2021 Vol. 3, No. 3
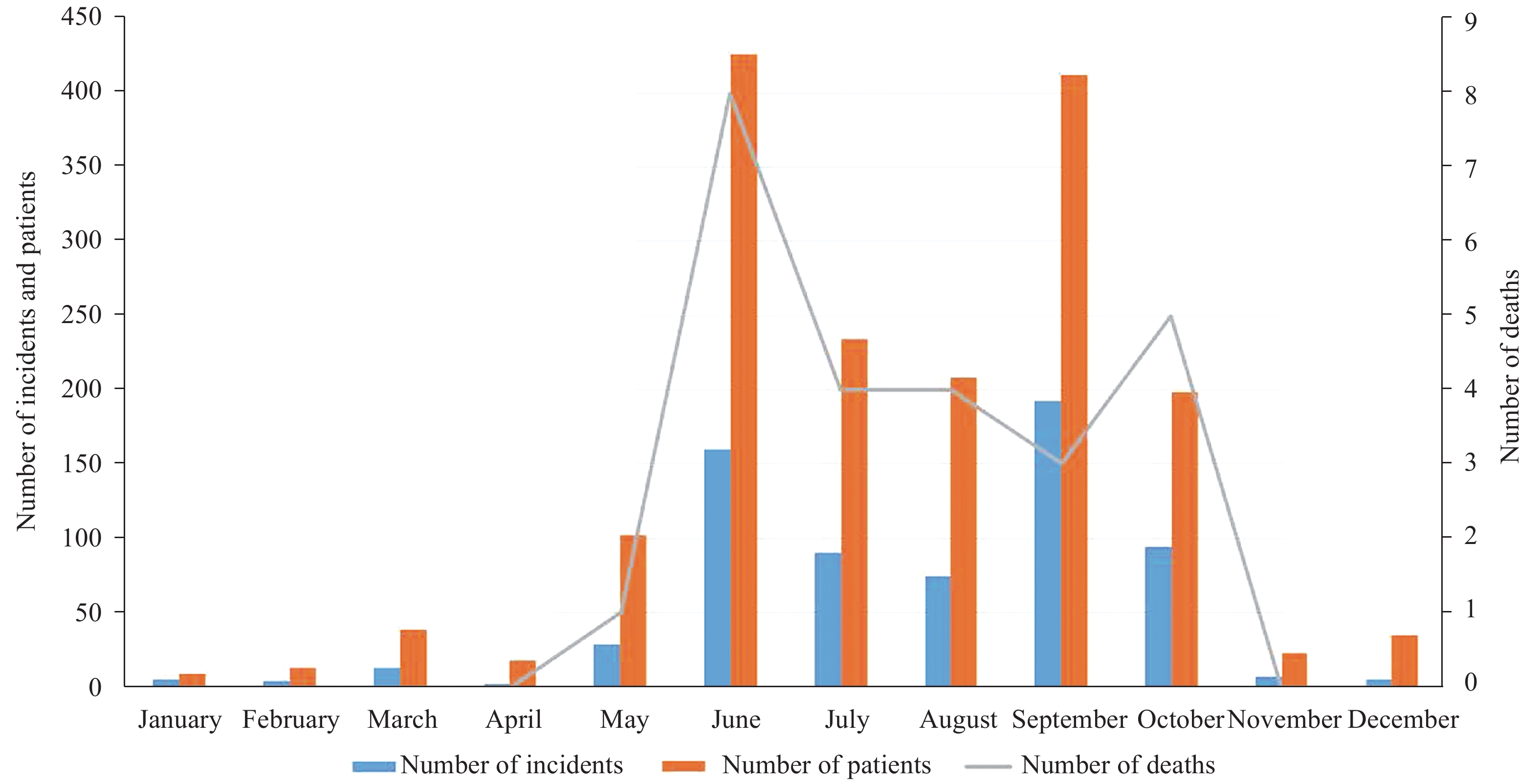
Acute liver failure, rhabdomyolysis, acute renal failure, and hemolysis caused by poisonous mushrooms are the most important mushroom poisoning threats to the Chinese population. The most notorious lethal mushrooms are the species from genera Amanita, Lepiota, and Galerina that cause acute liver failure, and Russula subnigricans that leads to rhabdomyolysis.
In 2020, the total number of investigations reached 676, involving an estimated 102 species of poisonous mushrooms, 24 of which were newly recorded in China. Gyromitra venenata was newly discovered in incidents in Yunnan and Guizhou provinces and were the first reported poisonings due to gyromitrins in China since 2000. The rare poisoning Shiitake mushroom dermatitis was recorded in China. Hemolysis poisoning caused by Paxillus involutus was recorded for the second time since the beginning of the new century, resulting in one death in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region.
Promoting knowledge about safe consumption of mushrooms is essential to reduce mushroom poisonings. It is not wise to collect and eat wild mushrooms. For southwestern provinces such as Yunnan, especially, caution must be exercised with unfamiliar mushroom species.
The incidence of diabetes is on the rise in the world, and it is increasingly affecting young people. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) has published the 2020 Diabetes Medical Standard, but there is no blood glucose standard for teenagers by age and sex.
In this study, quantile regression was used to analyze the data of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) and found that blood glucose varied significantly based on demographics.
This study provides reference for formulating the normal ranges of adolescent blood glucose and helping to screen out high-risk groups at an early stage for key interventions. The quantile regression method can give a set of curves, which could better describe the situation.
What is already known on this topic?
Based on different pregnancy risk levels, the implementation of the “Five-Color Management” for pregnant women can prevent adverse pregnancy outcomes and ensure the safety of mothers and infants.
What is added by this report?
The proportions of being multipara and of advanced maternal age in the 4 cities (Beijing, Chengdu, Shenzhen, and Wuhan) were 47.4% and 13.3%, respectively. The proportions of “Yellow and above” pregnancy risk ranged from 54.5% to 65.0% and ranged from 7.4% to 16.3% for “Orange and above” pregnancy risk. Among women with “Orange and above” pregnancy risk, most of them gave birth in public tertiary institutions (71.8%–79.4%).
What are the implications for public health practice?
The implementation of the “Five-Color Management” for pregnant women with different pregnancy risks should be strengthened, especially those with “Orange and red” pregnancy risk who should be hospitalized for delivery in tertiary medical institutions if they have conditions.
What is already known about this topic?
China has a significant population of left-behind children, and their health and living environments remain a major public health challenge. Children under 6 years old are especially vulnerable to poor health knowledge and behaviors of their caregivers.
What is added by this report?
The prevalence of stunting, being underweight, and often sick were 13%, 3.4%, and 5%, respectively. Only 53.9% of left-behind children could eat meat often, and 59.5% could control their intake of sugary drinks. The proportions of children who had a safe home environment, a safe play environment, and no family violence were 22.5%, 75.3%, and 45.9%, respectively. The percentages of caregivers who ensured that they rarely left their children alone and were always in their sight are 76.1% and 92.4%, respectively.
What are the implications for public health practice?
The implementation of early home visits is necessary to improve the physical health and safety of the living environment of left-behind children. Primary health workers should pay attention to improving the health knowledge and behaviors of caregivers.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed