2019 Vol. 1, No. 5
What is already known about this topic?
Scarlet fever had high incidence between the 1950s and 1980s, but during the 1980s and 1990s, the incidence of scarlet fever dropped to a relatively low and stable levels in China.
What is added by this report?
Starting in 2011, scarlet fever incidence significantly increased in China. In the eight years between 2011 and 2018, 479,555 cases were reported, which exceeded the total number of 241,365 cases reported in the previous twelve years 1999–2010.
What are the implications for public health practice?
Both patient and pathogen epidemiological surveillance need to be heightened to monitor serious cases of scarlet fever and to implement timely control measures.
What is already known about this topic?
Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is a type of tuberculosis with resistance to common treatments such as isoniazid and rifampicin. MDR-TB is a major global health challenge and needs to be controlled tightly through prevention measures, early diagnosis, and full treatment and management.
What is added by this report?
This outbreak was the first MDR-TB related public health emergency in Hubei Province. In total, five MDR-TB cases and nine clinically diagnosed cases were identified within one class in a secondary school. Students and teachers from other classes were monitored, but no other cases were found.
What are the implications for public health practice?
The implementation of TB prevention and control measures in schools is important to increase knowledge on TB and to raise awareness on protecting personal wellbeing. The Automatic Early Warning Information System alerted the local health department and allowed for a timely response to prevent further disease spread.
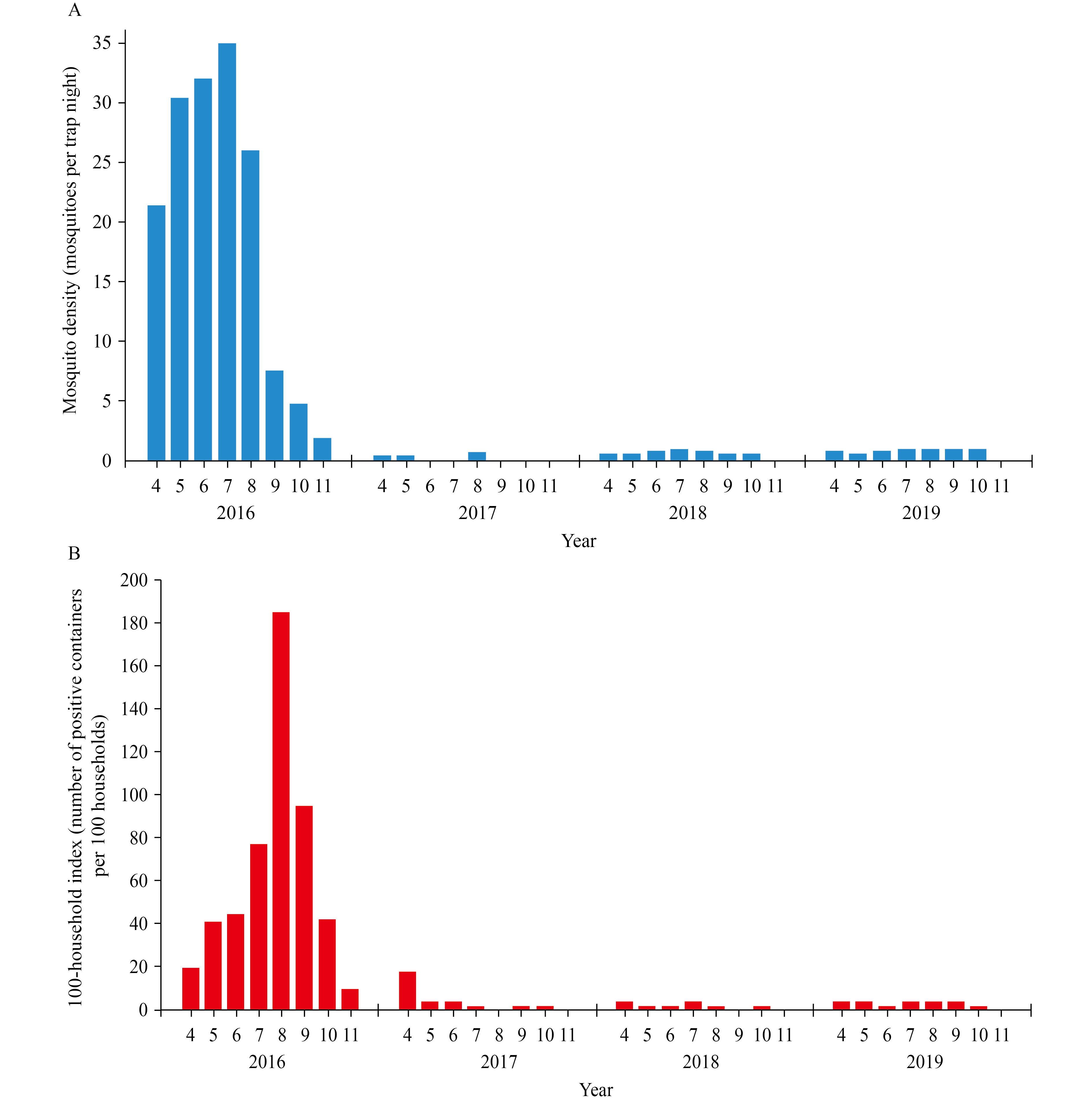
Mosquitoes and mosquito-borne diseases have always been a great threat to human health. Mosquito control based on sustainable vector management strategy is particularly important. In Zhejiang Province, exemplary villages of sustainable mosquito control (“mosquito-free villages”) have been successful operated, providing a new model of mosquito control in rural areas based on local conditions. The construction of “mosquito-free village” will apply environmentally-friendly and appropriate technologies to eliminate and transform mosquito breeding sites and to establish mechanisms of cultivating villagers’ health literacy of scientific mosquito control and voluntary participation in control activities to keep mosquito density low long-term.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed