2024 Vol. 6, No. 29
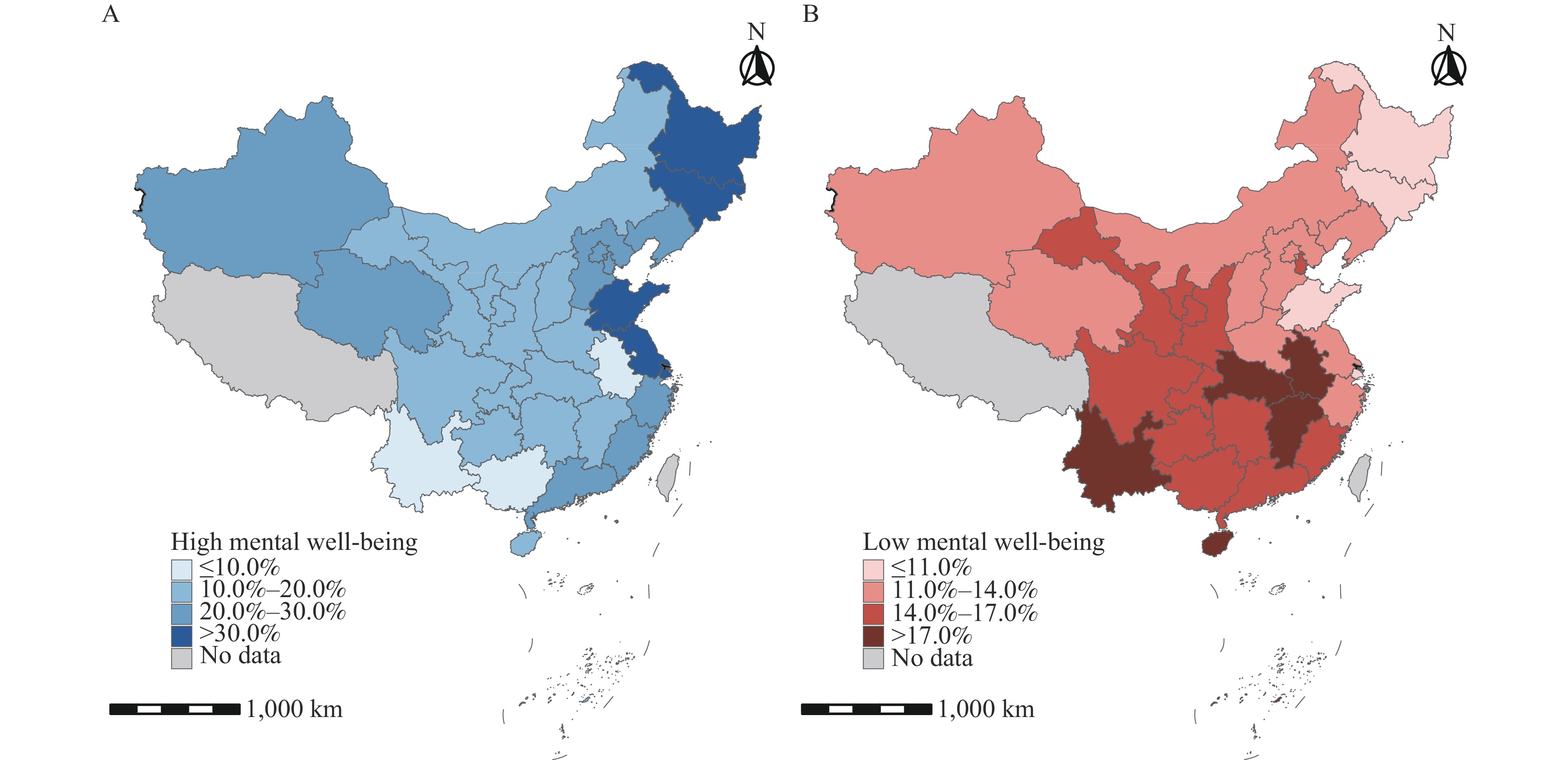
High levels of mental well-being are linked to favorable life outcomes. Nonetheless, compared to the research on psychiatric disorders, the understanding of mental well-being among Chinese adolescents is still relatively underexplored.
This report fills a significant void in the literature concerning the mental well-being of Chinese adolescents by providing updated data. This information is critical for developing evidence-based interventions and strategies aimed at improving mental well-being and addressing mental health issues among adolescents.
Enhancing psychological support for vulnerable populations is essential to improve mental well-being among adolescents, reduce health disparities, and achieve global Sustainable Development Goals.
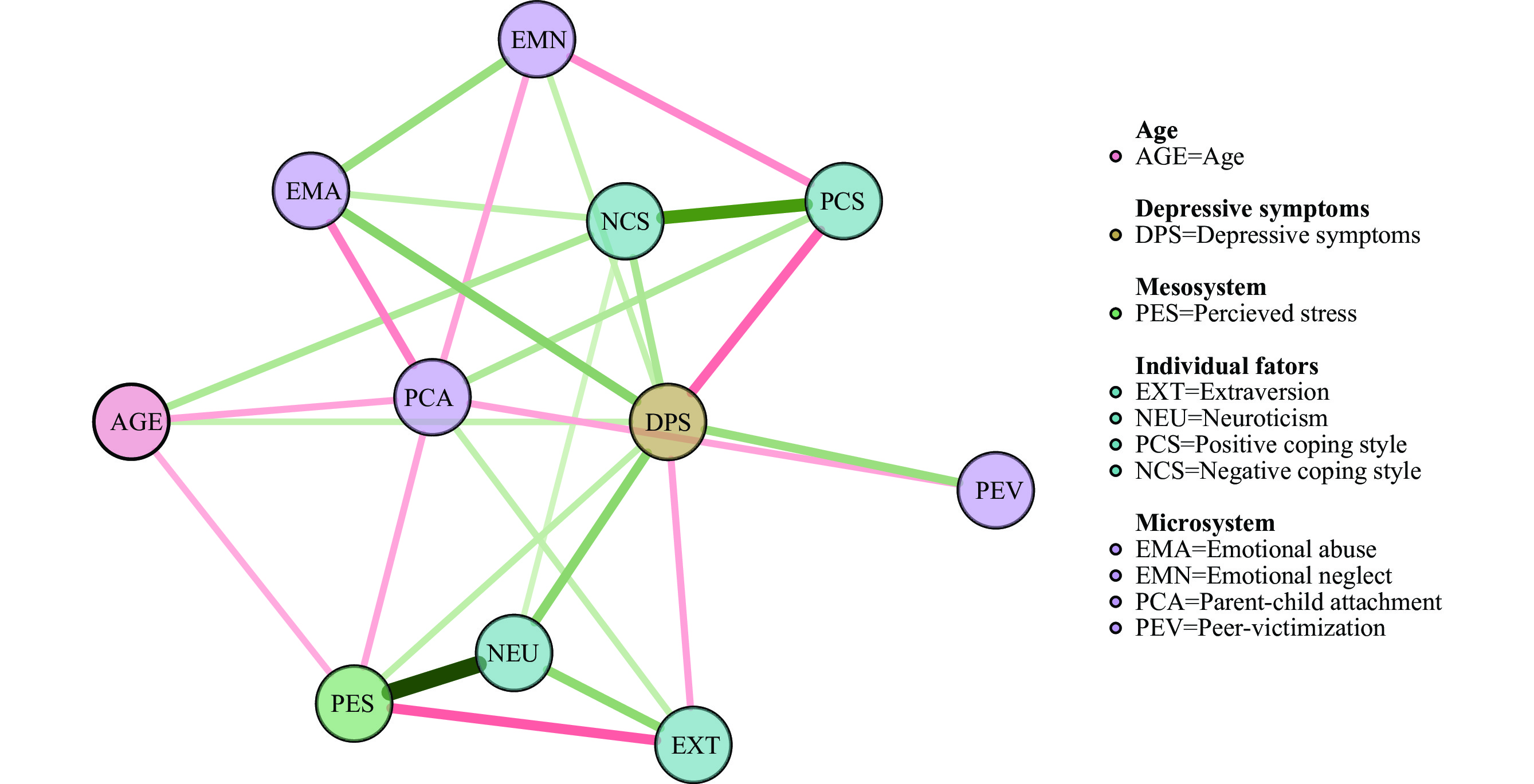
Depression significantly impacts the mental health of Chinese adolescents. Identifying risk factors specific to adolescent depression is crucial for prioritizing intervention strategies.
Neuroticism and emotional abuse were associated with an increased risk of depressive symptoms, whereas a positive coping style was directly and strongly associated with a decreased risk.
Parental awareness of emotional abuse is critical in addressing adolescent depression. Future intervention strategies should aim to enhance individuals’ positive coping mechanisms to improve mental health outcomes.
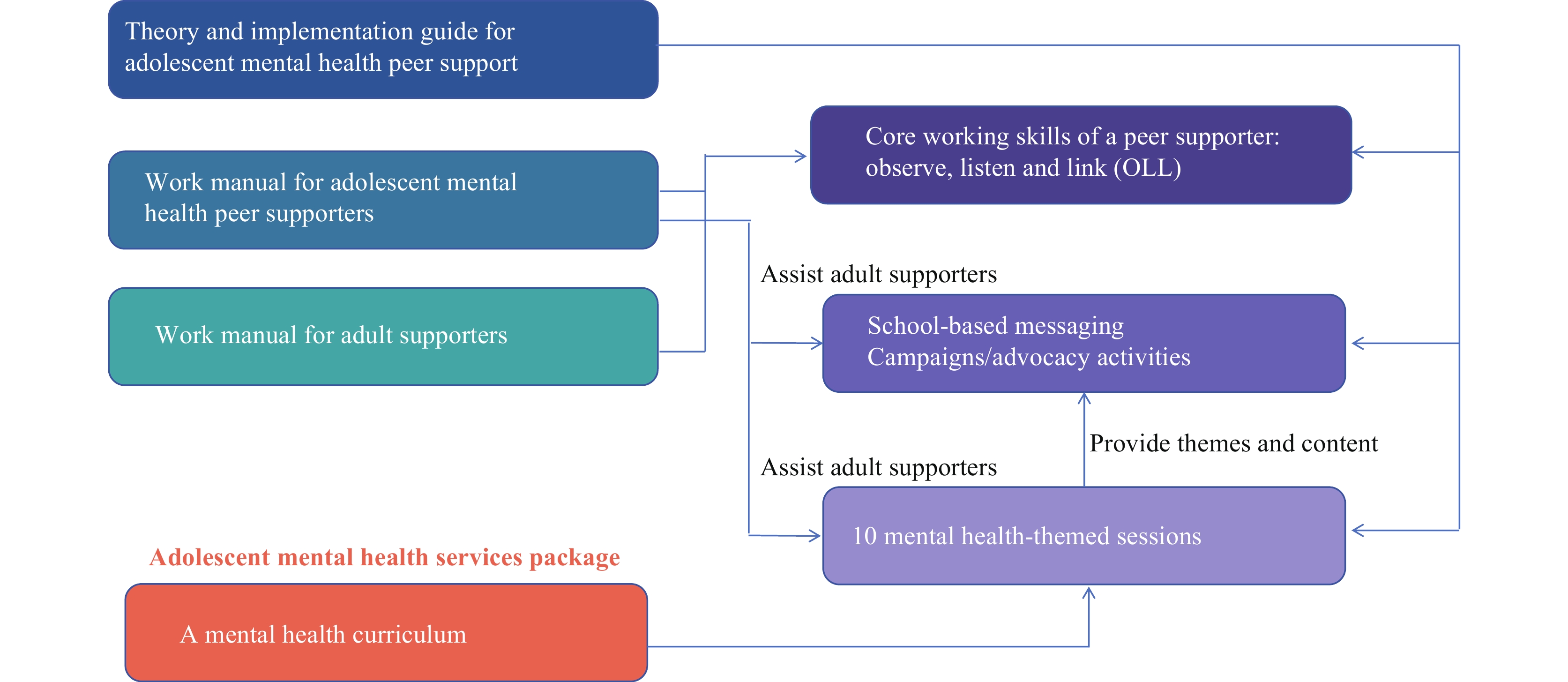
Mental health issues in Chinese children and adolescents have emerged as a substantial public health concern, causing distress and strain among families and society.
This study examines the effects of gender and school grade on mental health symptoms and risky behaviors among Chinese children and adolescents, with a particular focus on the role of family and school environments.
Caregivers and educators should enhance their awareness and skills in supporting the mental health of children. These findings offer critical insights for the early detection and intervention of mental health issues in Chinese children and adolescents.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed