2025 Vol. 7, No. 17
Measles, mumps, and rubella remain significant global health threats despite being vaccine-preventable diseases. The World Health Organization aims to achieve regional elimination of measles and rubella by 2030, yet substantial disparities in vaccination coverage and disease incidence persist across regions. We analyzed global vaccination and disease data to provide evidence for optimizing immunization strategies.
The study analyzed World Health Organization data on measles, mumps, and rubella from 2014–2023. Our analysis included vaccine types, recommended vaccination schedules, coverage rates, supplemental immunization activities, and disease incidence. We employed descriptive epidemiological methods for data synthesis and analysis.
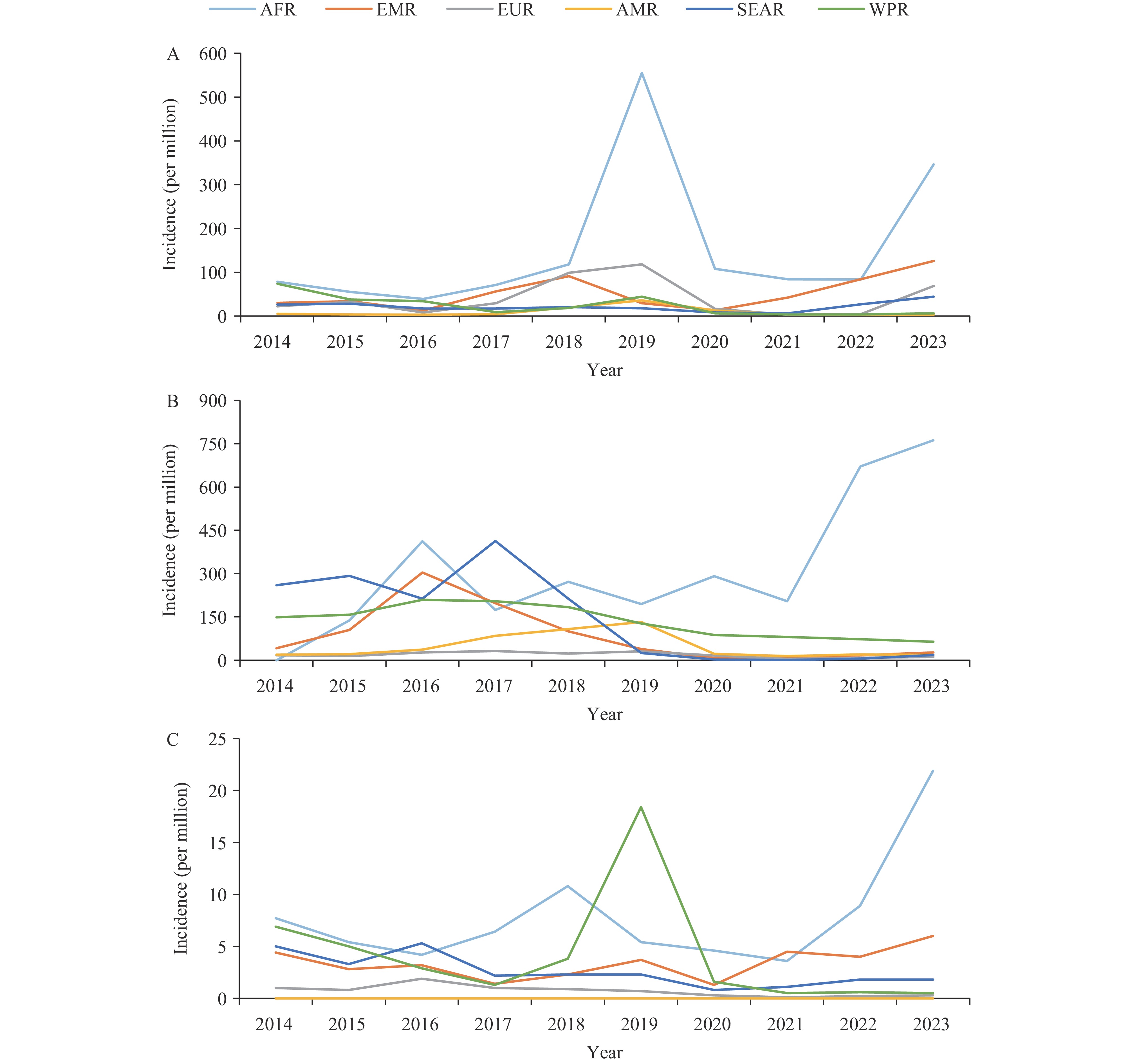
All countries implemented ≥1 measles-containing vaccine dose, with 190 (97.9%) countries using a ≥2-dose schedule. Global 2nd dose of measles-containing vaccine coverage increased from 59% to 74% during the study period. High-income regions maintained >90% coverage, while the African Region reported the lowest coverage (70% for the 1st dose and 49% for the 2nd dose of measles-containing vaccine). Supplemental immunization activities helped address coverage gaps but required integration with routine immunization systems. Rubella vaccine was implemented in 90.2% of countries, while mumps vaccine adoption remained lower at 63.9%. The African Region experienced high incidence rates for both measles (551.8 per million) and rubella (21.9 per million). The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted vaccination coverage (3%–5% decline globally), with the African Region experiencing a post-pandemic U-shaped resurgence in cases. China’s transition to the measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine has reduced mumps incidence to below 100 cases per million by 2020.
While global control of measles, mumps, and rubella has progressed, inequities in vaccination coverage and pandemic-related disruptions threaten elimination goals. Strengthening routine immunization systems is critical. Achieving the World Health Organization’s 2030 targets will require sustained investment in health systems and implementation of equity-focused innovations.
Infants have the highest incidence of meningococcal meningitis (MM) among all age groups in China. Infants receive their first and second doses of serogroup A meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine at 6 and 9 months of age.
We extracted data on MM cases among 0–11-month-old children reported during 2006–2023 from the National Notifiable Diseases Registry System and the National Meningococcal Disease Surveillance System and conducted an epidemiological and clinical analysis.
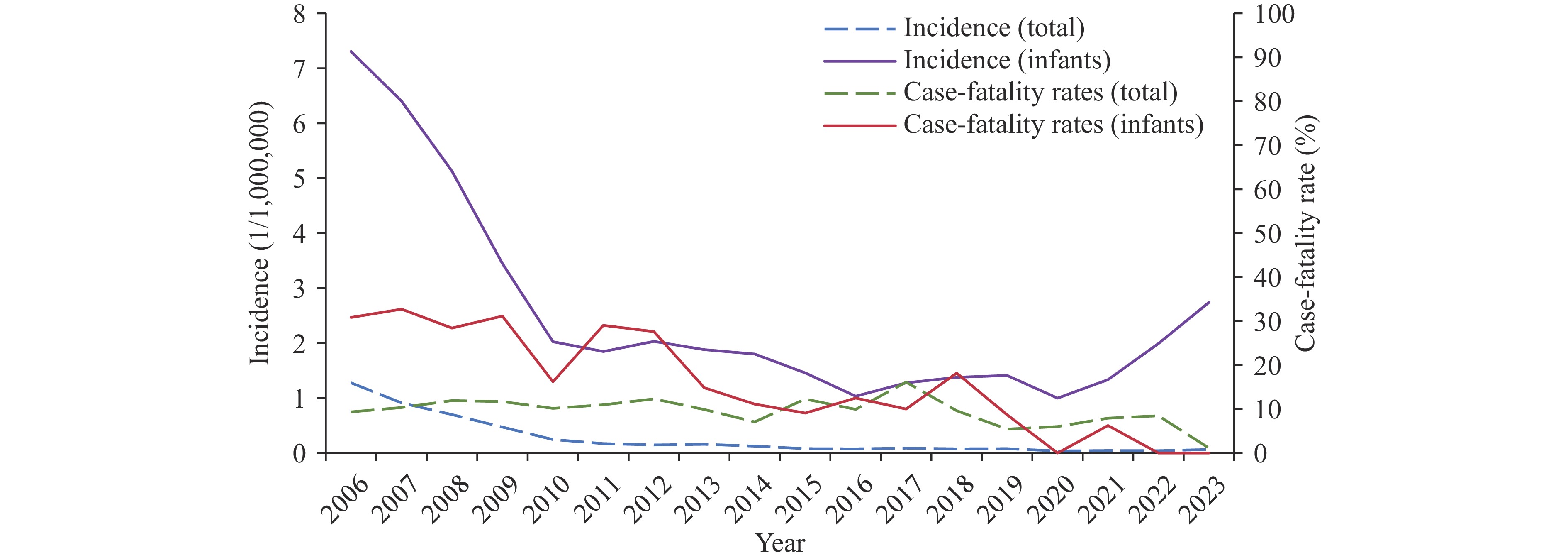
During the study period, 721 infant MM cases were reported. Incidence decreased from 7.31 cases per million to 2.74 per million, while the all-age incidence declined from 1.27 cases per million to 0.06 per million. Among 210 cases with serogrouping results, five serogroups (A, B, C, W, Y) and non-groupable strains were detected. Serogroup A cases decreased from 36.36% to 1.87% during the study period, while serogroup B increased from 14.55% to 67.29%. Fever, nausea, and/or vomiting were common symptoms across all serogroups. The frequencies of petechiae and/or purpura in serogroup A (73%) and C (92%) were substantially higher than in other serogroups. Among serogroup B cases, 26.42% developed petechiae and/or purpura, 26.42% exhibited neck stiffness, and 13.21% had positive Kernig’s and/or Brudzinski’s signs.
The incidence of MM in infants has significantly decreased but remains higher than incidence across all age groups. Serogroup B cases were the most common. Atypical symptoms in infant cases challenge timely diagnosis. We suggest eligible infants receive meningococcal vaccination timely, and the development of serogroup B meningococcal vaccines should be accelerated.
To assess adverse events following recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) in China during the post-marketing period.
The study obtained data on adverse events following immunization (AEFI) and vaccination doses of RZV from the Chinese National Immunization Information System (CNIIS). We analyzed RZV AEFI reports from 2020 through 2023.
During the study period, 1.99 million doses of RZV were administered, and 10,525 RZV AEFI cases were reported. The reporting incidence of AEFI was 527.76 per 100,000 doses administered, with serious AEFI at 0.55, common vaccine reactions (usually minor) at 518.19, and rare vaccine reactions (possibly serious) at 4.06 per 100,000 doses. Among adverse vaccine reactions, the most frequently reported common vaccine reactions were fever (333.76/100,000) and local redness and swelling (213.51/100,000), while the main reported rare vaccine reaction was allergic rash (3.01/100,000).
Most RZV AEFIs were common vaccine reactions, consistent with adverse events reported in RZV clinical trials. The incidence of rare vaccine reactions was very low, and most of which were allergic rash. No special safety concerns were identified and AEFI surveillance should be continued.
Two live attenuated rotavirus vaccines (RVs) were licensed in China. Passive surveillance for adverse events following immunization (AEFI) provides valuable evidence for potential safety signal detection of RV in China.
We obtained data on RV doses administered and RV AEFI reports from the Chinese National Immunization Information System (CNIIS) during January 2013 to December 2023. We conducted a descriptive analysis of RV AEFI characteristics and estimated incidences of RV AEFI.
During the study period, 77.36 million doses of RV were administered, and 20,556 RV AEFI reports were made, yielding an overall incidence of 26.57 AEFI per 100,000 doses administered; incidences were 26.42 for RV1 and 26.85 for RV5. Among all RV AEFI, 20,334 (98.92%) were non-serious. Vaccine product-related reactions accounted for 95.68% of AEFI reports, including 18,192 (88.50%) common and 1,476 (7.18%) rare vaccine reactions. Among common vaccine reactions, case reports per 100,000 doses administered were 16.85 (13,031 reports) for fever, 5.84 (4,520 reports) for gastrointestinal disorders, and 1.28 (988 reports) for rash. Among rare vaccine reactions, case reports per 100,000 doses were 1.43 (1,104 reports) for allergic rash, 0.07 (56 reports) for thrombocytopenic purpura, 0.03 (26 reports) for febrile convulsion, and 0.01 (5 reports) for intussusception.
Most RV AEFIs were mild and non-serious, and the incidence of rare vaccine reactions was very low. RVs have reasonable safety surveillance profiles and AEFI evaluation should be continued.
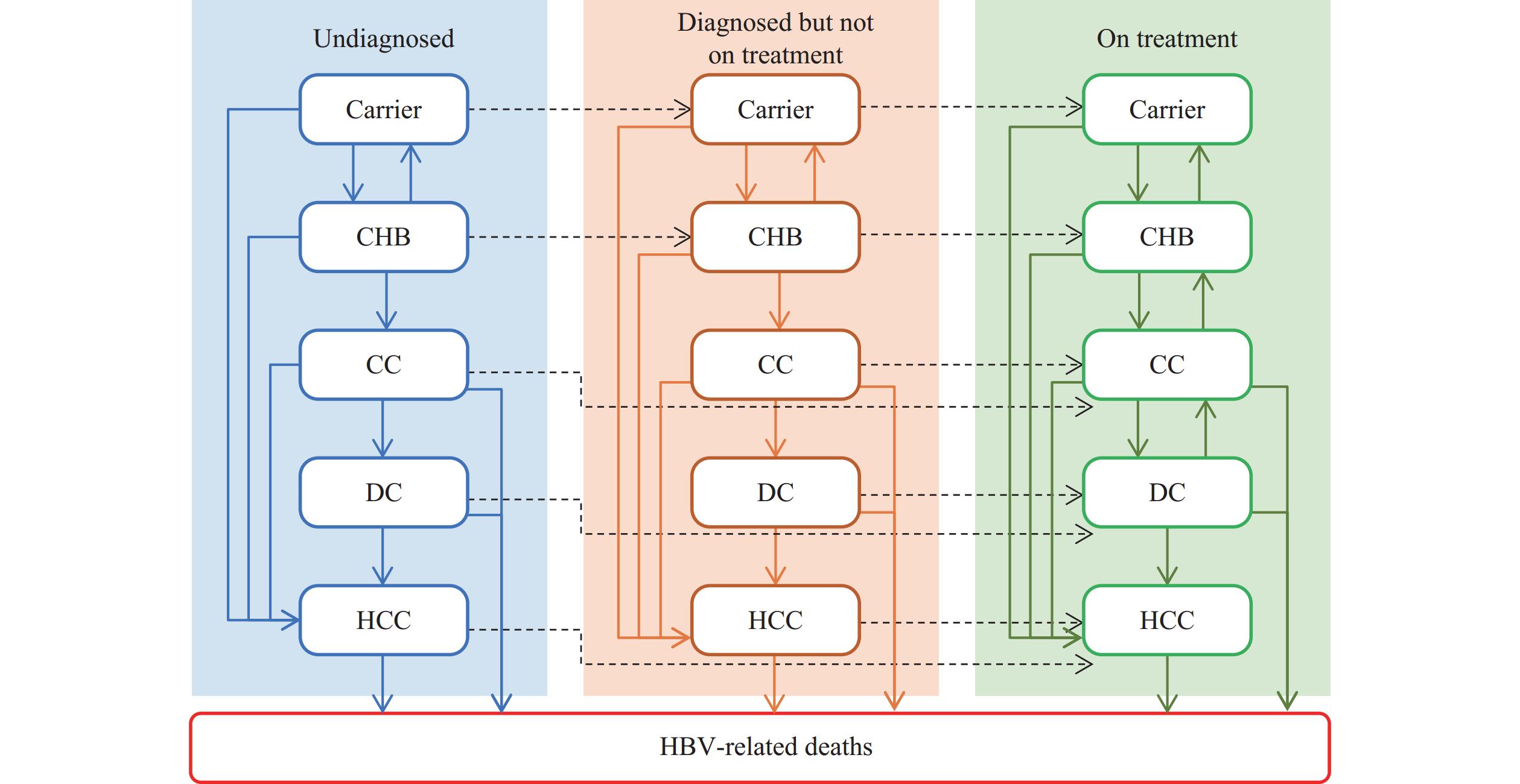
Eliminating hepatitis B virus (HBV) as a major public health threat is a global health priority that requires cost-effective screening strategies. This study evaluated the cost-effectiveness of sequential birth cohort HBV screening strategies in China.
Using a Markov model, we compared five screening strategies with current practice, calculating HBV-related deaths averted, quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) gained, and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICER). One-way deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses were conducted to evaluate the robustness of the results.
The sequential birth cohort screening strategy (Sequential Screening 1: screening the 1991–2000 cohort in 2025–2026, the 1971–1990 cohort in 2027–2028, and the 1951–1970 cohort in 2029–2030) was the most cost-effective, with an ICER of 58,523 Chinese Yuan (CNY) per QALY at a willingness-to-pay threshold of three times the per-capita Gross Domestic Product (GDP). An alternative strategy that prioritized the 1951–1970 cohort in 2025–2026 averted the most HBV-related deaths (approximately 3.44 million) and gained 24.9 million QALYs, with an ICER of 60,113 CNY per QALY, also showing cost-effectiveness.
Our findings support sequential birth cohort screening as an optimal and innovative approach to achieving the WHO HBV elimination targets, offering evidence-informed guidance for policymakers to optimize screening programs and resource allocation.
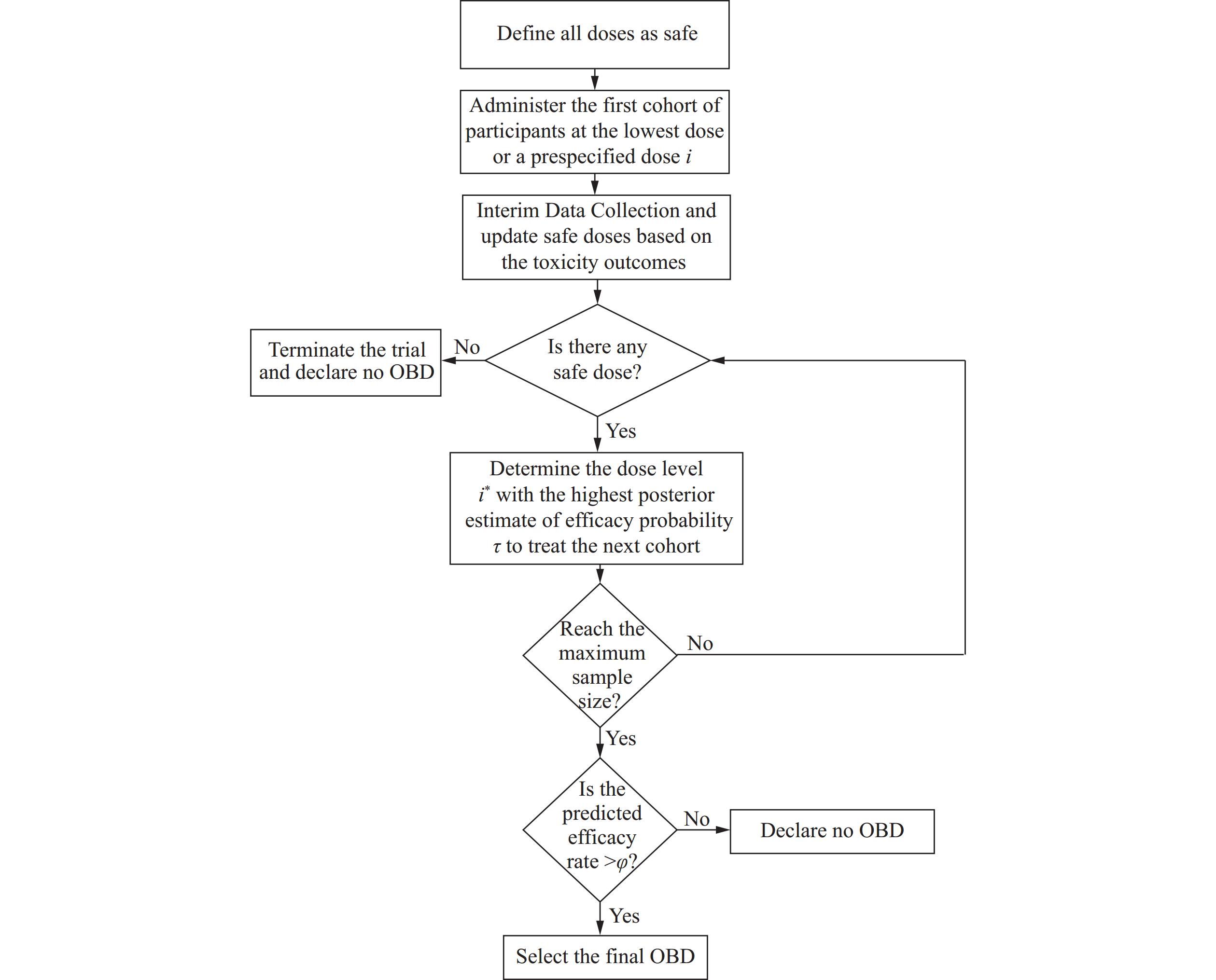
Vaccines are a cornerstone of global health, with their efficacy and safety dependent on appropriate dosage determination. Early-phase vaccination trials face significant challenges due to minimal toxicity and nonmonotonic dose response curves, creating a major obstacle in vaccine development. To address this gap, we propose a novel Bayesian phase I/II trial design for dose response curves exhibiting plateau or unimodal patterns to identify the optimal biological dose (OBD), effectively balancing efficacy and toxicity.
We employ a logistic dose-efficacy design that makes dose-escalation and de-escalation decisions while simultaneously considering both efficacy and safety parameters. Extensive simulation studies evaluate the performance of this design.
Comparative analyses with commonly used vaccine dose-finding designs demonstrate that our method excels in identifying the optimal toxicity-efficacy trade-off, offering both simplicity and accuracy. Sensitivity analyses across various prior settings confirm the robustness and efficiency of our approach. Additionally, our design provides a user-friendly framework for clinicians, with superior operating performance compared to existing designs, particularly in terms of accuracy and robustness.
Our innovative Bayesian design represents a significant advancement in addressing the inherent challenges of early-phase vaccination clinical trials, offering improved accuracy and efficacy in vaccine dosage determination.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed