2025 Vol. 7, No. 36
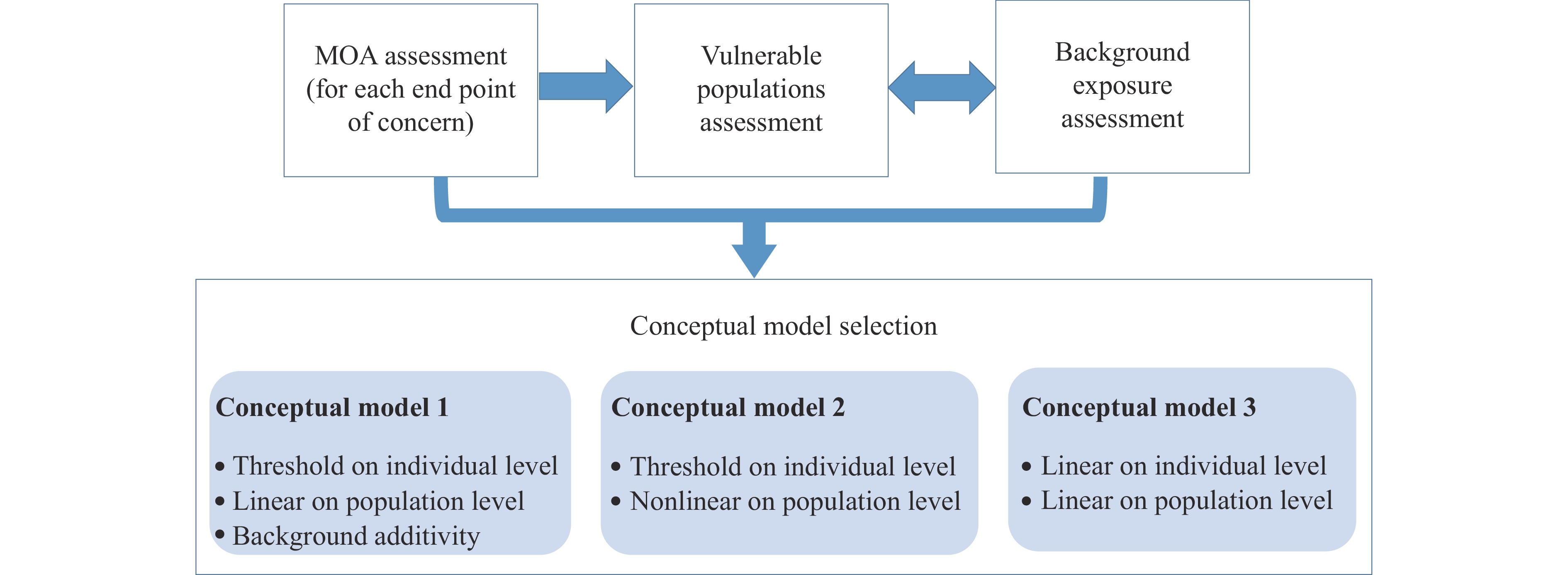
This article systematically reviews the significant progress China has made in the field of air pollution health risk assessment since 2013, including the establishment of the national monitoring network, the improvement of relevant laws and formulation of technical guidelines. The paper focuses on an in-depth discussion of the current core challenges: the disconnection between health risk and decision-making, the lack of a multi-sectoral coordination mechanism, the imperfection of the technical system (particularly for mixed exposures and emerging pollutants), and the novel risks posed by global climate change. Based on this analysis, we prospectively propose fundamental pathways to advance the field: 1) constructing a robust management mechanism and coordination framework; 2) promoting the integration of the full environmental health risk assessment process into the decision-making pipeline (an “assessment-management interaction” paradigm); and 3) strengthening interdisciplinary collaboration and leveraging innovative technologies to refine the technical assessment system.
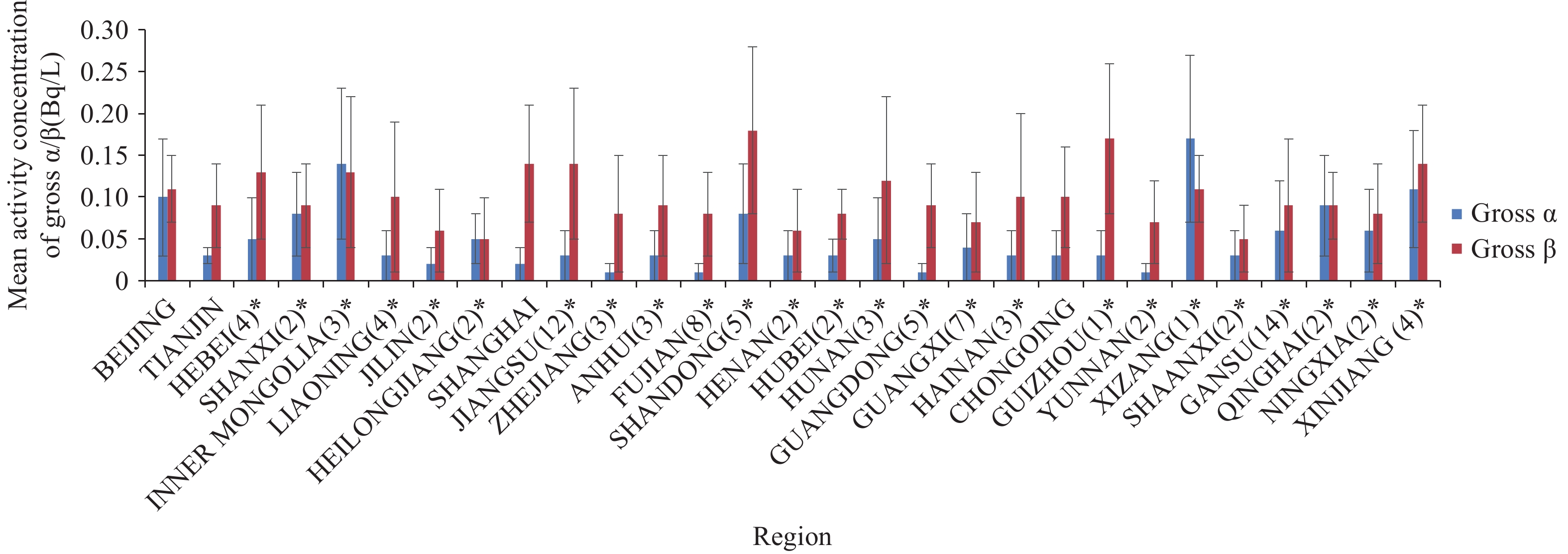
To establish baseline radioactivity levels and ensure the safety of drinking water quality in China, gross alpha and gross beta radioactivity levels in drinking water were surveyed from 2012 to 2024.
The surveillance was conducted through the national monitoring system for radioactivity in drinking water, organized by The National Institute for Radiological Protection (NIRP) during the period 2012–2024. Drinking water samples were collected and pretreated in accordance with a unified protocol, and radioactivity was determined using alpha/beta counting systems by local laboratories.
From 2012 to 2024, over 11,000 drinking water samples were collected and analyzed across 29 provinces, including areas surrounding nuclear power plants. The mean concentration ranges of gross alpha and gross beta radioactivity levels in all regions and various water bodies were 0.01–0.17 Bq/L and 0.05–0.38 Bq/L, respectively, all of which are below the guidance values specified in the national standard GB 5749 (0.5 Bq/L for gross alpha and 1 Bq/L for gross beta). However, the gross alpha and gross beta activity levels in well water were higher than those in other water bodies. The results indicate that radioactivity in drinking water primarily originates from natural radionuclides.
Drinking water in China maintains normal background levels of radioactivity. Nuclear power plant operations do not seem to have an impact on surrounding water sources.
Traditional dengue surveillance operates reactively, frequently lagging behind viral transmission patterns and thereby impeding timely public health responses. Wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) presents significant potential for proactive early warning systems. This study sought to implement and validate the first community-level WBE system for dengue during an active outbreak, evaluating its capacity to detect cryptic transmission and provide actionable intelligence for public health interventions.
During a dengue virus serotype 1 (DENV-1) outbreak, we collected 618 wastewater grab samples from manholes within a 200-m radius of 8 reported cases, along with matched patient serum and urine samples. We systematically compared magnetic bead and polyethylene glycol (PEG) concentration methods for viral recovery efficiency. DENV-1 ribonucleic acid (RNA) was detected and quantified using reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Positive samples underwent genomic sequencing and phylogenetic analysis to confirm environmental signals and determine viral lineages.
The magnetic bead method demonstrated superior performance with a limit of detection of 10 copies/mL and was selected based on its higher recovery efficiency (59.7%). We successfully detected DENV-1 in 14 of 618 wastewater samples tested. Critically, a positive wastewater signal from one residential building preceded the clinical diagnosis of a new case within that same location by several hours. For a single patient, we successfully generated matched viral genomic sequences from serum, urine, and wastewater samples, providing definitive validation of the environmental signal’s authenticity.
Community-level wastewater surveillance represents a powerful and effective tool for dengue control programs. This approach provides actionable early warnings by detecting cryptic viral transmission before cases receive clinical identification. Such capabilities enable public health authorities to deploy preemptive, geographically-targeted interventions, including vector control measures, fundamentally improving both the speed and precision of outbreak responses while helping to mitigate disease spread.
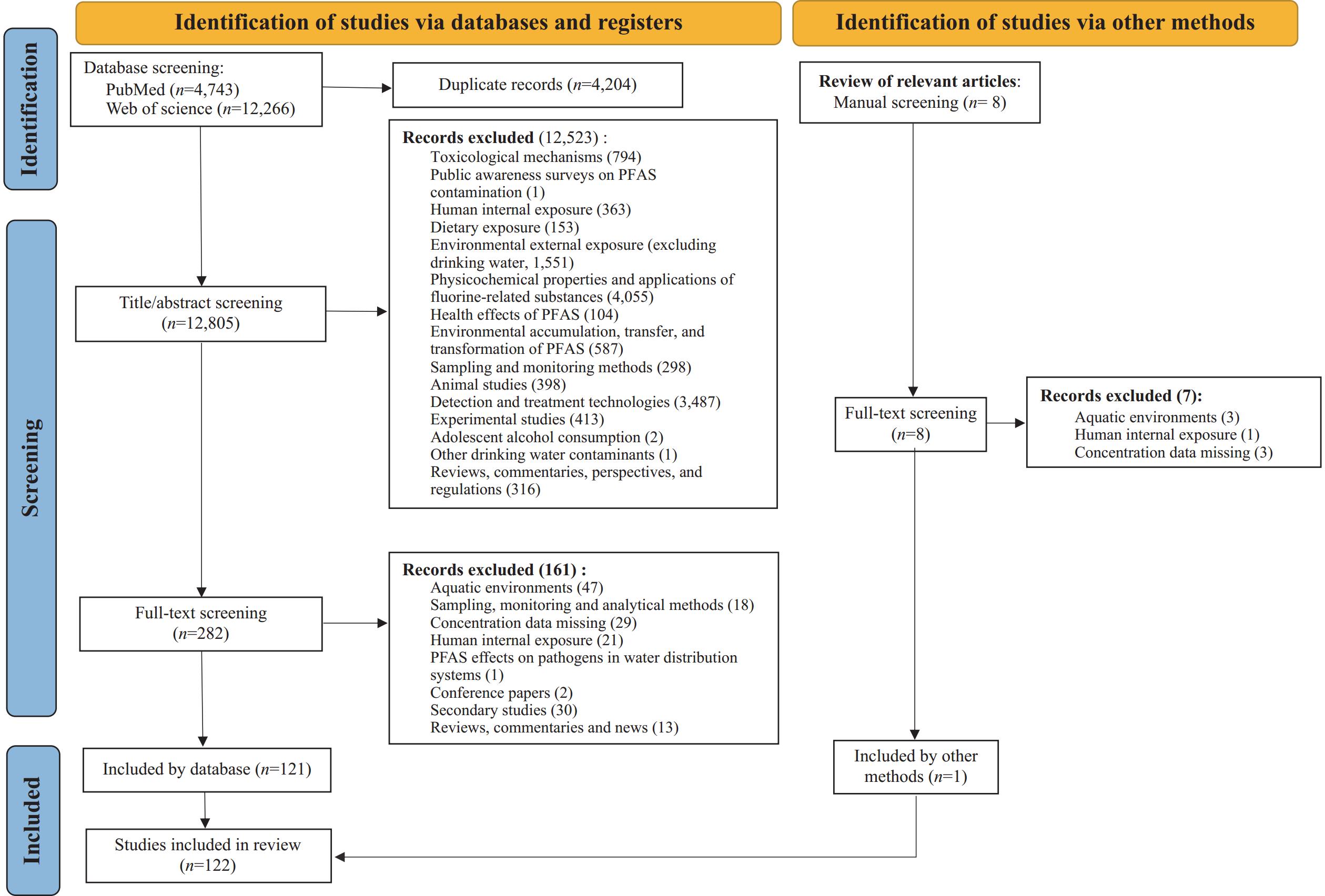
This study systematically evaluated the spatial distribution, health risks, and regulation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in global drinking water using the PubMed and Web of Science databases (January 1, 2000 to February 25, 2025). Among the 122 studies reviewed, perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) received the greatest research attention (detected in 102 and 100 studies, respectively) and showed the highest detection rates (64.69% and 60.72%, respectively). Several other compounds, including perfluorooctane sulfonamide, perfluorobutanesulfonamide, and perfluoropropane sulfonate, also exhibited high detection rates but remain underregulated, underscoring the need for further research and regulatory oversight. The three countries with the highest concentrations of



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed