2021 Vol. 3, No. 2
The World Health Organization has estimated the impact of reductions in the performance of global tuberculosis (TB) detection and care on TB deaths. However, the actual impact of COVID-19 pandemic on TB deaths in China remains unclear.
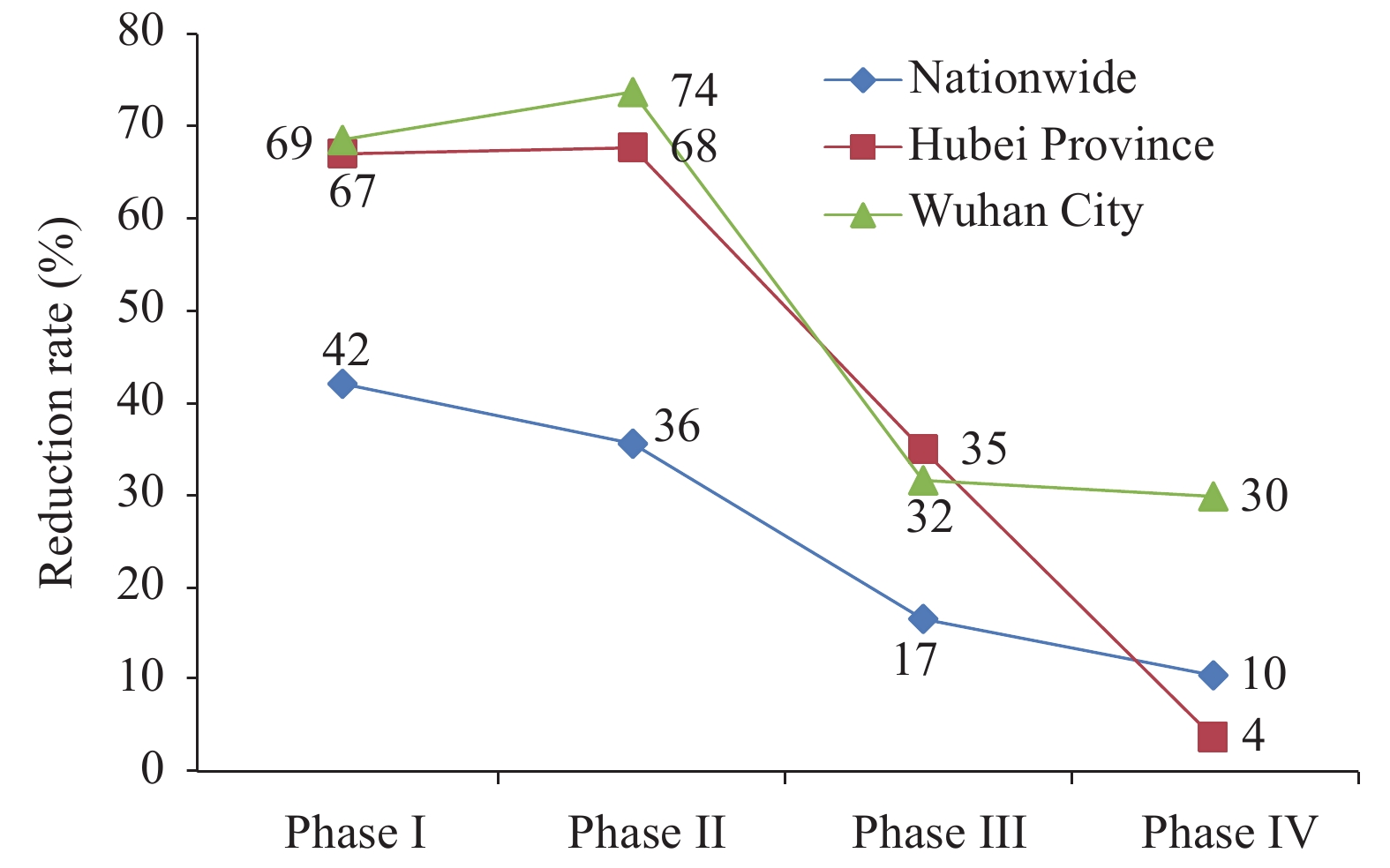
The stringent public interventions to fight COVID-19 including lockdown led to more than 20% decrease of TB detection in China. It was predicted that the reduction of TB detection might result in 11,700 excess deaths based on assumption of no detection rebound. Based on the prediction the total deaths will be 51,100 in 2020 which might surpass the deaths in 2011.
Rapid restoration of TB diagnosis and care services is critical for minimizing the potential effects on TB-related deaths and bringing TB burden back to control. It is urgent to ramp up case detection including active case finding and to provide an uninterrupted supply of quality-assured treatment and care for TB cases in post-COVID-19 outbreak.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed