-
Benzene is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon, which is widely used in industrial production. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classified benzene as human carcinogen in 1982 (1). Benzene can cause acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome and other hematological malignancies, such as non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (2). Chronic exposure to high concentration of benzene can cause chronic benzene poisoning (CBP) (3) which is strongly associated with an increased risk of leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes (4). This study aims to analyze industry distribution of benzene-induced leukemia (BIL) from seven provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs). A total of 699 BIL cases diagnosed from 2005 to 2019 (for four periods, 2005–2008, 2009–2012, 2013–2016, and 2017–2019) from 7 PLADs (Guangdong, Zhejiang, Fujian, Sichuan, Jiangsu, Shandong, and Beijing) were included. The 7 PLADs were selected because most of them (5/7) had serious CBP hazards (5). The industrial distribution characteristics of BIL also were compared with that of CBP (5). The data have shown that BIL mainly occurs in the manufacturing industry and is dominated by small and medium-sized enterprises, just like CBP. Monitoring the benzene concentration in related industries and taking corresponding measures can effectively reduce the number of BIL.
The BIL cases in this study were obtained from the China Disease Control and Prevention Information System — Occupational Diseases and Occupational Health Monitoring Information System. All BIL cases were diagnosed by local occupational disease diagnostic teams. The Industrial classification for national economic activities (GB/T 4754–2017) and Division Standard of Large/Medium/Small Sized Industrial Enterprises (6) document were used to standardize benzene related industries. All data were processed via Excel software (version Home and Student 2019, Microsoft, Albuquerque, America).
The number of BIL cases in 7 PLADs was shown in Table 1. From 2005 to 2019, BIL mainly occurred in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) (χ2=56.07, P<0.05). The proportion of BIL cases from SMEs increased from 47% in 2005–2008 to 72.7% in 2009–2012, decreased slightly to 62.4% in 2013–2016, and increased to 70.8% in 2017–2019 (Table 1). When enterprises with BIL cases were categorized according to the type of ownership, the total number of cases in private enterprises was the highest in 2005–2019 (170 cases, 24.3% of the total) and grew rapidly in 2009–2012 (175% year on year) (Table 1) (χ2=80.55, P<0.05). By comparing the enterprise distribution of BIL and CBP cases in 5 PLADs (Guangdong, Jiangsu, Sichuan, Shandong, and Beijing) from 2005 to 2019, we found that BIL and CBP cases were mainly distributed in private and SMEs (Supplementary Figures S1 and S2. The number of cases reported from SMEs in the 5 PLADs accounted for 65% of total BIL cases and 71 % of total CBP cases in the past 15 years.
Item Number of BIL (%) * 2005−2008 2009−2012 2013−2016 2017−2019 Total 115 260 216 108 Enterprise scale Large 36 (31.3) 46 (17.7) 57 (26.5) 16 (14.7) Medium 33 (28.7) 108 (41.5) 64 (29.8) 43 (39.4) Small 21 (18.3) 81 (31.2) 70 (32.6) 34 (31.2) Mini-sized 0 (0) 0 (0) 1 (0.5) 5 (4.6) Unrevealed 25 (21.7) 25 (9.6) 23 (10.7) 11 (10.1) Ownership type State-owned 18 (15.7) 18 (6.9) 19 (8.8) 8 (7.3) Collective 5 (4.3) 6 (2.3) 2 (0.9) 0 (0) Pooling 1 (0.9) 4 (1.5) 1 (0.5) 2 (1.8) Private 20 (17.4) 55 (21.2) 59 (27.3) 36 (33) Foreign 14 (12.2) 54 (20.8) 34 (15.7) 12 (11) Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan of mainland China 2 (1.7) 43 (16.6) 24 (11.1) 31 (28.4) Stock 43 (37.4) 51 (19.7) 56 (25.9) 17 (15.6) Unrevealed 12 (10.4) 28 (10.8) 21 (9.7) 3 (2.8) Abbreviations: BIL=benzene-induced leukemia; PLADs=provincial-level administrative divisions.
* The proportion of new cases of leukemia in the total cases of leukemia in different enterprise categories.Table 1. Distribution of enterprise scale and ownership type with BIL in 7 PLADs, 2005−2019.
For the industry distribution, BIL cases were mainly distributed in manufacturing industry, accounting for 86.4% of all cases from 2005 to 2019 (Figure 1A). Nine of the top ten industries with BIL cases were from the manufacturing industry (Figure 1C). Compared with the industrial distribution of CBP cases in the same period, the manufacturing industry also had the highest numbers of CBP cases (87.1% of the total). Although CBP and BIL cases were distributed slightly differently among manufacturing sub-industries, they were mainly distributed in the following seven sectors: general and special equipment, chemical, leather/fur/feather, shoe, computer/electronic, transportation equipment, culture/education, arts/crafts/sports, entertainment, and plastics and rubber products manufacturing (Figure 1C–D). We found that some BIL cases were from emerging industries, such as computer/electronic product manufacturing. The number and proportion of BIL cases in computer/electronics manufacturing increased from 3 cases in 2005–2008 (2.9% of the total number of leukemia cases in the same period) to 13 cases in 2017–2019 (11.9% of the total number of leukemia cases in the same period). A total of 62 cases (8.9% of all BIL cases) were reported in the computer/electronics manufacturing over 15 years (2005–2019).
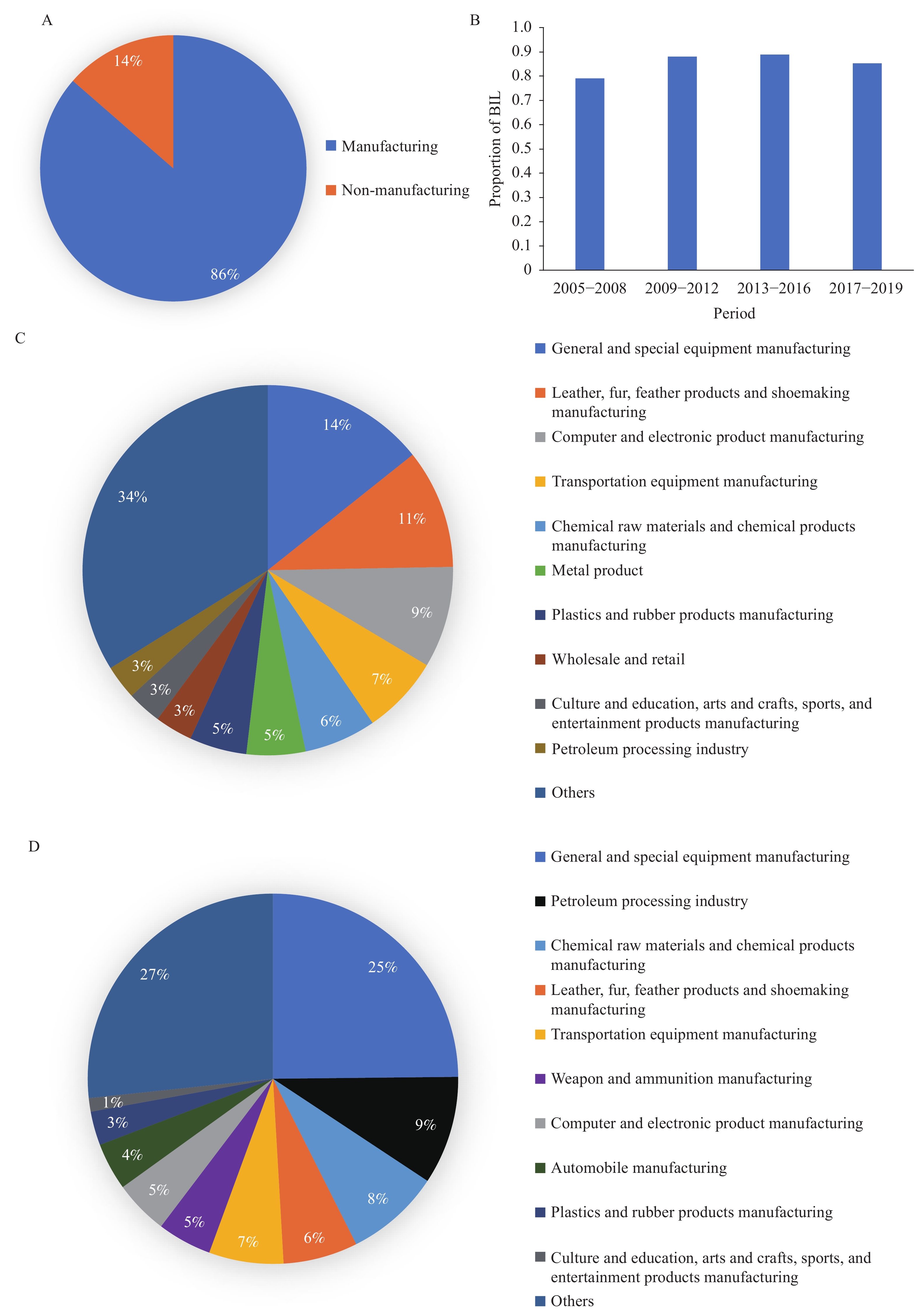 Figure 1.
Figure 1.The industry distribution of BIL and CBP cases from 2005–2019. (A) Distribution of BIL cases between manufacturing and non-manufacturing industries; (B) The proportion of manufacturing with BIL in 7 PLADs in 4 periods (2005−2008, 2009−2012, 2013−2016, 2017−2019); (C) The top ten industries with BIL cases; (D) The top ten industries with CBP cases.
Abbreviations: BIL=benzene-induced leukemia, CBP=Chronic benzene poisoning, PLADs=provincial-level administrative divisions.As shown in Table 2, among the 7 PLADs, the distribution of industries related to BIL cases differed. For example, from 2005 to 2016, the BIL cases were mainly distributed in general/special equipment manufacturing (7 case, 26.9% of the same period) and chemical raw materials and chemical products manufacturing (7 case, 26.9% of the same period) in Jiangsu Province, respectively; from 2017 to 2019, the total number of cases of BIL was only 3 in Jiangsu, involving the computer/electronic product manufacturing, transportation/warehousing and postal industry, and metal products for fire protection manufacturing. From 2005 to 2008, the petroleum exploitation industry, printing and recording media reproduction industry, and transportation equipment manufacturing have the highest number of BIL cases in Guangdong Province, with 2 cases (14.2% of the same period) in each of these 3 industries. From 2009 to 2019, BIL cases were mainly distributed in the computer/electronic product manufacturing (44 cases, 14.8% of the same period) and leather/fur/feather products and shoemaking manufacturing (52 cases, 17.5% of the same period). Third, from 2005 to 2019, general/special equipment manufacturing (73 cases, 21.7% of the same period) and transportation equipment manufacturing (39 cases, 11.7% of the same period) have been the industry with the largest number of BIL cases in Shandong Province.
PLAD Year The top three industries Number of BIL (%)* Jiangsu 2005−2008 General and special equipment manufacturing 3 (37.5) Chemical raw materials and chemical products manufacturing 3 (37.5) Leather, fur, feather products and shoemaking manufacturing 1 (12.5) 2009−2012 General and special equipment manufacturing 2 (40) Chemical raw materials and chemical products manufacturing 1 (20) Petroleum exploitation 1 (20) 2013−2016 Leather, fur, feather products and shoemaking manufacturing 3 (23.1) Chemical raw materials and chemical products manufacturing 3 (23.1) General and special equipment manufacturing 2 (15.3) 2017−2019 Computer and electronic product manufacturing 1 (33.3) Transportation, warehousing, and postal Industry 1 (33.3) Manufacturing of metal products for fire protection 1 (33.3) Guangdong 2005−2008 Petroleum exploitation 2 (14.3) Printing and recording media reproduction industry 2 (14.3) Transportation equipment manufacturing 2 (14.3) 2009−2012 Computer and electronic product manufacturing 26 (19.5) Leather, fur, feather products and shoemaking manufacturing 21 (15.8) Plastics and rubber products manufacturing 14 (10.5) 2013−2016 Leather, fur, feather products and shoemaking manufacturing 20 (20.2) Computer and electronic product 10 (10.1) Metal product 9 (9.1) 2017−2019 Leather, fur, feather products and shoemaking 11 (16.9) Plastics and rubber products 9 (13.8) Computer and electronic product 8 (12.3) Shandong 2005−2008 General and special equipment manufacturing 20 (22.2) Transportation equipment manufacturing 11 (12.2) Petroleum processing industry 9 (10.0) 2009−2012 General and special equipment manufacturing 39 (33.3) Transportation equipment manufacturing 22 (18.8) Chemical raw materials and chemical products manufacturing 10 (8.5) 2013−2016 Chemical raw materials and chemical products manufacturing 11 (11.8) General and special equipment manufacturing 10 (10.8) Petroleum processing industry 6 (6.5) 2017−2019 General and special equipment manufacturing 4 (11.8) Computer and electronic product 4 (11.8) Chemical raw materials and chemical products manufacturing 3 (8.8) Abbreviations: BIL=benzene-induced leukemia; PLAD=provincial-level administrative division.
* The proportion of benzene-induced leukemia cases in all cases of the same period.Table 2. Distribution characteristics in the top three industries with the most benzene-induced leukemia (BIL) cases in Jiangsu, Guangdong, and Shandong, 2005−2019.
-
The incidence of leukemia in China was on the rise from 2005 to 2017, reaching 10.00/100,000 in 2017 (7). Benzene exposure significantly increases the risk of leukemia (3). This study found that BIL mainly occurred in manufacturing industries, especially in private enterprises and SMEs. Consistent with our study, private enterprises and SMES also have the highest number of benzene poisoning cases (4), suggesting the need to strengthen supervision and monitoring of these enterprises. The number of BIL cases in SMEs has been accounting for more than 60% of the total number of leukemia cases in all enterprises. Since 2009, the number of BIL cases in SMEs has increased significantly. This phenomenon may be related to the further development of SMEs in China during the Eleventh Five-Year Plan period. Although SMEs are developing rapidly, their production technology and occupational health conditions are relatively poor compared with large state-owned enterprises. As a result, the number of BIL cases in SMEs has increased.
The two manufacturing sub-industries with the highest number of leukemia cases were the leather/fur/feather products and shoemaking, and general/special equipment manufacturing. These two industries also have the highest number of benzene poisoning cases (4). This may be related to the relatively higher concentration of benzene exposure in these two industries. During 1983–2014, the mean benzene concentrations in the above two industries in China were 5.68 mg/m3 and 4.32 mg/m3, respectively, ranking the top two in all benzene exposure industries (8). In 2020, benzene concentrations in leather/fur/feather products and shoemaking manufacturing were still relatively high, with 2.72% of enterprises exceeding 6 mg/m3 and the highest benzene exposure reaching 67.08 mg/m3 (9).
This study had limitations. First, we could not calculate the incidence because there was no accurate count of benzene exposed workers in 7 PLADs. Therefore, the effect of an increase in the number of workers exposed to benzene on the results could not be eliminated. Second, our BIL cases only come from 7 PLADs; the description of the distribution characteristics of BIL industry in China may not be comprehensive.
This study suggests a reduction in the hazards of occupational benzene exposure and the occurrence of BIL and strengthening of the detection of benzene and its homologues in the workplace of SMEs, private enterprises, and emerging industries. Additionally, measurements must be taken to reduce the air benzene concentration in the workplace and improve the working environment. Also, enterprises with high benzene poisoning incidence should be supervised in order to provide regular occupational health examinations for workers. Finally, health education should be provided to workers to raise their awareness of self-protection and encourage them to wear protective equipment.
-
No conflicts of interest reported.
HTML
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download:




