2024 Vol. 6, No. 9
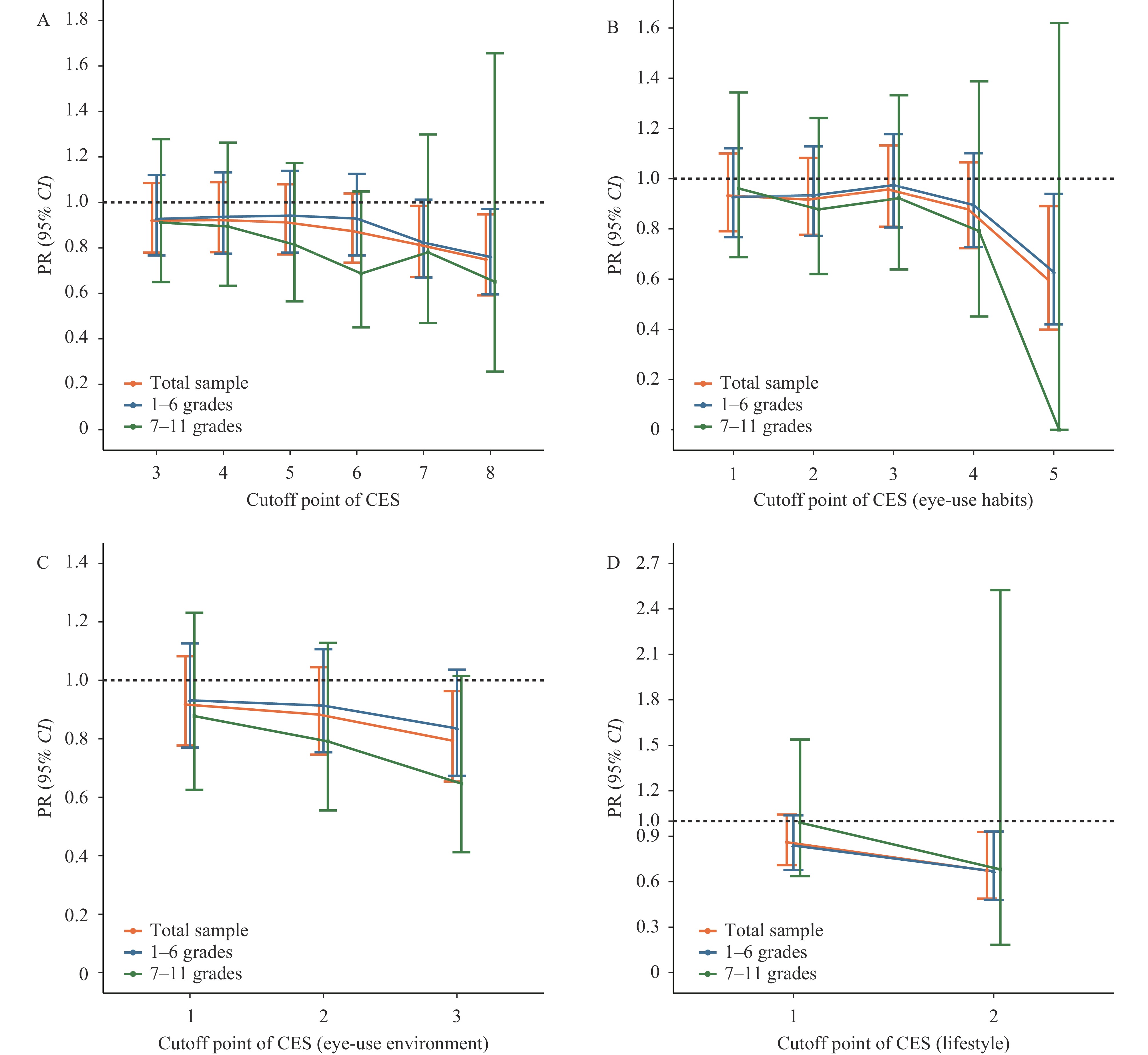
Myopia has been identified as a significant emerging challenge and policy priority among children and adolescents in China by the Ministry of Education and seven other departments. Limited research has been conducted to investigate the collective impact of outdoor time and other modifiable factors on the incidence of myopia.
This study provides support for the protective effect of combining increased outdoor time with other prevention strategies in reducing the incidence of myopia. The results indicate the presence of a dose-response relationship.
To effectively prevent myopia, it is important to implement comprehensive interventions that encompass various aspects such as outdoor time, eye-use habits, eye-use environments, and lifestyle modifications.
With the assistance of the internet, big data, cloud computing, and other technologies, the concept of smart elderly care has emerged.
This study presents information on the countries or regions that have conducted research on smart elderly care, as well as identifies global hotspots and development trends in this field.
The results of this study suggest that future research should focus on fall detection, health monitoring, and guidance systems that are user-friendly and contribute to the creation of smarter safer communities for the well-being of the elderly.
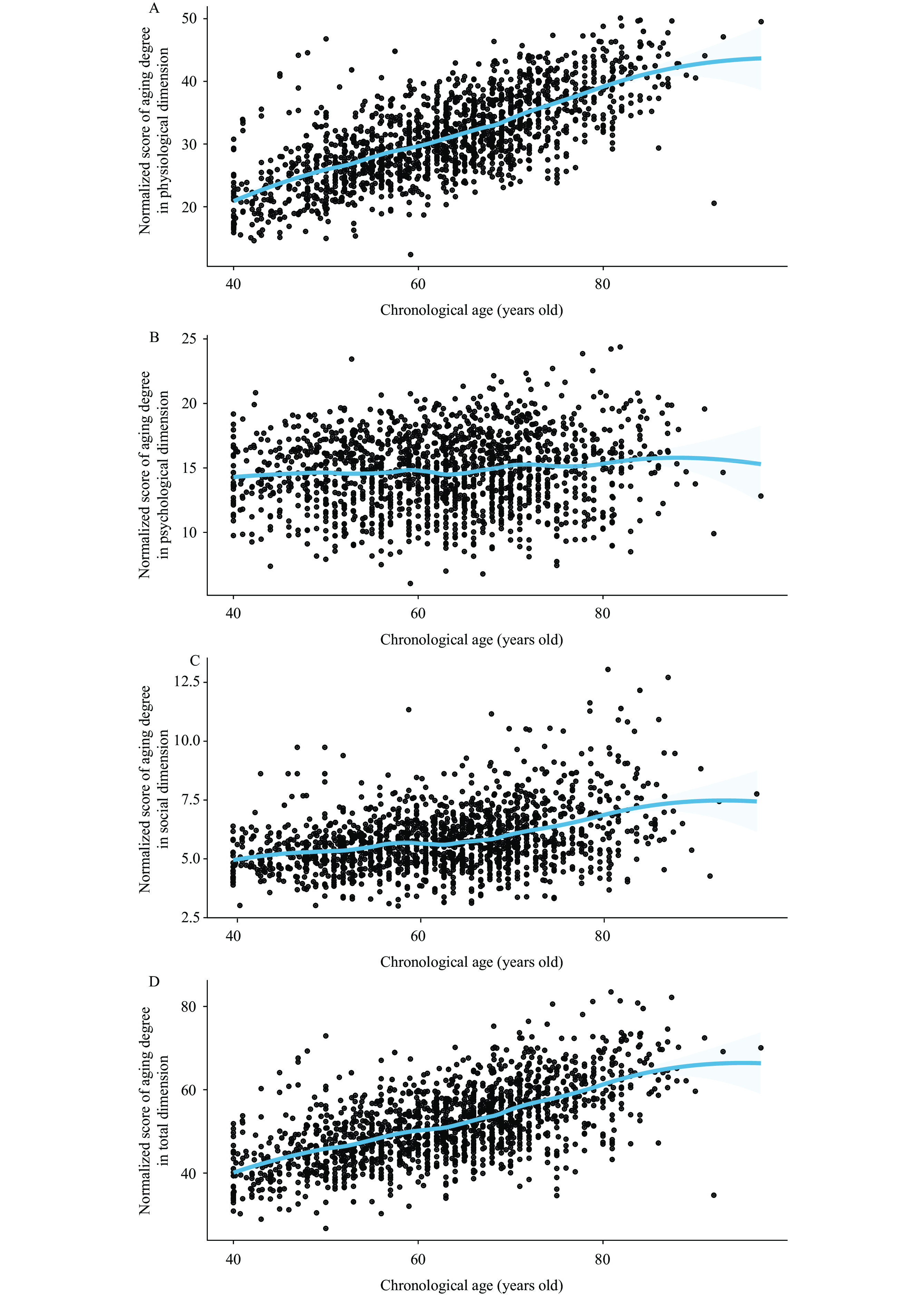
Previous studies have predominantly examined the micro-level aspects of women aging inflection points, while macro-level research using big data on the inflection points of aging among middle-aged and elderly women in China is currently limited.
This study determined the inflection ages for physiological, psychological, social, and total dimensions in middle-aged, young elderly, and elderly women [(48.0–53.2) vs. (66.3–70.0) vs. (78.4–81.2) years old].
This study is important for gaining a deeper understanding of aging, identifying patterns of aging, and implementing targeted interventions to promote the overall health of Chinese women.
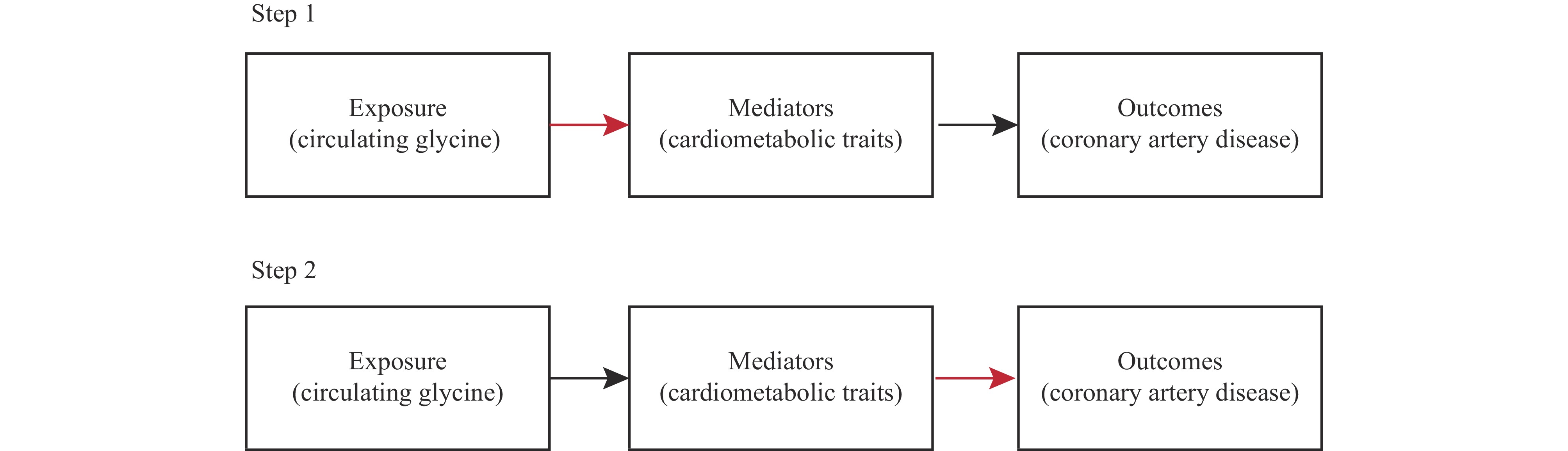
The purpose of this study is to examine the potential causal relationship between levels of circulating glycine and coronary artery disease (CAD) using a two-step Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis.
We analyzed data from genome-wide association studies (GWAS) conducted on European and East Asian populations. To assess the causal effects of circulating glycine levels on the risk of CAD. We used the inverse-variance weighting (IVW), weighted median (WM), MR-Egger, and Mendelian Randomization Pleiotropy RESidual Sum and Outlier (MR-PRESSO) methods. Furthermore, we conducted mediation analysis to investigate the contribution of blood pressure and other cardiovascular disease-related traits.
The two-step Mendelian randomization analysis revealed that higher levels of glycine in the blood were associated with a reduced risk of CAD in Europeans [odds ratio (OR)=0.84, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.72, −0.98; P=0.029] and East Asians: (OR=0.76, 95% CI: 0.66, −0.89; P=3.57×10−4). Sensitivity analysis confirmed the robustness of these findings. Additionally, our results suggest that about 6.06% of the observed causal effect is mediated through genetically predicted systolic blood pressure (SBP) in the European population.
Our results contribute to the current knowledge regarding the involvement of glycine in the progression of CAD, and provide valuable methodological insights for the prevention and treatment of this condition.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed