2023 Vol. 5, No. 1
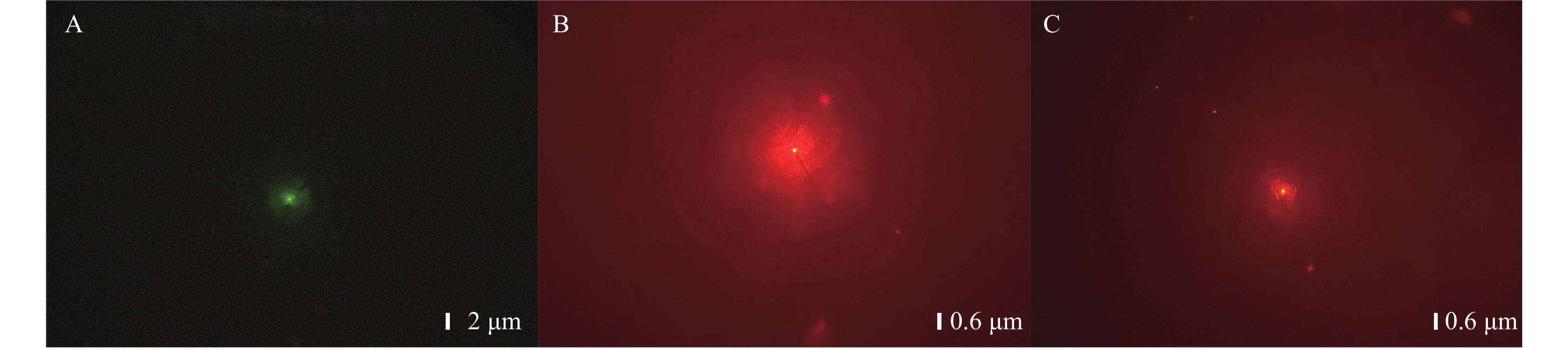
There is a toilet flush-soil stack-floor drain pathway of aerosol transmission in multistory and high-rise buildings, but the influencing factors are not completely clear.
The poor airtightness of the connecting parts of the floor drain, as well as pressure fluctuations in the sewage pipe during toilet flushing caused by blockage of the soil stack vent, may lead to the cross-floor transmission of viral aerosols through the soil stack and floor drains.
In multistory and high-rise buildings, the bathroom floor drains should be kept sealed, and floor drain connecting parts should be airtight. Furthermore, the soil stack vent should not be blocked. In this way, the cross-floor transmission of viral aerosols can be effectively reduced.
Although a third coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination (booster) dose is highly recommended for diabetic patients, the vaccination behaviors and related adverse events are unclear among diabetic patients with a COVID-19 booster dose.
Diabetic patients with higher postprandial blood glucose, worrying about the safety of the booster dose were less likely to get the vaccine. While having positive attitudes towards COVID-19 booster vaccination, trusting the health professionals' advice on vaccination, diabetic patients were more likely to get the booster vaccine. Furthermore, the prevalence of adverse events was not significantly different between the homologous and heterologous boosting groups.
Effective measures should be taken to promote the COVID-19 booster dose uptake among diabetic patients. Health professionals should educate Chinese diabetic patients about the safety and efficacy of booster doses and continue to increase the COVID-19 booster dose vaccination coverage.
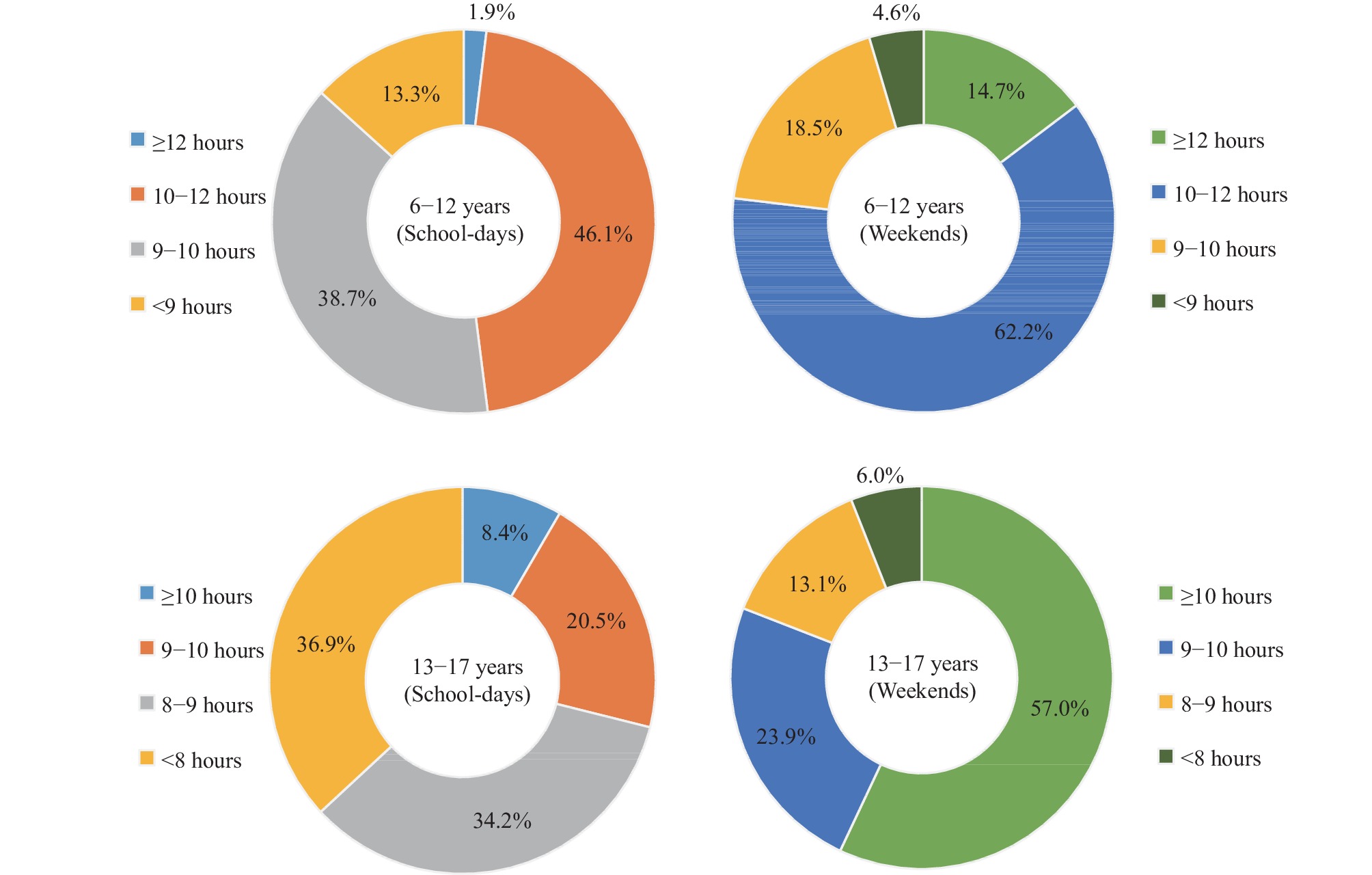
There has been little to no description of sleep status among children and adolescents nationwide in recent years.
This report assesses the sleep duration and sleep patterns of children and adolescents in China. Approximately half of the adolescents did not get the recommended amount of sleep on school days, and more than half overslept on weekends.
The importance of children and adolescents meeting recommended sleep durations needs greater emphasis, especially among older age groups and those in urban areas.
Analyze the recent epidemiological and temporal-spatial characteristics of human brucellosis in China and provide information for adjusting strategies for brucellosis control.
Human brucellosis data were obtained from the National Notifiable Disease Reporting System (NNDRS). A geographical information system (GIS) was used to visualize high-risk areas with annual incidence based on county (district) polygons. The space-time scan statistic (STSS) was applied to detect the space-time clusters of human brucellosis.
A total of 69,767 cases were reported from 2,083 counties in the mainland of China in 2021, a 47.7% increase from 2020 (47,425). About 95.5% of the total cases were centralized in northern China and 31.8% in Inner Mongolia (IM). The number of counties with an incidence exceeding 100 per 100,000 was 34 in 2020 and 65 in 2021. From 2020 to 2021, 24 space-time clusters were detected. The two primary clusters were located northeast of IM, including 109 counties. The secondary clusters affected 208 counties in 2020 and spread to 297 counties in 2021, the majority of which were located in the middle of IM, exhibiting a trend spreading west from IM to neighboring provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs).
From 2020 to 2021, the incidence of human brucellosis nationwide was exponential, demonstrating distinct spatiotemporal characteristics. Space-time clusters were located in IM and neighboring areas. Therefore, considerable efforts are required to curb this momentum.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed