2021 Vol. 3, No. 26
What is already known about this topic?
The number of students with tuberculosis (TB) has been increasing since 2015. However, the prevalence of rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis (RR-TB) among student population is unclear.
What is added by the report?
The number of students with RR-TB has significantly increased from 2015 to 2019, especially in the western region of China. The majority of patients were college students. Students with RR-TB were mainly new patients.
What are the implications for public health practice?
The following measures are recommended: strengthening TB surveillance in schools, promoting the application of convenient and rapid molecular drug susceptibility testing tools, and actively carrying out drug resistance screening and follow ups for cohabiting children of adult RR-TB patients.
What is already known on this topic?
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has disrupted the tuberculosis (TB) service system. However, the impact on TB patients in China remains unknown.
What is added by this report?
This report firstly addressed the impact of COVID-19 on TB patients in China. About half of TB patients did not revisit the hospital due to personal reasons. The reasons for irregular medication and postponing or cancelling examination after full treatment course were different.
What are the implications for public health practice?
Health education and risk communication should be strengthened for better TB patient management and treatment adherence, especially in light of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Introduction: National Notifiable Disease Reporting System (NNDRS) plays an important role in the early detection and control of tuberculosis (TB) in China. This study analyzed the epidemiological characteristics of pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) in Kashgar Prefecture, Xinjiang Uygur Autnomous Region, China from 2011 to 2020 to provide a scientific basis for developing TB control strategies and measures in Kashgar.
Methods: The data were collected from the NNDRS, which included the geographical distribution, age, sex, occupation, and pathogenic classification of reported PTB cases in 12 counties/cities of Kashgar Prefecture from 2011 to 2020. Descriptive statistics were used to describe the characteristic of PTB epidemic in Kashgar.
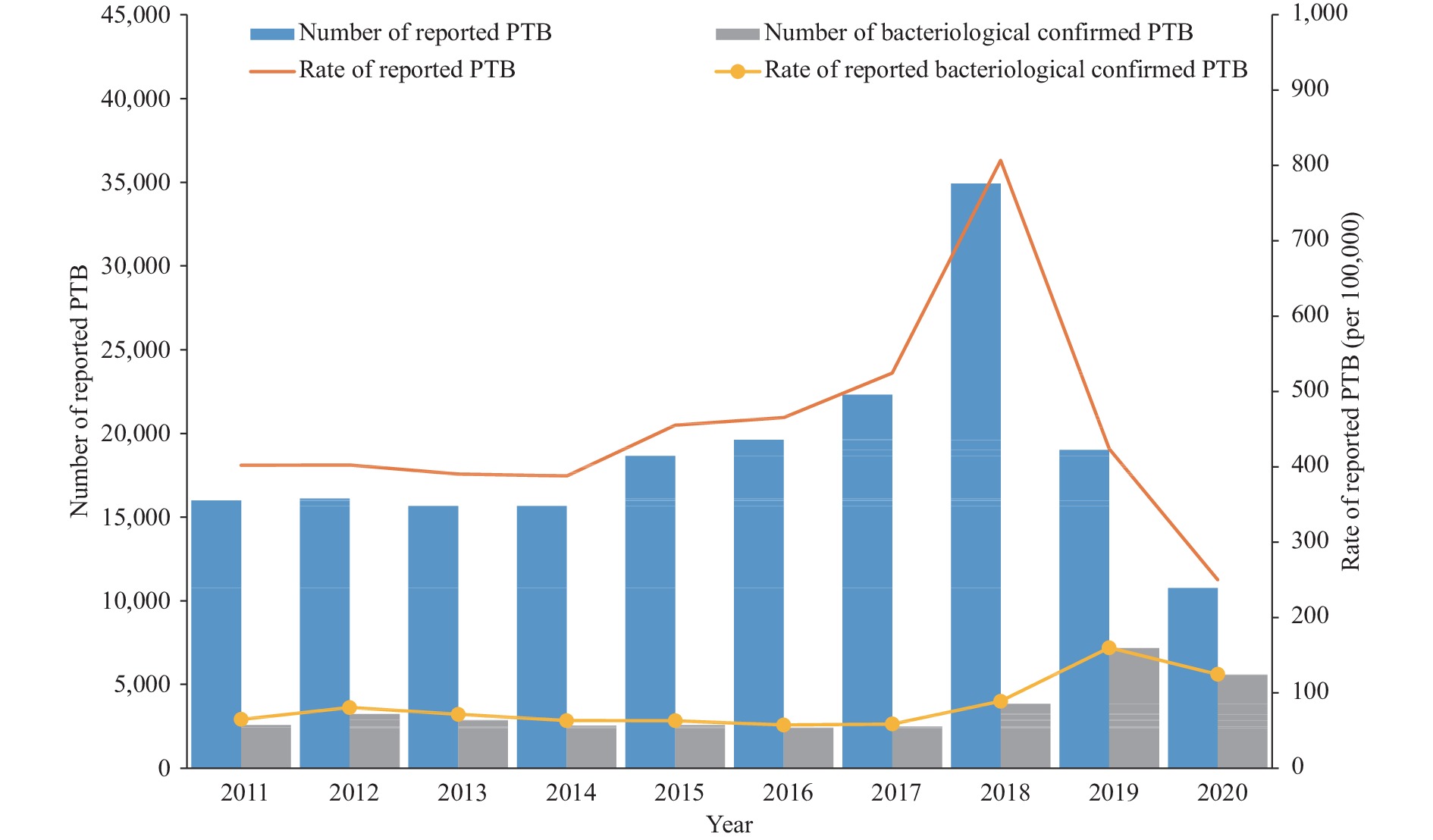
Results: There were 189,416 PTB cases reported during 2011–2020, with a mean annual PTB case notification rate (CNR) of 451.29/100,000. A rising trend in the rate of reported PTB between 2011 and 2017 (χ2trend=26.09, P<0.01) and a declining trend between 2018 and 2020 (χ2
Conclusions: The CNR of reported PTB in Kashgar showed a significant declining trend in the past three years. Males, elderly population, winter and spring, and farmers as an occupation were the main factors associated with high incidence of tuberculosis in Kashgar. Targeted prevention and treatment of TB should be strengthened in key groups in this region.
What is already known about topic?
Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) has become a growing threat to public health. There were few reports about family-to-school MDR-TB outbreaks in China, especially during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
What is added by this report?
A tuberculosis (TB) outbreak happened in Hubei Province during the COVID-19 pandemic. The transmission chain was probably from a father (MDR-TB case)with retreated TB history to his daughter, who then spread TB to her classmates.
What are the implications for public health practice?
We should enhance TB control both in schools and households, including strengthening TB/MDR-TB detection, health education, and ventilation. The TB contact screening cannot only be limited to outside school settings and should be conducted in the school when a TB student is absent from school for 2 or 3 months, or even longer especially during the COVID-19 pandemic.
What is already known about this topic?
The World Health Organization consolidated guidelines on recommend care for tuberculosis (TB) and support for multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) patients. But guidelines have not provided detailed guidance or tools for health services providers to implement comprehensive patient care.
What is added by this report?
China CDC and the United States Agency for International Development-funded Control and Prevention of MDR-TB program introduced a differentiated and personalized comprehensive and supportive care services (CSC) to improve treatment adherence.
What are the implications for public health practice?
The CSC model helps MDR-TB patients complete treatment and improve treatment success rates, and scaling up the program and implementation in other parts of the country is worth consideration.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed