2020 Vol. 2, No. 47
What is already known on this topic?
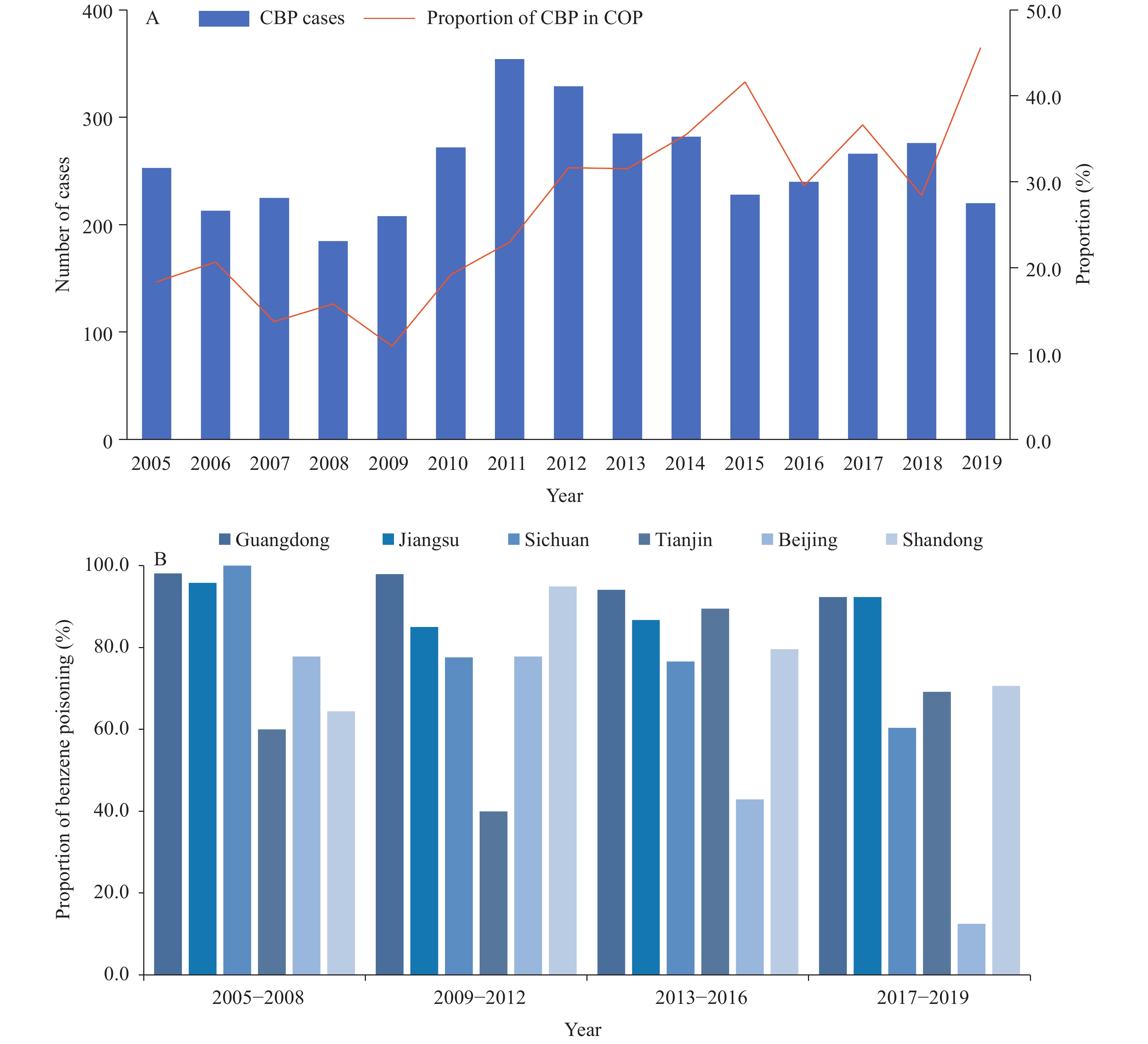
Starting in the early 1950s, the main industries in China associated with chronic benzene poisoning (CBP) included painting, pharmaceuticals, and shoemaking. However, because of rapid socioeconomic development, the distribution of industries associated with CBP likely changed.
What is added by this report?
From 2005 to 2019, CBP has become an increasingly important type of chronic occupational poisoning (COP) in China. CBP was mainly found to have occurred in manufacturing industries, especially private enterprises and small and medium-sized enterprises. The sub-industry with the highest proportion of CBP cases was general and special equipment manufacturing, followed by chemical raw materials and chemical manufacturing.
What are the implications for public health practice?
CBP was found to be the main component of COP in China, so the supervision and management in manufacturing, especially in the medium-sized and small enterprises, need to be strengthened. Occupational benzene exposure limits should also be adjusted accordingly.
China’s rapid socioeconomic development has led to the coexistence of traditional and modern occupational hazards, and workers are facing increasingly serious risks of physical and mental health issues.
Combined with the Healthy China strategy acting as the innovative force in advancing China’s public health, a series of national action plans has been implemented providing comprehensive strategies for protecting worker’s benefits and strengthening occupational disease prevention by integrating the sources of government, employers, workers, and other stakeholders. This article interprets the objectives, strategies, and features of the Occupational Health Protection Campaign and the Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Pneumoconiosis as two national programs for promoting occupational health and the Healthy Enterprises initiative as a great practice in integrating national theories of workplace health promotion and the World Health Organization’s concepts of the healthy workplace model.
It concludes that all occupational health progress achieved in the Healthy China Initiative contributes to defending health and well-being of occupational populations and promoting the sustainable development of the economy and society in China.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed