-
On August 28, 2019, Jiangxi Province Center for Disease Control and Prevention (Jiangxi CDC) received a report of a suspected dengue case from Xin’gan County, and a second suspected case was reported from the same county a day later. The two cases were identified as dengue virus infections cases on August 29 and prompted the deployment of a team composed of an epidemiologist and a vector control specialist to Xin’gan County to provide health support, to investigate the infection source, to assess the effects of mosquito control, and especially to assess the risk of regional transmission.
-
On August 28, 2019, a patient visited Nanchang City Ninth Hospital with fever, dizziness, headache, fatigue, and rash. The patient’s blood sample was tested in Jiangxi CDC and the result showed the patient was experiencing dengue fever viremia. This event was notified to Ji’an City CDC and Xin’gan County CDC. County, city, and provincial CDCs responded to the event immediately, and over the next several days, 80 more local dengue cases were identified in Xin’gan county.
County, city, and provincial CDCs carried out epidemiological investigations in medical institutions and affected areas in Xin’gan County, in which searching definition for suspected dengue cases included fever and the presence of two or more symptoms among the following: rash, arthralgia, myalgia, or headache. By September 8, 2019, a total of 81 patients were identified without serious cases or death.
-
On August 29, 2019, the first local suspected dengue case in Xin’gan County was laboratory-confirmed in a patient with symptoms including fever, dizziness, headache, fatigue, and rash. The first case occurred in a 55-year-old male patient without recent travel history. The real-time RT-PCR test result suggested his blood sample was positive for DENV, and additional sample testing identified DENV-1.
During investigation two suspected dengue cases were found in brothers aged 13 and 14 and were likely the initial cases. They presented dengue fever-like symptoms on August 10 and 11 including fever, headache, and muscle or body aches. In late July, they followed their grandfather to visit their parents for summer vacation in Shiling Town, Huadu District, Guangzhou City. They returned to Xin’gan County on August 7 due to a local dengue fever outbreak in Shiling Town. On August 30 and 31, their grandparents presented dengue fever-like symptoms and tested positive for DENV on September 2.
The time distribution indicated that the date of onset of the first case was August 23, and the last case reported was September 8. The incidence was bimodal with the first peak from August 31 to September 2 (26 cases) and second peak from September 4 to September 5 (15 cases). The number of cases decreased rapidly after September 6 (Figure 1).
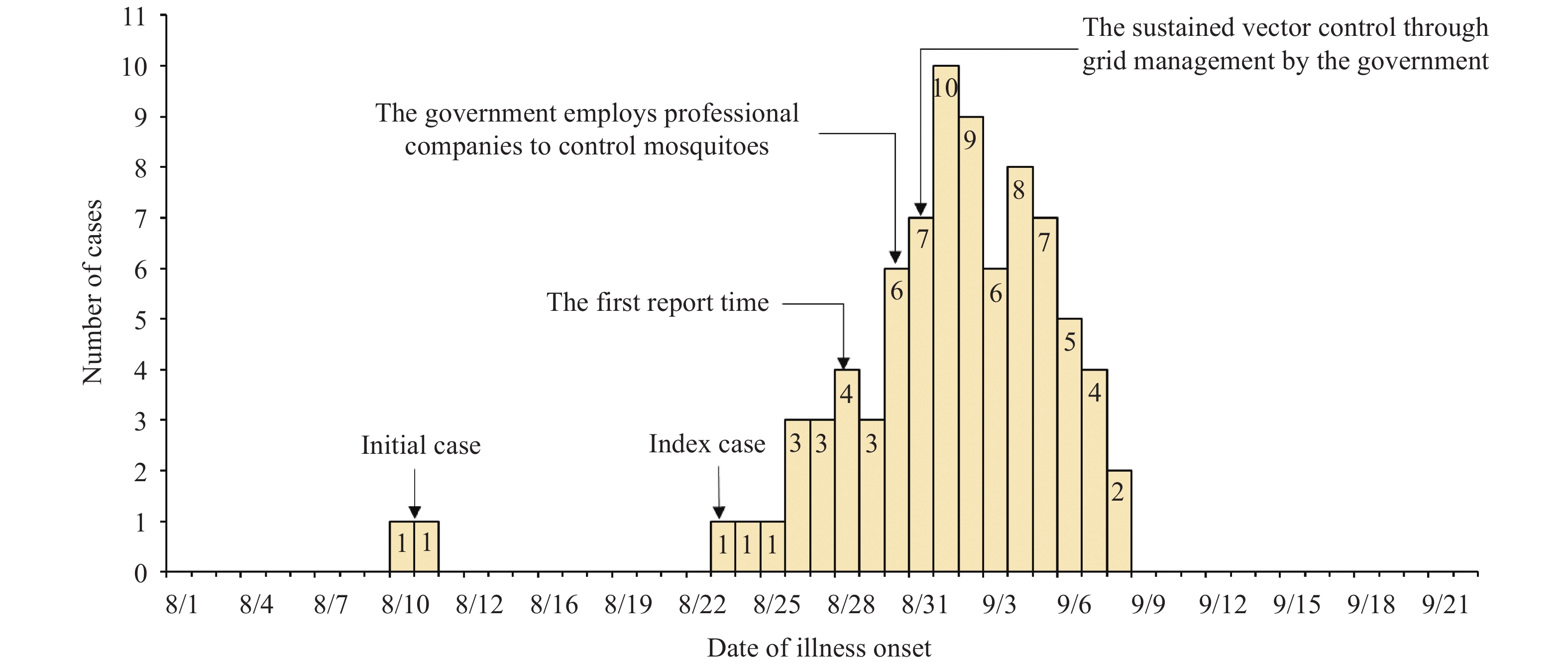 Figure 1.
Figure 1.The onset time curve among the outbreak cases of dengue fever in Xin’gan County, Jiangxi Province, 2019. The date of onset of the first case was August 23, and the last case reported was September 8. After implementation of emergency mosquito control and clearing of breeding places led by the local government, the number of cases decreased rapidly after September 6.
The outbreak occurred in Jinchuan Town, Xin’gan County, including Huachengmen Village, Mexiang, Zhongshan, Binyang, Chengnan, Hejiashan, Chengbei, Shanzheng, and Wenchang communities. Overall, 70 cases (86.4%) occurred in Mexiang, Zhongshan, Binyang, and Chengnan communities and were surrounded by Binjiang Avenue, Yaocai Street, Shangye Road, and Chuannan Road covering an area of about 1.2 km2.
Most of the patients experienced atypical symptoms mainly including influenza-like symptoms such as fever, body ache, chills, headache, fatigue, etc. (Table 1).
Symptoms No. of cases Percentage/% Fever(≥38 ℃) 63 77.8 Body aches 35 43.2 Chills 31 38.3 Headache 25 30.8 Fatigue 24 29.3 Muscle pain 12 14.8 Arthralgia 9 11.1 Bleeding point of skin 4 4.9 Rash 2 2.5 Table 1. The main clinical symptoms among the outbreak cases of dengue fever in Xin’gan County, Jiangxi Province, 2019.
The median interval of time from onset to diagnosis was 2 days (1–8 days), and 23 (28.4%) cases were diagnosed at 4 days or longer after onset of symptoms. Doctors had a significantly improved capacity to diagnose dengue fever after training as the median onset-to-diagnosis interval of patients that were referred was found to be significantly longer than that of those who were not referred (Table 2). SPSS software (version 24.0, IBM Corporation, New York, USA) was used to carry out statistical analysis on data, non-parametric rank sum test were used for comparing population means among different groups if the normality assumption was violated, and the significance test level is α=0.05.
Characteristics The median interval (days) p value Hospital type Hospital 3(1–7) 0.130 Clinic 3(1–8) Referral status No 1(1–7) 0.002 Referral 3(1–8) Training Before 4(2–7) 0.004 After 2(1–8) Table 2. The median onset-to-diagnosis time interval among the outbreak cases of dengue fever in Xin’gan County, Jiangxi Province, 2019.
The dynamic density of the Aedes vector was investigated daily by the Breteau index (BI), which investigates the number of positive containers per 100 houses, in the epidemic area to begin the adoption of control measures. At the beginning, the mean BI in the epidemic area was 24.45 with the highest BI being 48.00 in Meixiang Community and the lowest BI being 14.01 in Binyang Community. An elevated BI is consistent with an increased risk for DENV transmission and demonstrates that Xin’gan County was at risk for local DENV transmission. The BI quickly declined below the safety thresholds 2.55 days after implementation of emergency mosquito control and clearing of breeding places led by the local government.
All cases presenting dengue fever-like symptoms were tested with a dengue rapid diagnostic test (RDT) for DENV nonstructural protein 1 (NS1). Specimens that were RDT positive were further tested by real-time RT-PCR. From August 29 to September 10, 2019, a total of 510 samples were tested for evidence of DENV infection (all by RDT-NS1 alone, and 35 by both methods), 81 (15.9%) of whom tested positive for dengue. By September 10, 2019, 35 cases were laboratory-tested confirmed as being infected with DENV-1. Therefore, 35 out of 81 patients were confirmed by real-time RT-PCR tested results and the remaining 46 patients were clinically diagnosed.
The E genes of some strains were sequenced to construct a phylogenetic tree with the length of the amplified fragment being 1,782 base pairs (bp). The analysis result indicated that about 99.8% to 100% of the 35 strains of DENV-1 isolated from the patients in Xin’gan County were highly homologous. Compared to some strains isolated domestically and overseas, the virus strains from Xin’gan county in 2019 were closest to the strains isolated in Singapore (MF033254|25657|Singapore|2016) and Henan (MK905537|Henan201903|China: Henan Province|2019), and the strains isolated in cases imported from Cambodia to Jiangxi Province in 2019 had a homology of 99.4%, 99.6%, and 99.6%–100%, respectively.
-
The public health response to this outbreak included disposal of waste to remove mosquito breeding sites, indoor residual spraying of pesticides in public places, conducting case monitoring and search, reinforcement of dengue patient management and treatment, outdoor spraying of mosquito repellent, and public education on mosquito avoidance and seeking medical care for symptoms of dengue. The government controlled dengue transmission with sustainable, effective interventions including enhancing the ability of medical institutions to detect, diagnose, and report dengue cases to continue emphasizing health education for the public. One of the most important measures was the sustained mosquito control and environmental improvement under the grid management led by government.
-
The incidence of dengue has grown dramatically around the world in recent decades. An estimated 3.9 billion people in 128 countries are at risk of infection with dengue viruses (1), and an estimated 70% of the burden is shouldered by Asia (2). In recent years, the outbreak of dengue in China has gradually spread from southeast coastal areas to northern parts of the country. During 2005–2018, an average 0–15 imported dengue fever cases were reported annually in Jiangxi Province, which increased the likelihood of a local outbreak of dengue fever, and on August 29, 2019, the local dengue outbreak was reported for the first time in Xin’gan County, Ji’an City, Jiangxi Province.
The retrospective investigation found that there was an epidemiological correlation among two suspected cases of dengue and the index case in terms of time and space. From August 10 to August 23, all three patients walked or played in Chengdong Wetland Park at dusk. The two suspected patients lived in Chengnan Community and the index patient lived in Meixiang Community, and the linear distance from the houses was about 130 meters. Therefore, it is possible that the outbreak may be caused by the two suspected cases that were imported from Huadu District, Guangzhou City, but the DENV-1 strains isolated from Xin’gan in 2019 may be originally originated from Cambodia.
The distribution of cases reported in this outbreak showed a high degree of spatial aggregation, which is consistent with some studies (3). A total of 70 (86.4%) cases were concentrated in four adjacent communities Mexiang, Zhongshan, Binyang, and Chengnan, and the time in which community residents play or walk in parks and squares was consistent with the active time for mosquitoes, which provided evidence for the community transmission of dengue virus through human mobility.
The prompt diagnosis and management of cases are key measures in controlling the spread of the outbreak, and the clinical manifestations of dengue were closely related to the diagnosis, so that correct understanding and analysis of clinical symptoms, combined with investigations of the epidemiological history, are helpful to improve the efficiency of diagnosis and treatment (4-5). By investigating and analyzing the median onset-to-diagnosis interval in this outbreak, we found that enhancing the ability of medical faculty to quickly detect and diagnose dengue cases is highly needed.
In Xin’gan County, primary care doctors did not have awareness for the initial cases early in the outbreak that led to missed diagnoses and misdiagnoses. There are two main reasons: base-level health workers lack essential knowledge about dengue fever, and barefoot doctors have insufficient training to properly address dengue fever. Taking this outbreak as an example, accurate diagnosis depended on the ability to intensively collect epidemiological information such as travel history two weeks prior to onset, the dengue condition in countries or areas of origin, etc., the ability to master recognition of the symptoms and signs of dengue fever patients, and the ability to grasp the laboratory diagnosis methods of dengue fever. The professional skills regarding dengue fever in rural health workers could be improved through further education, training, and reallocating experts to rural areas to assist with prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
The outbreak tells us early detection and diagnosis of cases is key to controlling the spread of an epidemic; timely and effective mosquito control in the early stage of epidemic is another key measure. Thus, during the epidemic period of dengue, more proactive countermeasures must be taken such as intensifying surveillance for dengue cases, virus, and the vector Aedes; strengthening the cooperation with customs and tourism departments to yield close partnerships that will be integral components of successful public health initiatives to combat dengue (6); and improving the capacity of medical institutions to promptly detect and diagnosis dengue cases. Through early warning and coordination, we can detect the spread of dengue-fever.
Acknowledgments: We thank China CDC colleagues guiding the outbreak investigation and response and Jiangxi CDC colleagues participating in the outbreak investigation and response. We are also grateful to Ji’an and Xin’gan County CDC colleagues participating in the investigation and response.
HTML
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download:




