48 samples were collected in sampling tubes from Cangzhou Yongkang Co., Ltd., China.
-
A RT-RAA reaction system included 42.5 µL of reaction buffer, 2.5 µL of 280 mmol/L magnesium acetate, 5 µL of extracted nucleic acid or 5 µL negative/positive control. After capping the tube, the reaction tube was symmetrically placed in the pretreatment system RAA-B6108 for pre-defined vortex and centrifugation for 7 min, the reaction tube was then removed and transferred to the nucleic acid amplification detector RAA-F1620. The reaction temperature was set at 39 ℃ for 15 min, and the results could be observed in real time.
The result was considered positive when ORF1ab channel was positive and GAPDH was positive or negative. The result was considered negative when ORF1ab channel was negative and GAPDH was positive. The sample needed to be re-tested when both target genes (ORF1ab and GAPDH) were negative, probably resulting from the presence of inhibitors in the sample or the sampling errors.
-
All the experimental operations and biosafety protection in this study strictly abided by Novel Coronavirus Nucleic Acid Testing Work Manual for Medical Institutions (2nd Edition) (6) and SARS-CoV-2 Laboratory Biosafety Guidelines (2nd Edition) (7) issued by National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China.
-
COVID-19 prevention and control protocols (8th Edition) recommended that confirmed cases of COVID-19 infection should be identified by qRT-PCR kits (6). The qRT-PCR kit (BioGerm, Shanghai) approved by NMPA was selected in this study for parallel experiment. SPSS Statistics software (version 21, IBM, NY, USA) was used to perform the statistical analysis. The results of qRT-PCR assay and RT-RAA assay were analyzed using Kappa and McNemar's tests, and a value of P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Scatter diagram analysis was used to analyze the relationship between the time threshold (min) detected by RT-RAA and the cycle threshold (Ct) of qRT-PCR method using 292 positive samples of both assays.
-
S1–S6 produced positive results for all 8 replicates, and the sensitivity of RT-RAA was 137 copies/mL (S6) as shown in Figure 2. No cross reactions with four common coronaviruses or other viral and bacterial pathogens were observed.
 Figure 2.
Figure 2.Sensitivity of the duplex RT-RAA assays for SARS-CoV-2 RNA using diluted National Reference (S1–S6).
Note: The blue curve represents National Reference S1 (33,333 copies/mL); the brown curve represents National Reference S2 (11,111 copies/mL); the dark green curve represents National Reference S3 (3,703 copies/mL); the purple curve represents national reference S4 (1,234 copies/mL); the light green curve represents national reference S5 (411 copies/mL); the red curve represents national reference S6 (137 copies/mL).
Abbreviations: SARS-CoV-2=severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; RT-RAA=reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification.
-
Totally, 808 samples were extracted using automatic RNA extraction kits and detected by RT-RAA and qRT-PCR (Table 1). Among the 808 samples, RT-RAA results for 778 samples were consistent with qRT-PCR (292 were positive, 486 were negative) and 30 were inconsistent (6 were RT-RAA positive only and 24 were qRT-PCR positive only). These 24 samples were positive only by qRT-PCR but negative by RT-RAA, and the corresponding Ct values were all distributed between 35 and 40. Compared with qRT-PCR, the sensitivity of RT-RAA was 92.41% and the specificity was 98.78%. The total coincidence rate was 96.29% and the Kappa was 0.92 (P<0.05). As shown in Figure 3, we observed that the fluorescence signal of most samples reached the threshold within 4 min. Most of the samples with low viral load (Ct≥35) had higher threshold time values within 10 min, plus the pre-reaction of 7 min, the duration of total process was within 20 min.
Method qRT-PCR Performance characteristics Positive Negative Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) Kappa RT-RAA (automatic RNA extraction) Positive 292 6 92.41 98.78 0.92 Negative 24 486 Total (n=808) 316 492 RT-RAA (simplified RNA extraction) Positive 12 0 40 100 0.39 Negative 18 28 Total (n=58) 30 28 Abbreviations: RT-RAA=reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification; qRT-RAA=reverse transcriptase real-time quantitative PCR. Table 1. The clinical performance of the RT-RAA using simplified RNA extraction or automatic RNA extraction compared with qRT-PCR as the reference method.
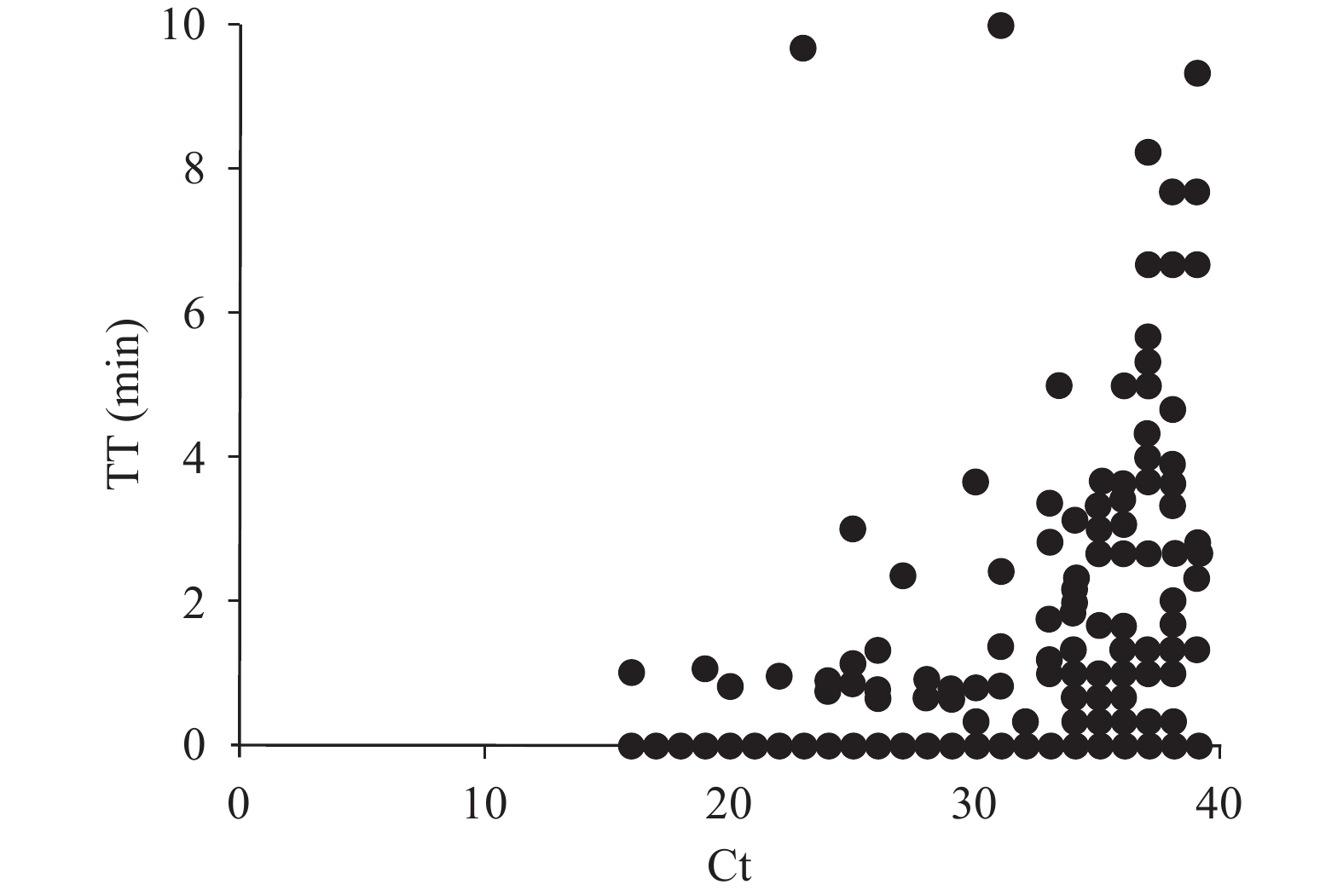 Figure 3.
Figure 3.Scatter diagram analysis of RT-RAA threshold time (TT) (y-axis) and qRT-PCR cycle threshold values (Ct) (x-axis).
Note: Data were analyzed by GraphPad Prism software (version 8, GraphPad Software, San Diego, USA).
Abbreviations: RT-RAA=reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification; qRT-PCR=reverse transcriptase real-time quantitative PCR.
Furthermore, 58 samples were extracted using simplified extraction method and detected by RT-RAA and qRT-PCR (Table 1). Among the 58 samples, RT-RAA results of 40 samples were consistent with qRT-PCR (12 were positive, 28 were negative), and the Ct values of 12 RT-RAA-positive samples ranged from 20 to 32. Additionally, the Ct values of 18 samples (positive only by qRT-PCR) ranged from 32.2 to 36.4.
-
At present, commercial qRT-PCR kits are widely used for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 (8–9). Our current results indicated that the clinical performance of the RT-RAA kit was comparable to that of the qRT-PCR kit. Nevertheless, the samples with Ct≥35 were steadily detected by RT-RAA within 20 min, much shorter than qRT-PCR kits (1–2 h), suggesting that RT-RAA assay had adequate sensitivity to rapidly identify clinical samples with very low viral load (4). This RT-RAA kit incorporated an endogenous internal control that ensured its reliability by monitoring sample collection, RNA extraction, and RAA reaction. With added advantages of simple operation, quick training, and portability, RT-RAA is thus a valuable alternative to qRT-PCR to meet the needs of rapid, sensitive, and accurate detection in community-level medical institutions (such as fever clinic, county, and township) (10-11).
We observed that the selection of nucleic acid extraction methods had a dramatic impact on the sensitivity of RT-RAA detection. Particularly, the extraction efficiency and quality of sampled nucleic acids are greatly affected by the virus sampling tubes with inactivation agents. The influence of sampling tubes could be eliminated by using a fully automatic nucleic acid extraction instrument and a matching extraction kit. While using a simplified extraction method, the sensitivity of RT-RAA dropped to 40%, suggesting that the RT-RAA was not compatible with the inactivator of sampling tubes. At present, RT-RAA is only moderately suitable for simplified extracted nucleic acid with a few brands of sampling tubes containing inactivated agents (such as Changchun Zhihe Biotechnology Co., LTD.). The use of nucleic acid lysis solution could achieve manual extraction of nucleic acid within 5 mins, but only samples with a high nucleic acid concentration (Ct value not higher than 32) could be stably detected.
However, this study had a few limitations. Firstly, only single gene (ORF1ab) was targeted for SARS-CoV-2. Secondly, this study only tested 58 throat swab samples using simplified RNA extraction, different clinical sample types and more samples are needed to verify this method.
Our clinical evaluation results highlighted the feasibility of RT-RAA and its potential utilization in rural areas. Herein, we propose two schemes for practical reference. Scheme 1: this combination (Any sampling tube with inactivation agent + fully automated nucleic acid extraction instrument + RT-RAA kit) is recommended for routine use in county health centers and fever clinic laboratories equipped with biosafety cabinets. Scheme 2: this combination (Sampling tube from Changchun Zhihe Biotechnology Co., LTD. + 5 min of manual simplified extraction + RT-RAA kit) is recommended for emergency use in township health centers and fever outpatient laboratories without biosafety cabinets.
-
No conflicts of interest declared.
-
Hebei Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
HTML
Specimens
Analytical Sensitivity and Specificity of RT-RAA Kit
Automatic RNA Extraction
Simplified RNA Extraction
Protocol of RT-RAA Kit for SARS-CoV-2 RNA Detection
Operation Standard
Statistical Data Analysis
Sensitivity and Specificity of the RT-RAA Kit
Comparison of RT-RAA and qRT-PCR
| Citation: |




 Download:
Download:




