2024 Vol. 6, No. 42
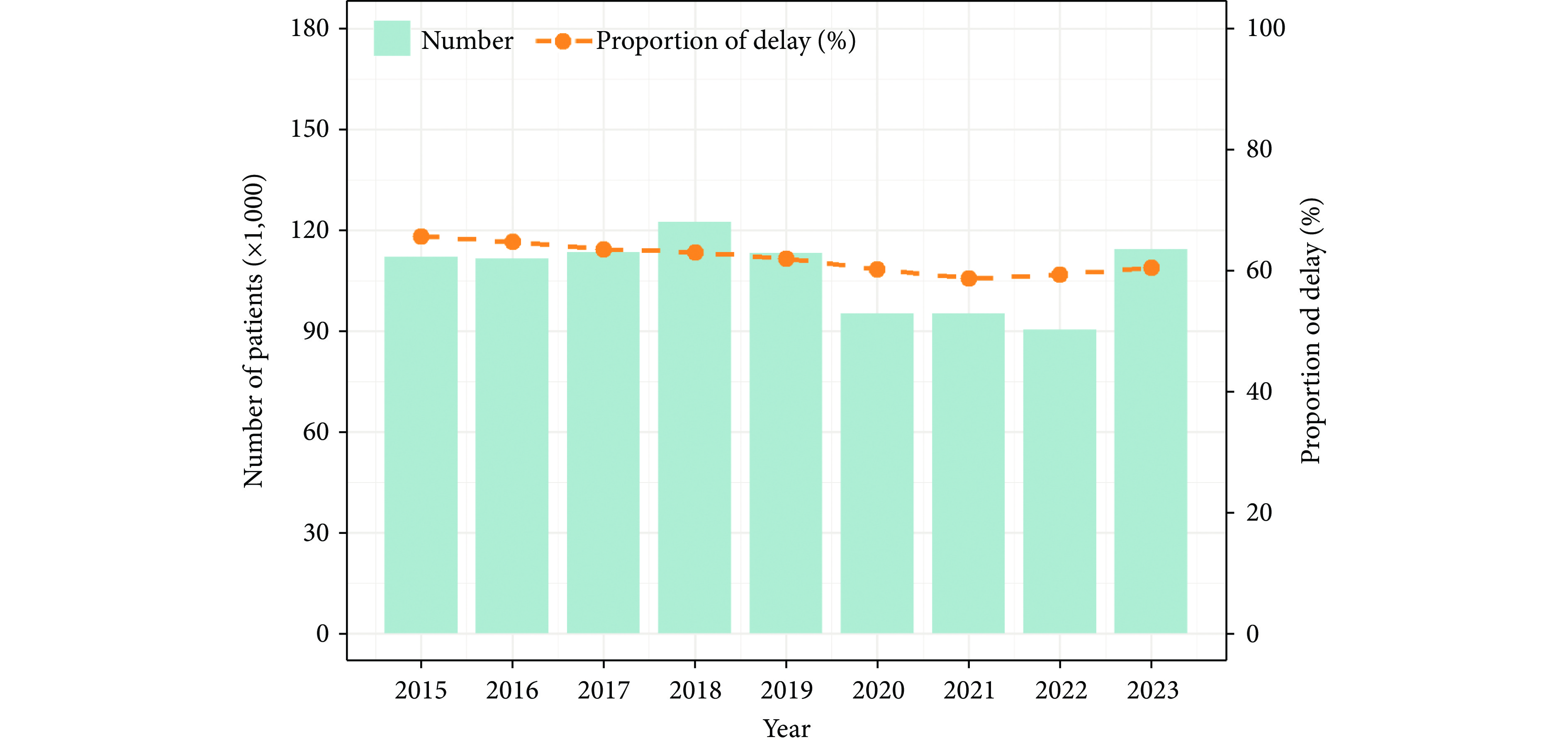
Patient delay in seeking medical care for pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB), especially among elderly individuals with weakened immune systems and mild symptoms, not only slows their recovery but also increases the risk of tuberculosis spread because cases are not identified promptly.
In China, patient delays experienced by elderly PTB patients showed a modest decrease from 2015 to 2023. Notably, longer patient delays were observed among agricultural workers and those identified through passive case-finding methods. Furthermore, the patient delay in the western regions was longer than in the eastern and central regions.
The study underscores the imperative of accessible healthcare for the elderly to minimize patient delay in pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosis and treatment.
Recombinant strains dominate the human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) epidemic in China. Yunnan Province was the first region in China to report HIV-1 infections in batches. The long-term HIV-1 epidemic led to the generation of various recombinant forms. Among the 47 circulating recombinant forms (CRFs) reported in China, more than 20 were first identified in Yunnan Province.
This study reported a previously unrecognized HIV-1 CRF (CRF142_BC) characterized by the insertion of four short subtype B fragments into the subtype C backbone. CRF142_BC was estimated to have emerged in the mid-1990s, close to the time of the emergence of most known CRF_BCs in China.
The discovery of new CRFs will provide a basis for HIV-1 molecular tracing and intervention research. In addition, HIV-1 recombination can alter viral biological properties. The study of HIV-1 gene variants needs to be intensified.
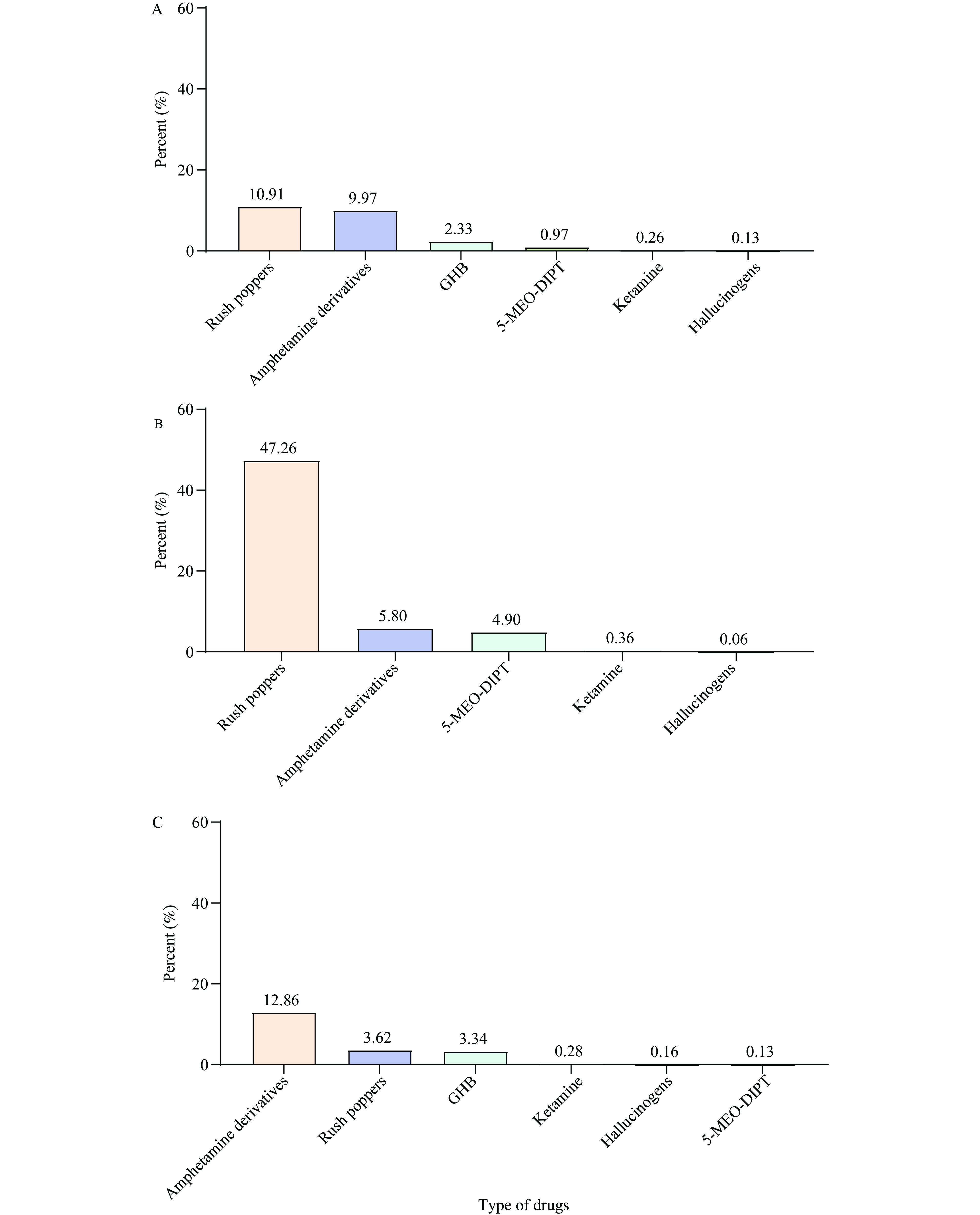
There is a correlation between psychoactive substance use and heightened human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) susceptibility in men who have sex with men (MSM) populations, although the precise impact on transmission risk remains unclear.
In MSM populations, rush poppers and amphetamines are widely used, with rates of 10.91% and 9.97%. In China, rush poppers usage is notably higher at 47.26%. For other regions and coutries, amphetamines (12.86%), rush poppers (3.62%), and GHB (3.34%) are most common. Overall, 17% of MSM use psychoactive substances, with higher HIV risk from amphetamines [Odds ratio (OR) 3.06] compared to rush poppers (OR 1.51) and general substances (OR 1.76).
This study supports the idea that targeting specific regions and types of psychoactive substances for reduction among MSM populations can help decrease HIV transmission as well as promote prevention strategies.
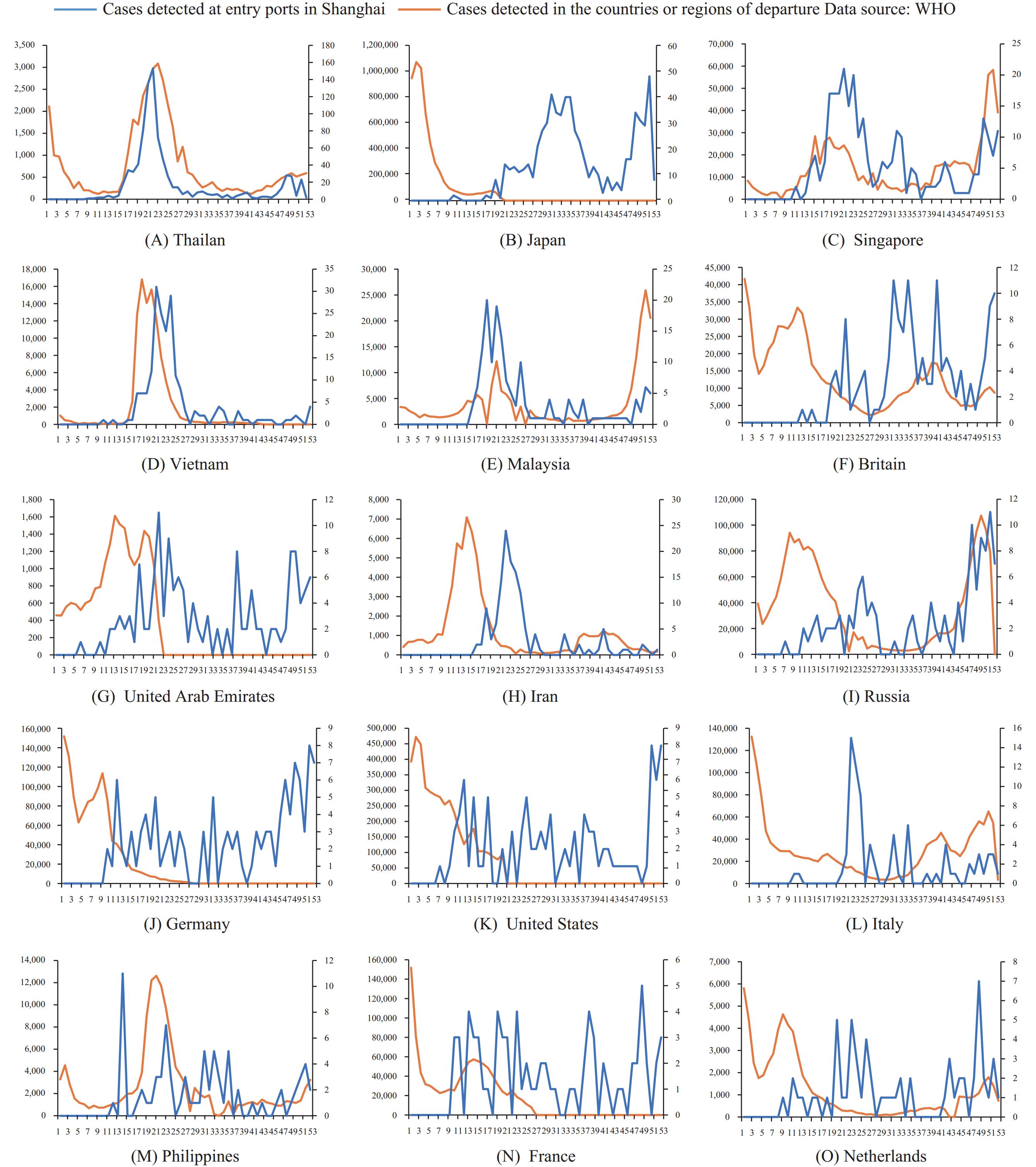
Despite the end of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) as a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC), the changes in risks of travel-related infectious diseases and their impact on global health quarantine still call for great concern.
Our study indicated that the pattern of changes in the positive detection rate of arrivals was basically in line with the disease incidence in countries from which travel was initiated.
Accurate risk assessment at entry-exit ports can significantly enhance the efficiency of targeting high-risk international arrivals, especially in the early stages of epidemic control and prevention when available data are insufficient.
All countries face the potential threat of imported polioviruses, including both wild type and circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses. In response, we conducted a province-level assessment in China to evaluate the risk of importation and transmission of type 1 wild poliovirus (WPV1) and type 2 vaccine-derived poliovirus (VDPV2).
Distinct risk assessment tools for WPV1 and VDPV2 were employed, incorporating three primary indicators — population immunity, poliovirus surveillance, and importation risk. WPV1 was assessed using 13 secondary indicators, whereas VDPV2 utilized 21 secondary indicators. Assessments used comprehensive provincial data from the preceding five years. Scores (S-values) were derived from the secondary indicators’ criteria and ratings, and used to classify the provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) into three risk categories: high, medium, and low. The top 10% of PLADs were designated as high-risk, with the remaining provinces equally distributed into medium- and low-risk categories.
In 2023, Xizang, Qinghai, and Xinjiang PLADs faced the highest risk of WPV1 importation and transmission; Xizang, Shaanxi, and Hainan PLADs were at the greatest risk for VDPV2 importation and transmission.
Risk assessment for VDPV2 importation and transmission has identified a distinct set of high-risk provinces compared to those identified by WPV1 risk assessment. Preventive and proactive response measures tailored to the specific risks should be implemented to maintain China’s polio-free status.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed