2023 Vol. 5, No. 12
The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic could have a damaging impact on access to tuberculosis (TB) diagnosis and treatment.
The overall delay experienced by TB patients during the COVID-19 pandemic has shown a modest decrease in comparison to the period before the pandemic. Notably, higher patient delays were observed among agricultural workers and those identified through passive case-finding methods. Furthermore, the patient delay in eastern regions was shorter compared to western and central regions.
The observed increase in patient delay in 2022 should be of concern for ongoing TB control efforts. Health education and active screening initiatives must be enhanced and broadened among high-risk populations and regions characterized by extended patient delays.
Tuberculosis (TB) is often referred to as “a disease of poverty,” yet the information regarding the financial burden of TB care is limited and regionally representative.
This manuscript reported the national representative total and breakdown costs associated with TB care in China. The total cost per patient was 1,185 USD, of which 88% was direct cost and 37% was incurred prior to TB treatment.
TB patients experience a significant financial burden, and disparities exist among different regions and populations. Current TB care policies and packages are not sufficient to address this issue.
Pneumococcal diseases (PDs) are serious threats to child health. Although vaccination is one of the most effective ways to prevent these diseases, the pneumococcal vaccination coverage rate is still relatively low in China.
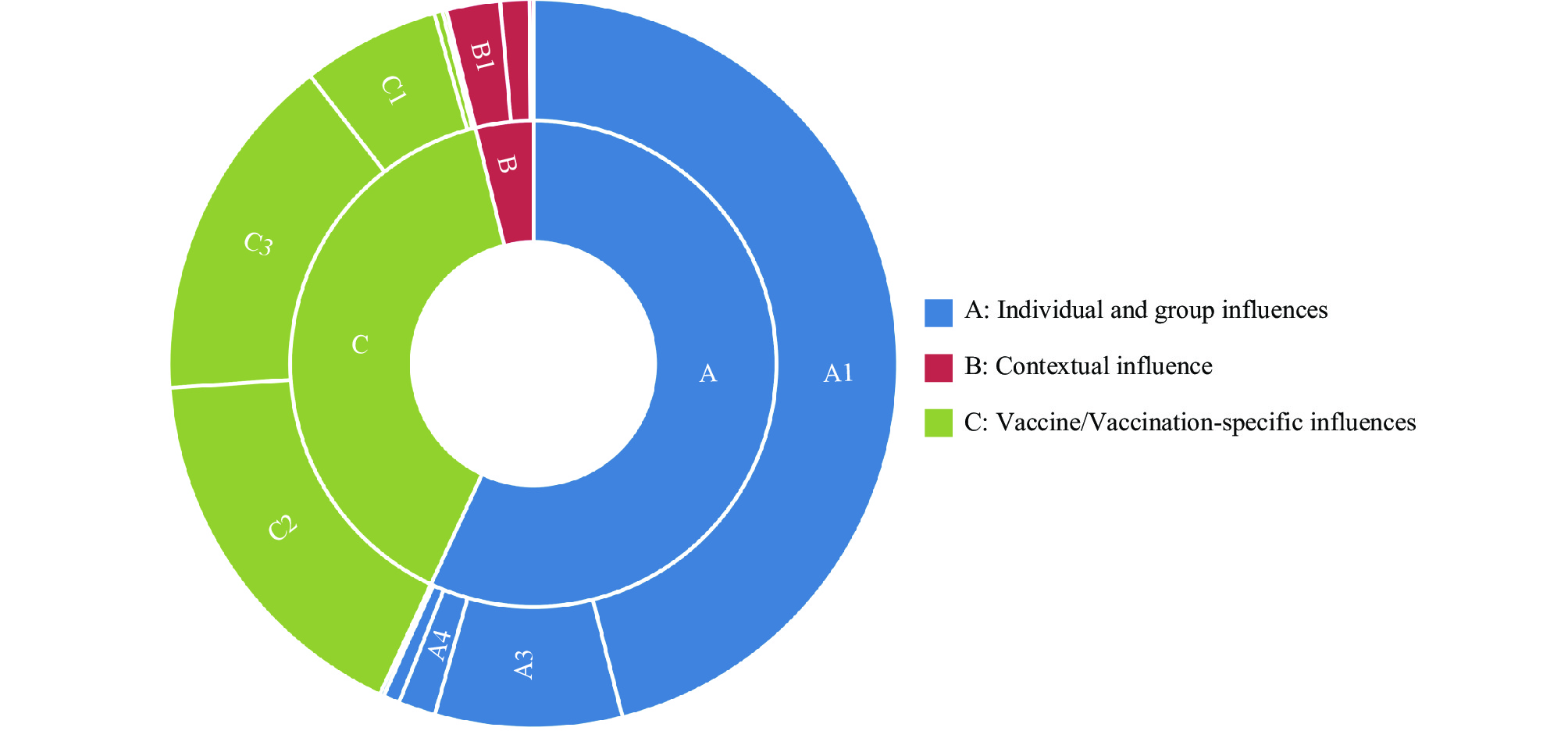
This study investigated the factors associated with 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) vaccine hesitancy in parents under an innovative immunization strategy. This study found that 29.7% of the participants hesitated to vaccinate their children against PCV13 and the main reasons for vaccine hesitancy were individual and group influences.
This study can provide scientific evidence for further improving children’s PCV13 vaccination rate and improving the prevention and control strategy for PDs.
This report analyzes the national surveillance data for schistosomiasis in 2021 to understand the current status and provide evidence for further policy actions to promote elimination. This analysis is in line with the National Surveillance Plan of Schistosomiasis, which was revised in 2020 to adapt to the new stage of moving towards elimination.
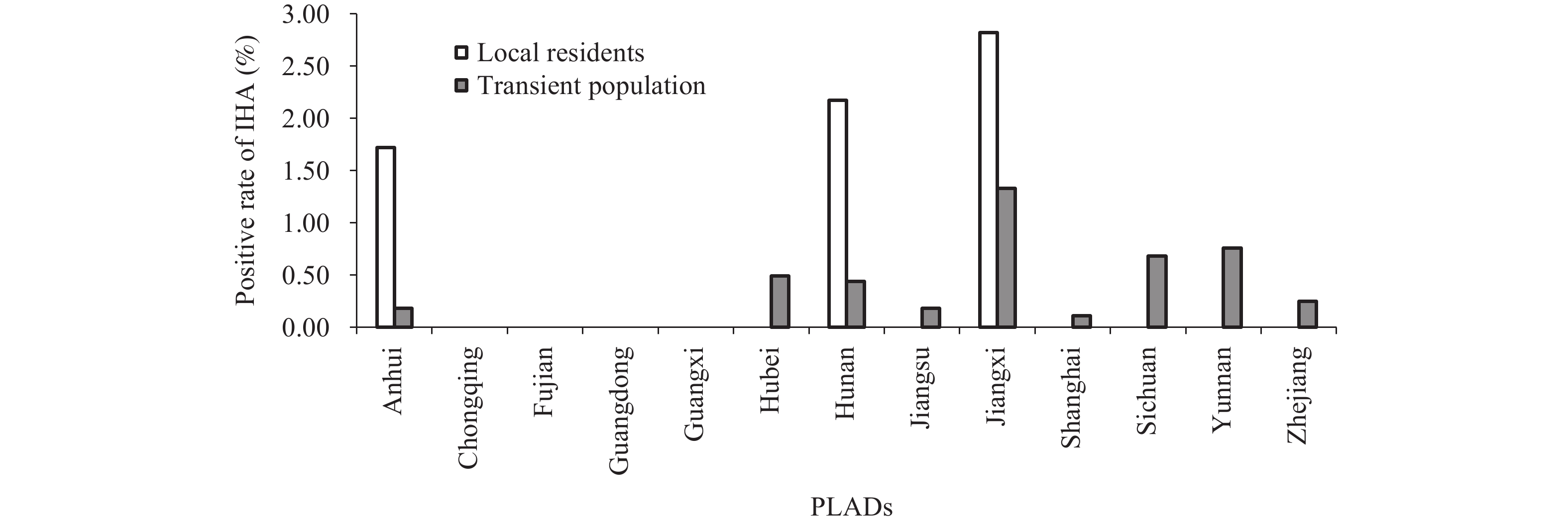
Data from the 2021 national surveillance of schistosomiasis in humans, livestock, and snails were collected from 13 provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) and analyzed using descriptive epidemiological methodology. The antibody-positive rate and area of newly discovered and re-emergent snail habitats were calculated.
In 2021, a total of 31,661 local residents and 101,558 transient population were screened for antibodies using indirect hemagglutination assay (IHA). Of those who tested positive, 745 local residents and 438 transient population underwent further parasitological examination, with only one stool-positive result in the transient population. Additionally, 12,966 livestock were examined using the miracidia hatching test, with no positives detected. The total area of newly discovered and re-emergent snail habitats was 957,702 m2 and 4,381,617 m2, respectively. No infected snails were found using the microscopic dissection method, but six pooled snail samples were reported as positive using the loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for detecting specific sequences of Schistosoma. japonicum, in Anhui and Jiangxi Provinces.
The prevalence of schistosomiasis among humans and livestock was found to be low, however, a potential transmission risk was identified in certain areas. To reduce the risk of transmission, a comprehensive control strategy should be continued and new techniques should be implemented in the surveillance and early warning system.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed