-
Occupational cancers are specific cancers suffered by workers after long-term exposure to carcinogenic factors in the working environment after a long latent period (1). The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has identified 40 carcinogens with relevant occupational exposure conditions (2). Approximately 2%–8% of all cancers were estimated to be caused by occupational exposures to carcinogens (3). In China, with the rapid development of industries, occupational cancers due to carcinogens in the workplace have become a major threat to workers’ health. A total of 11 occupational cancers were included in the latest version of “Classification and Catalogue of Occupational Diseases” (4) published in 2013, including: 1) lung cancer and mesothelioma caused by asbestos; 2) bladder cancer caused by benzidine; 3) leukemia caused by benzene; 4) lung cancer caused by chloromethyl ether and dichloromethyl ether; 5) lung cancer and skin cancer caused by arsenic and its compounds; 6) hepatic angiosarcoma caused by vinyl chloride; 7) lung cancer caused by coke oven emissions; 8) lung cancer caused by hexavalent chromium compounds; 9) lung cancer and pleural mesothelioma caused by erionite; 10) skin cancer caused by coal tar, coal tar pitch and petroleum pitch; and 11) bladder cancer caused by β-naphthylamine.
Since 2006, occupational diseases, including occupational cancers, have been reported directly online to the National Occupational Disease Reporting System by occupational disease diagnosis institutions. The total number of occupational cancers reported each year is published annually by the National Health Statistical Bulletin. To better understand the prevalence of occupational cancers in China, we abstracted the case-based data from the system between 2006 and 2020, and analyzed the epidemiological characteristics of occupational cancers in China.
-
Cases of occupational cancers reported between January 1, 2006 and December 31, 2020 were obtained from the National Occupational Disease Reporting System. The system is a network-based reporting system that includes all occupational disease diagnostic institutions in the mainland of China. To ensure the integrity and accuracy of the data, all data reported will be reviewed at county, city, and provincial levels. Descriptive analysis was conducted by year, region, disease type, industry, gender, the average age at diagnosis and exposure duration to occupational hazards. Categorical variables were described using frequencies and constituent ratios, and numerical variables were described using mean and standard deviation or median and interquartile range. Statistical analysis was carried out in SPSS (version 26.0, SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA).
-
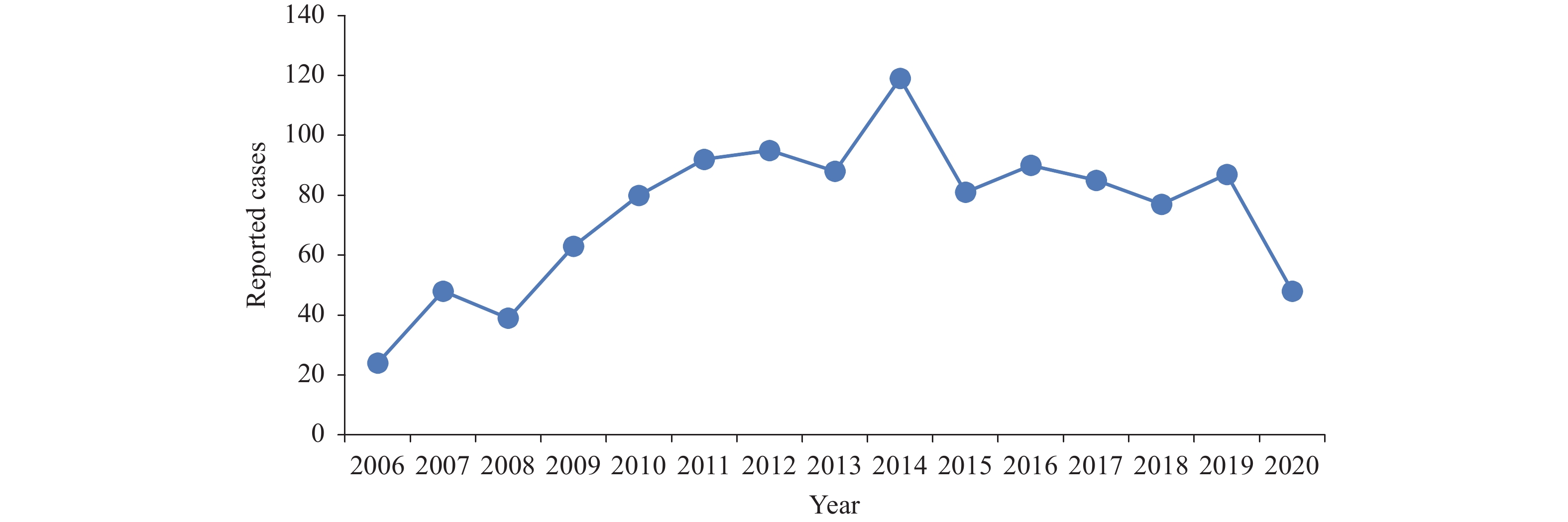
A total of 1,116 cases were reported between 2006 and 2020, and the cases reported annually were shown in Figure 1. As shown in Table 1, the three main types of reported cases were leukemia caused by benzene, lung cancers caused by coke oven exhaust, and lung cancer and mesothelioma caused by asbestos, with the numbers of reported cases being 511 (45.79%), 266 (23.84%), and 226 (20.25%), respectively. There were 6 types of occupational cancers (lung cancer caused by hexavalent chromium compounds; bladder cancer caused by benzidine; lung cancer and skin cancer caused by arsenic and its compounds; lung cancer caused by chloromethyl ether and dichloromethyl ether; skin cancer caused by coal tar; coal tar pitch, petroleum pitch, and bladder cancer caused by β-naphthylamine) with less than 50 reported cases. There were 2 types of occupational cancers (hepatic angiosarcoma caused by vinyl chloride, lung cancer and pleural mesothelioma caused by erionite) for which no cases were reported.
Disease type Number of cases Proportion (%) Leukemia caused by benzene 511 45.79 Lung cancer caused by coke oven emission 266 23.84 Lung cancer and mesothelioma caused by asbestos 226 20.25 Lung cancer caused by hexavalent chromium compounds 42 3.76 Bladder cancer caused by benzidine 41 3.67 Lung cancer and skin cancer caused by arsenic and its compounds 15 1.34 Lung cancer caused by chloromethyl ether and dichloromethyl ether 13 1.16 Skin cancer caused by coal tar, coal tar pitch,petroleum pitch 1 0.09 Bladder cancer caused by β-naphthylamine 1 0.09 Total 1,116 100.00 Table 1. Occupational cancer cases reported by disease type, 2006−2020.
There were 6 provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) with reported cases above 50: Guangdong Province (335, 30.02%), Shandong Province (135, 12.1%), Liaoning Province (122, 10.93%), Hubei Province (93, 8.33%), Beijing Municipality (86, 7.71%), and Jiangsu Province (68, 6.09%).
As for the industrial distribution, the cases were mainly distributed in manufacturing (913, 81.18%), followed by mining (41, 3.67%), transportation, storage, and postal services (39, 3.49%) (Table 2). In manufacturing, leukemia caused by benzene topped the list of occupational cancers cases, while mining and transportation reported the most lung cancer and mesothelioma cases caused by asbestos. Among the total reported cases of occupational cancers, 870 (77.96%) were male and 246 (22.04%) were female cases. The average age at diagnosis of all reported cases was 51.91±15.85 years old, and the median exposure duration to occupational hazards was 12 (5.29–23.25) years. The distribution characteristics of the 3 major occupational cancers showed that for leukemia caused by benzene, 68.88% of the cases were male, the average age at diagnosis was (39.76±10.57) years, and the median exposure duration to occupational hazards was 6.17 years (Table 3). Compared with leukemia caused by benzene, the proportions of male cases of lung cancer caused by coke oven emissions and lung cancer and mesothelioma caused by asbestos were higher at 96.24% and 70.35%, respectively. The average age at diagnosis were higher than that of leukemia caused by benzene, which were (62.64±10.99) years and (63.52±11.19) years, respectively. The exposure duration to occupational hazards were longer than that of leukemia caused by benzene which were 24.25 years and 18.54 years, respectively.
Industrial classification Number of cases Proportion (%) Manufacturing 913 81.81 Mining 41 3.67 Transport, storage, and postal services 39 3.49 Production and Supply of Electricity, Heat, Gas and Water 21 1.88 Leasing and commercial services 20 1.79 Wholesale and retail trades 18 1.61 Construction 16 1.43 Public administration, social security, social organizations 13 1.16 Resident, repair and other services 9 0.81 Scientific research and technical services 7 0.63 Education 7 0.63 Health and social services 5 0.45 Agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery 3 0.27 Administration of water conservancy, environment, public facilities 2 0.18 Finance 1 0.09 Real estate 1 0.09 Total 1,116 100.00 Table 2. Occupational cancer cases reported by industry, 2006−2020.
Demographic characteristics Leukemia caused by
benzene (N=511)Lung cancer caused by coke
oven emission (N=266)Lung cancer and mesothelioma
caused by asbestos (N=226)Gender, n (%) Male 352 (68.88) 256 (96.24) 159 (70.35) Female 159 (31.12) 10 (3.76) 67 (29.65) Age ($ \bar X $±s) 39.76±10.57 62.64±10.99 63.52±11.19 Exposure duration, Median ( inter quartile range) 6.17 (3.17−11.58) 24.25 (14.33−31.33) 18.54 (11.83−28.17) Table 3. Demographic characteristics of 3 main occupational cancers, 2006−2020.
-
Work-related carcinogens were responsible for a significant disease burden worldwide. According to Global Burden of Disease 2016 estimates (5), the burden of cancer due to exposure to 14 IARC Group 1 occupational carcinogens (asbestos, benzene, diesel engine exhaust, silica, etc.) was estimated at 349,000 deaths and 7.2 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) in 2016, accounting for 3.9% of all cancer deaths and 3.4% of all cancer DALYs. The World Health Organization/International Labour Organization joint estimates of the work-related burden of disease and injury (6) found that estimates for mesothelioma attributable to exposure to asbestos were 177,614 deaths and 3.29 million DALYs, and estimates for lung cancer were 23,104 deaths and 0.51 million DALYs, respectively.
However, in our study, only 1,611 cases have been abstracted from the national occupational disease reporting system over the last 15 years, which is far less than the data reported in some other countries. In Germany, for example, according to occupational disease data published by German Social Accident Insurance (7), the number of cases of lung, larynx, or ovarian cancer caused by asbestos; mesothelioma caused by asbestos; and lung cancer caused by asbestos and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon during 2018–2020 were 1,995, 2,533, and 102, respectively. This may be due to the different diagnostic criteria and disease types included in the list of occupational diseases in different countries. Moreover, the diagnosis and treatment of malignant cancers in China were mainly carried out in comprehensive medical institutions or specialized cancer hospitals. Data from the annual report of the China Cancer Registry (8) showed that the number of mesothelioma cases reported to the cancer registry in 2016 was 583.
Asbestos is the most important contributor to occupational mesothelioma, and there is a large discrepancy between the high morbidity of occupational cancers and the low number of cases diagnosed and reported. The problem is that most workers probably lack relevant knowledge and awareness and that the long latency period of cancer onset makes it difficult to determine occupational carcinogen exposure history. According to the diagnostic criteria for an occupational cancer in China (9), there must be a clear history of long-term occupational exposure to carcinogens, and after a comprehensive analysis, the occurrence of primary cancers should meet the requirements of years of total cumulative occupational exposure to carcinogens in the workplace and the latency period for the occurrence and development of occupational cancers. As there is a high mobility of workers in China, who are usually employed by several employers with similar jobs and exposed to the same industrial disease hazards, the working year of some patients at the last employer may not meet the diagnostic criteria of exposure years (10), which makes the diagnosis of occupational cancers difficult.
In summary, occupational cancers may be underestimated in China. Diagnosis and surveillance of occupational cancers should be strengthened, and a comprehensive surveillance system including occupational health monitoring, carcinogens monitoring in workplaces, and occupational disease reporting should be established and improved to better evaluate the prevalence and disease burden of occupational cancers and protect workers’ health.
HTML
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download:




