-
The Omicron variant was first identified in South Africa on November 9, 2021, and the World Health Organization (WHO) designated it as a variant of concern (VOC) on November 26, 2021, only 17 days passed (1). Due to the Omicron variant, the number of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases worldwide is growing rapidly. On December 13, 2021, Guangzhou City confirmed a Canada imported COVID-19 case, which was sequenced as Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant. Guangdong had reported a total of 65 imported COVID-19 cases infected with the Omicron variant (Omicron cases in brief) by second-generation sequencing as date of December 31, 2021. We selected 78 imported cases infected with the Delta variant (Delta cases in brief) reported in Guangdong from May to June, 2021, the first 2 months when Delta variant was discovered in Guangdong. These 78 Delta cases were compared with 65 Omicron cases. The results showed that 89.23% of Omicron cases completed whole course of vaccination against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), higher than that of Delta cases. Overall, 92.19% imported Omicron cases tested SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid positive after entering Guangdong within 3 days, which was earlier than Delta cases.
Information about these COVID-19 cases was collected by disease report cards and epidemiological investigation report in the China Information System for Disease Control and Prevention. Categorical variables were compared by chi-square test, continuous variables were compared by nonparametric test of Mann-Whitney U test. Data analysis was conducted by software IBM SPSS Statistics (version 25.0, IBM Corp, Chicago, USA). All statistical tests were 2-sided with α value at 0.05.
Among the 65 Omicron cases, 41 cases (63.08%) were male, 36.92% were female; 35.38% of Omicron cases were 21–30 years old, 21.54% were 31–40 years old, the mean age of Omicron cases was 34.2 years old, younger than Delta cases that had a mean age of 40.2 years old. Out of 65 Omicron cases, 56 cases were normal passengers, and 9 cases were flight crew members where 8 were from Ethiopian Airlines and 1 was from Israel Airlines. However, no flight crew members were reported in the 78 Delta cases, as Table 1 shows. Also, 65 Omicron cases came from 16 countries, of which 29 cases (44.62%) came from America, followed by Ethiopia, Canada, and Democratic Republic of the Congo. Overall, 78 Delta cases came from 20 countries, of which 27 cases (34.62%) came from South Africa, followed by Saudi Arabia, India, and the United Arab Emirates (not listed in table).
Variable Cases infected with
Omicron variant (%) (n=65)Cases infected with
Delta variant (%) (n=78)Chi-square test P value Gender Male 41 (63.08) 62 (79.49) 4.74 0.029* Female 24 (36.92) 16 (20.51) Age (years) 1–10 4 (6.15) 2 (2.56) 14.28 0.027* 11–20 2 (3.08) 0 (0.00) 21–30 23 (35.38) 12 (15.38) 31–40 14 (21.54) 26 (33.33) 41–50 13 (20.00) 26 (33.33) 51–60 7 (10.77) 7 (8.97) 61–70 2 (3.08) 5 (6.41) Type of traveler Passenger 56 (86.15) 71 (91.03) 16.73 0.000* Flight crew 9 (13.85) 0 (0.00) Seaman 0 (0.00) 7 (8.97) Doses of coronavirus vaccine None 7 (10.77) 55 (70.51) 56.03 0.000* 1 2 (3.08) 0 (0.00) 2 42 (64.62) 22 (28.21) 3 11 (16.92) 1 (1.28) 4 3 (4.62) 0 (0.00) Days from entry to SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid positive† 0–3 59 (92.19) 41 (52.56) 26.82 0.000* 4–7 5 (7.81) 32 (41.03) 8–10 0 (0.00) 4 (5.13) 11–14 0 (0.00) 1 (1.28) Ct values of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid§ ORF1ab gene Median (Range) 25.0 (15.0–39.0) 27.0 (14.0–37.0) −0.948 0.343 N gene Median (Range) 24.0 (14.0–38.0) 25.0 (12.0–35.0) −0.851 0.395 Abbreviations: SARS-CoV-2=severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; Ct values=cycle threshold value; ORF1ab gene=open reading frame 1ab gene; N gene=nucleocapsid protein gene.
* P<0.05, the difference is statistically significant.
† An imported COVID-19 infected Omicron variant was considered infection during centralized quarantine in other province, so days from entry to test SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid positive were not calculated.
§ Using nonparametric test of Mann-Whitney U test, the statistic for P value was Z.Table 1. Comparation between 65 imported cases infected with Omicron variant and 78 imported cases infected with Delta variant.
As more people were vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2, the proportion of Omicron cases that were vaccinated was significantly higher than the Delta cases. Except 7 cases without history of vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, the other 58 cases (89.23%) all completed the whole course of vaccination, including 2 cases receiving 1 dose of Johnson & Johnson vaccine. Further, 3 cases were vaccinated with 4 doses, and 11 cases were vaccinated with 3 doses. Among Delta cases, only 29.49% completed the whole course of vaccination, and 70.51% were never vaccinated. It seemed that breakthrough infection was more common in Omicron cases than Delta cases in this study.
Among 65 Omicron cases, 59 cases all tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid after entering Guangdong within 3 days, 5 cases within 4–7 days, except for 1 special case who was quarantined in another province for 14 days and tested positive for nucleic acid after returning to Guangdong where we considered he was likely infected during transition to centralized quarantine. As for Delta cases, 52.56% were tested positive using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) after entering Guangdong within 3 days, 41.03% in 4–7 days, 5.13% in 8–10 days, and 1.28% in 14 days. The period from entry into Guangdong to testing positive among Omicron cases was much shorter than Delta cases. Therefore, we speculated that the incubation period of Omicron variant was shorter than the Delta variant.
We still compared the cycle threshold value (Ct value) of open reading frame 1ab (ORF1ab) gene and nucleocapsid protein (N) gene when cases were confirmed positive using PCR in first time between two groups. For Omicron cases, the median Ct value of ORF1ab and N gene was 25.0 (with range of 15.0 to 39.0) and 24.0 (with a range of 14.0 to 38.0), respectively. For Delta cases, the median Ct value of ORF1ab and N gene was 27.0 (with a range of 14.0 to 37.0) and 25.0 (with a range of 12.0 to 35.0), respectively. The difference of Ct values between two groups was of no statistical significance. The results revealed the viral load of Omicron cases was not significantly higher than Delta cases.
We collected the most severe clinical states of 65 Omicron cases by following up to January 16, 2022. Among them, 11 cases were diagnosed as asymptomatic, 54 cases were diagnosed as patients where 25 were classified as ordinary cases, 29 were classified as mild cases, and no cases were deemed critical or severe. We also analyzed the symptoms among 65 cases (Figure 1). The most common symptom was coughing which occurred in 21 cases (32.31%), followed by pharyngoxerosis (29.23%), fever (26.15%), and throat pain (12.31%). Other symptoms such as diarrhea, headaches, and stuffy or runny noses also occurred in some cases. The proportion with symptoms was lower than that of the local epidemic by SARS-CoV-2 Delta in Guangzhou, where 75% of cases had a fever and 74% of cases coughed (2).
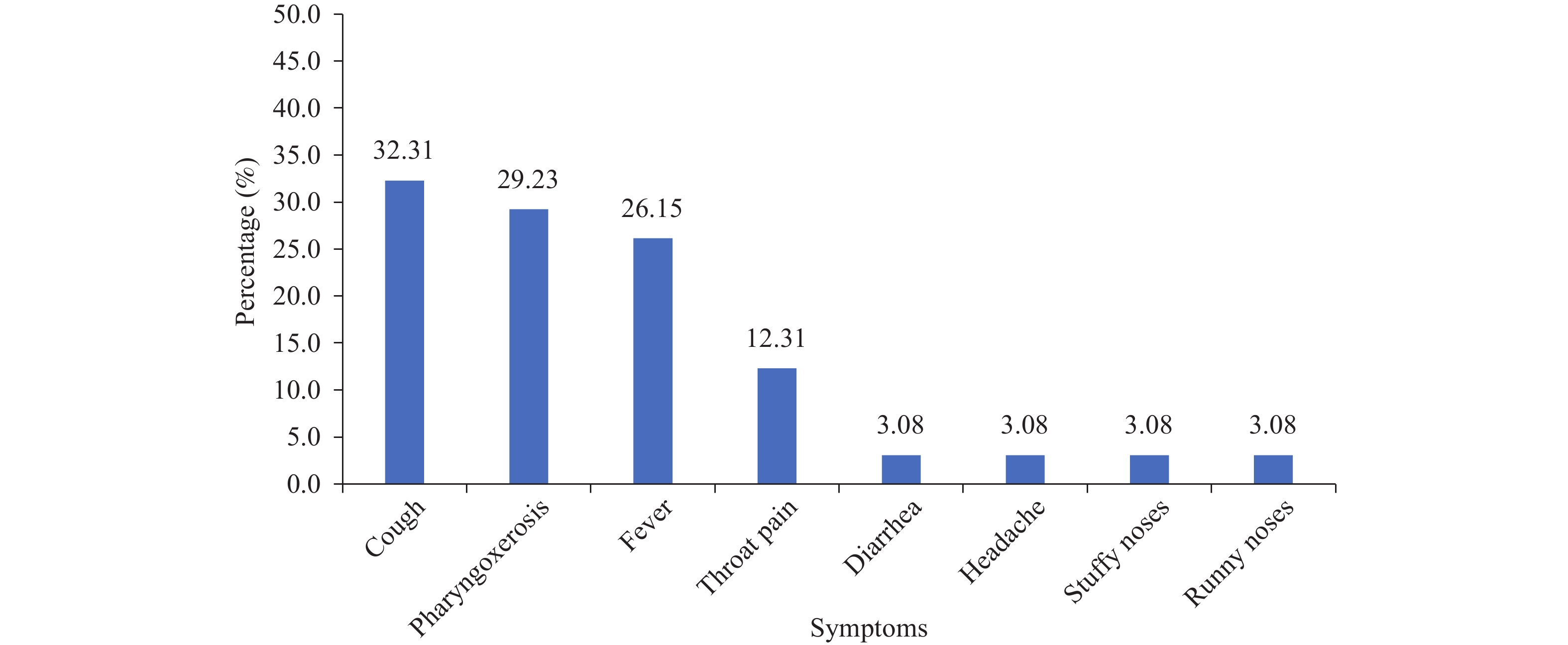 Figure 1.
Figure 1.Symptoms among 65 COVID-19 cases infected with Omicron variant.
Abbreviation: COVID-19=coronavirus disease 2019.According to the results, we should be on alert of local outbreaks caused by the Omicron variant. Guangdong had a local outbreak with 16 Omicron cases between January 13 and January 16, 2022, involving Zhuhai, Zhongshan, and Meizhou City. We roughly calculated the incubation period (time from exposure to date of illness onset or notification) among the 14 cases, except 2 cases who did not have clear dates of onset. The mean incubation period was 3.2 days, which was shorter than the 4.4 days of Delta variant in the former study (3).
-
Guangdong first found COVID-19 cases infected with Omicron variant on December 13, 2021, then the number of imported Omicron cases exceeded Delta cases in the same period. The in-process vaccination of the population may provide limited protection against infection due to the Omicron variant, but it was effective to reduce the incidence of severe illness.
According to the available evidence, the mean incubation period of Omicron variant was shorter than that of the Delta variant among both imported cases and local cases. The WHO also reported that the Omicron variant has a growth advantage with a doubling time of 2–3 days compared with the Delta variant (4), which may provide evidence that transmission capacity of the Omicron variant was stronger than Delta. On the other hand, breakthrough infection occurred in most Omicron cases in this study, this may be caused by high vaccination coverage in the whole population during Omicron epidemic. However, former study provided evidence that the Omicron mutations favored the escape of current vaccines than Delta (5). The result showed that personal protective measures, including wearing masks and maintaining social distance, should be taken even with complete vaccination against SARS-CoV-2. We also observed the symptoms caused by Omicron variant seemed to be relatively mild, the proportion of severe and critical cases was relatively low due to the contribution of vaccination (6). The viral load of hosts infected with Omicron variant was not statistically higher than that of Delta.
This study had two limitations. First, as of December 31, 2021, only 65 imported Omicron cases were reported in Guangdong Province, China. The limited cases may not show us a whole view of this novel variant. Second, this research was based on the field work of emergency responding, the designation and quality control were relatively limited. Further research is needed to obtain more evidence on characteristics of Omicron variant in future, including immune escape, transmission dynamics such as incubation period, the generation time, the serial interval, et al.
Our research reminds that we need to beware rebound of local outbreak by Omicron variant. Travelers entering China should be in closed loop management. Considering most imported Omicron cases were found within 7 days after entry, we suggest shortening the quarantine period from 14 days to 7 days. We also should avoid transmission risk during centralized or home quarantine, especially aerosol transmissio (7–8), which is relatively difficult to prevent. We should insist on nonpharmaceutical interventions, and Omicron surveillance should be strengthened to ensure early confirmation and treatment.
-
CDC staffs of conducting epidemiological investigations and gene sequencing.
-
No conflicts of interest.
HTML
| Citation: |




 Download:
Download:




