2021 Vol. 3, No. 29
What is already known on this topic?
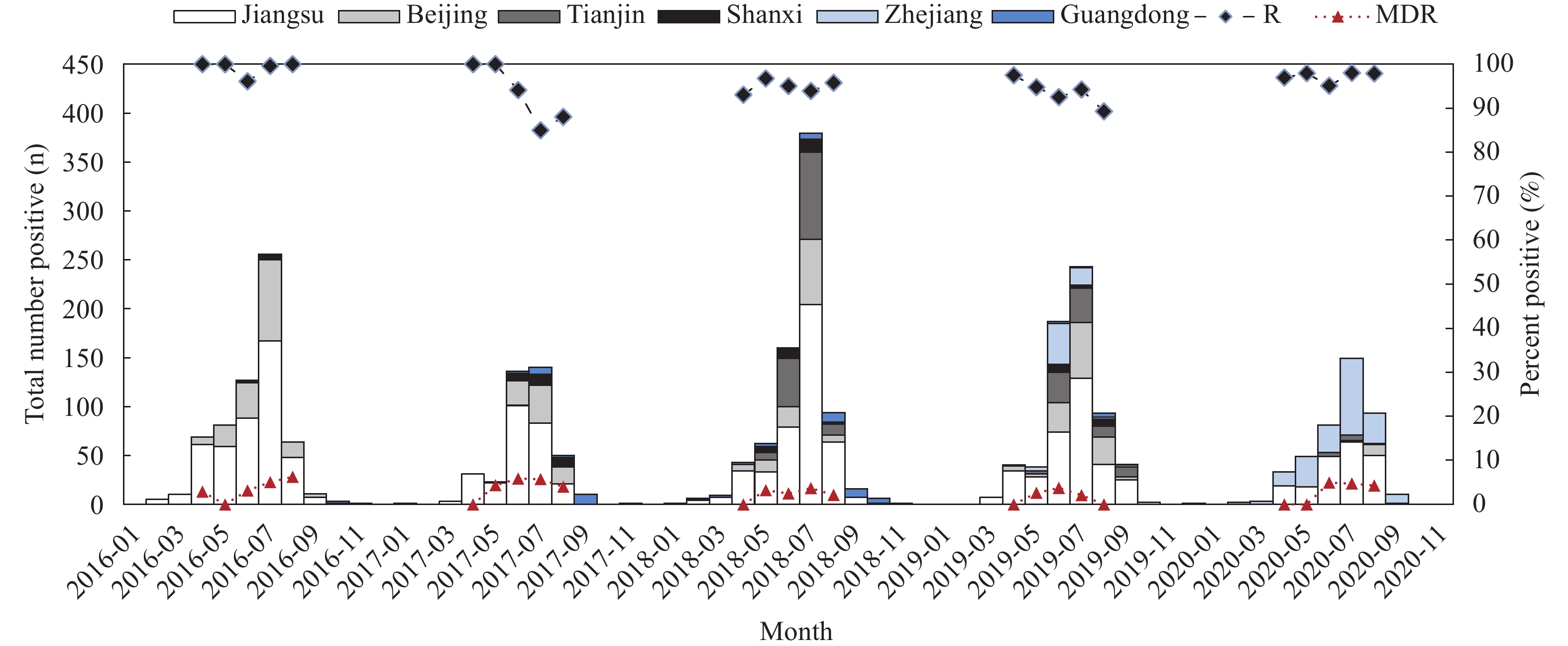
Vibrio parahaemolyticus (V. parahaemolyticus) is frequently resistant to common antimicrobials such as ampicillin and generally highly susceptible to most clinically used antimicrobials.
What is added by this report?
V. parahaemolyticus were highly resistant to cefazolin and ampicillin: 94.4% and 37.0%, respectively. However, it was below 3% resistance to all 10 other antimicrobials including clinically relevant agents and even imipenem. The overall levels of antimicrobial resistance and multidrug resistance were 95.1% and 3.3%, respectively. The distribution of antimicrobial resistance and the multidrug resistance had regional, temporal, sexual, and isolated source strain variation.
What are the implications for public health practice?
This study provides data on drug resistance of V. parahaemolyticus in Chinese clinical settings, which will help develop a public health strategy.
What is already known on this topic?
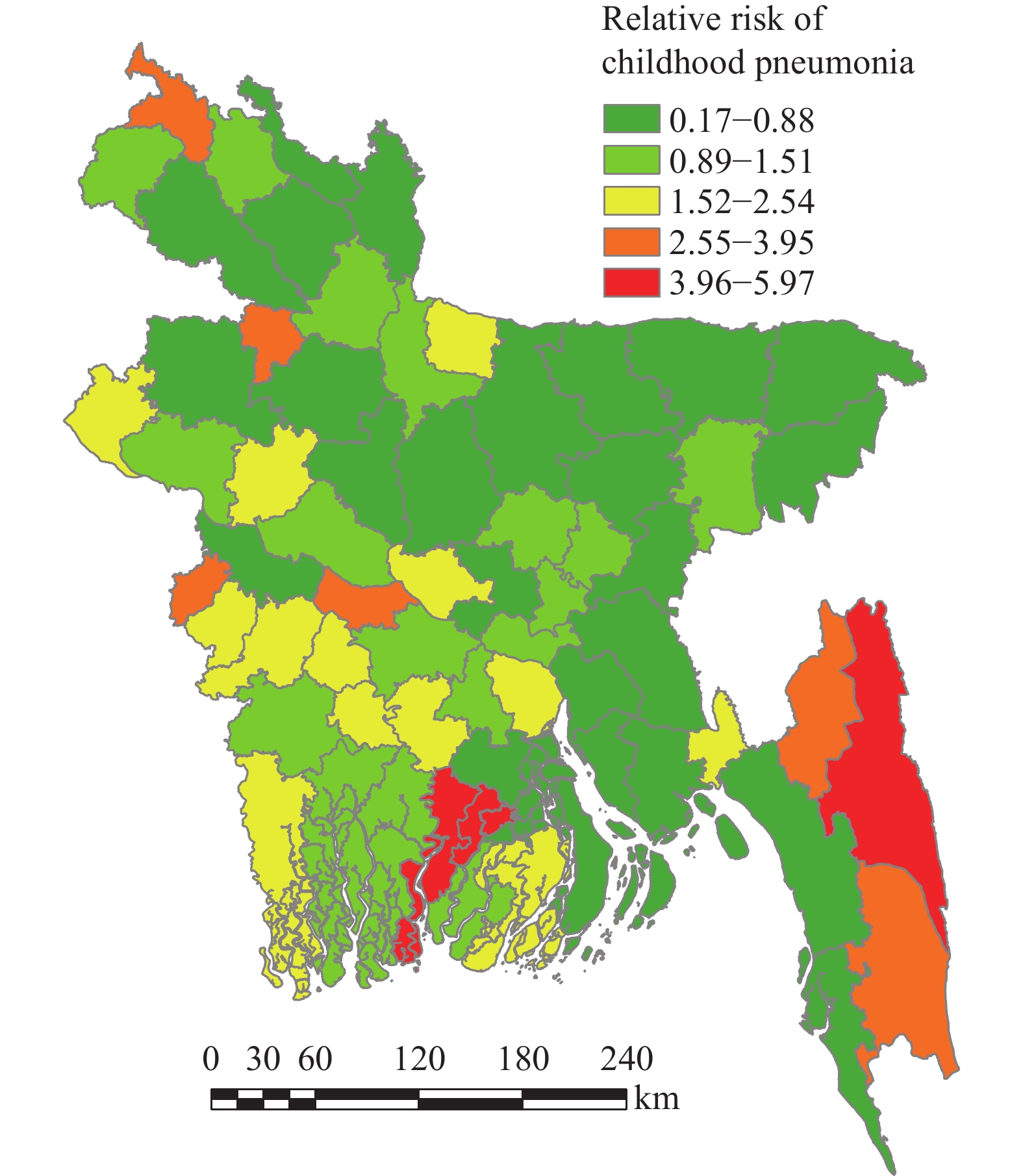
Different socioecological factors were associated with childhood pneumonia in Bangladesh. However, previous studies did not assess spatial patterns, and socioecological factors and spatial variation have the potential to improve the accuracy and predictive ability of existing models.
What is added by this report?
The spatial random effects were present at the district level and were heterogeneous. Average temperature, temperature variation, and population density may influence the spatial pattern of childhood pneumonia in Bangladesh.
What are the implications for public health practice?
The study results will help policymakers and health managers to identify the vulnerable districts, plan further investigations, help to improve proper resource allocation, and improve health interventions.
What is already known on this topic?
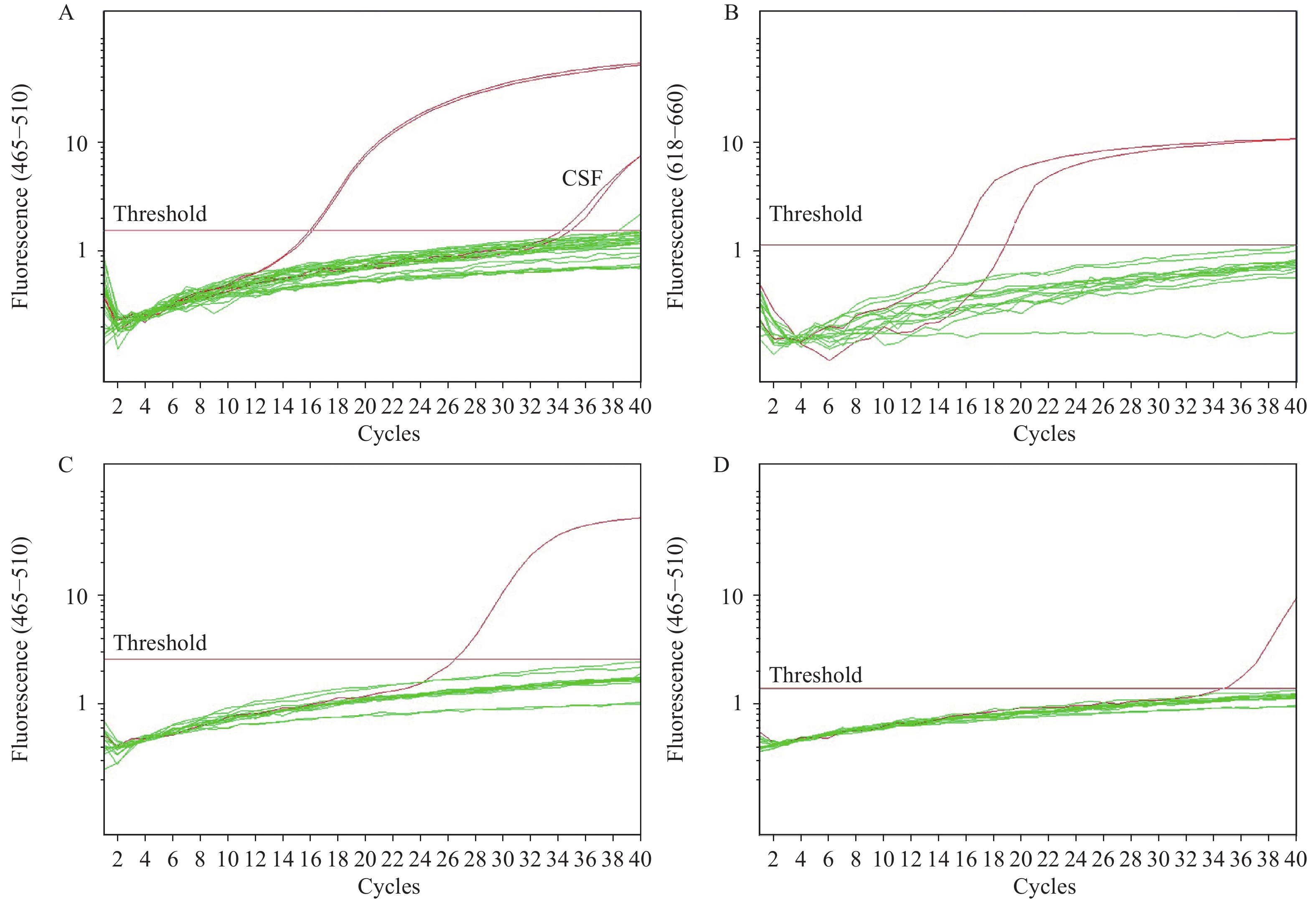
Hydrogen peroxide sterilizeation is widely used for luminal devices. However, the low penetrability of the sterilant is of major concern.
What is added by this report?
This report investigated the effective sterilization of low-temperature hydrogen peroxide gas plasma sterilizers and compared the applicability of different biological monitoring methods based on medical luminal devices.
What are the implications for public health practice?
It is recommended to use a biological process challenge device for monitoring the sterilization of luminal devices with low-temperature hydrogen peroxide gas plasma sterilizers.
Introduction: Fumonisins are a group of widespread mycotoxins mainly existing in staple foods. Their toxicological effects on humans cause worldwide public health threat. During 2015–2020, the 6th China Total Diet Study (TDS) was conducted to study the dietary exposure to fumonisins in the Chinese adult population.
Methods: Fumonisins were analyzed by LC-MS/MS in 288 composite dietary samples collected from 24 provincial-level administrative divisions. After combining the national consumption data with analytical results, estimated daily intakes (EDIs) were assessed and compared with health-based guide values (HBGV).
Results: In the 6th China TDS, the highest fumonisin B (FBs) levels were found in staple foods/cereals among the 12 food categories. EDI of FBs was 104.9 ng/kg of body weight (bw)/day at the upper bound accounting 5.25% of the provisional maximum tolerable daily intake set by Joint Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization Expert Committee on Food Additives. Among the 12 food categories, cereals and cereal products were the greatest contributor to FB exposure at 95%.
Conclusion: Although the estimated exposure to FBs in the 6th China TDS were well below the HBGV for FBs in general, it was 2 times higher than the exposure in the 5th China TDS. Furthermore, the exposure to FB3 has increased remarkable and is worth further attention in China.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed