2023 Vol. 5, No. 31
Allergic diseases have affected an estimated 40% of the population in China. However, our understanding of the full spectrum of these diseases remains insufficient.
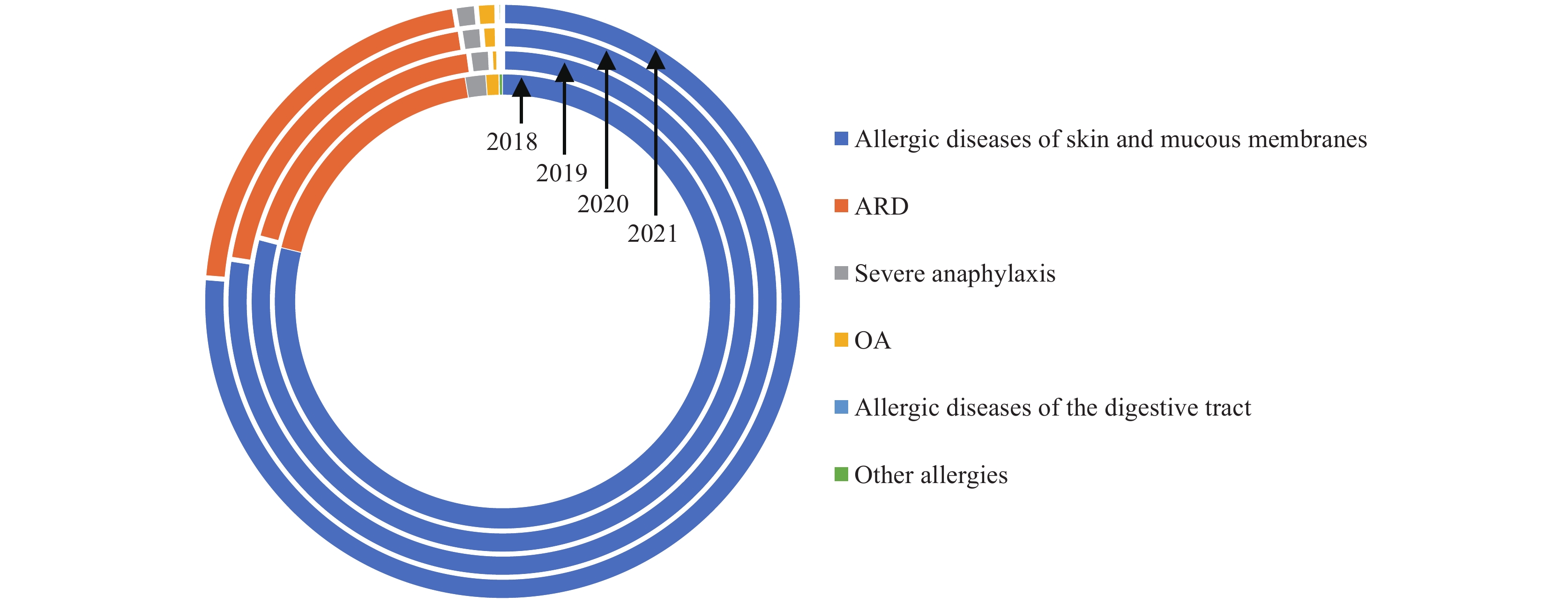
Between 2018 and 2021, Yichang City documented 625,929 outpatient visits mainly related to skin and mucous membrane allergies (77.90%) and allergic respiratory conditions (19.64%). In 2021, the occurrence of outpatient visits for conditions such as allergic rhinitis, acute atopic conjunctivitis, and atopic dermatitis increased. The demographic analysis revealed that male patients comprised the majority of the under 18 age bracket (56.05%), while female patients were predominantly represented in the 18 to 65 age bracket (61.79%).
This constitutes the first analysis of the spectrum of allergic diseases, utilizing regional outpatient data, which has substantial implications for understanding the disease burden.
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is a growing concern as an emerging tick-borne infectious disease originating from the SFTS virus (SFTSV), a recent addition to the Phlebovirus genus under the family of bunyaviruses. SFTS is typically identified by symptoms such as fever, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and gastrointestinal problems, accompanied by a potentially high case fatality rate. Thus, early and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and disease management. This review delves into the existing methodologies for SFTS detection, including pathogenic, molecular, and immunological technologies.
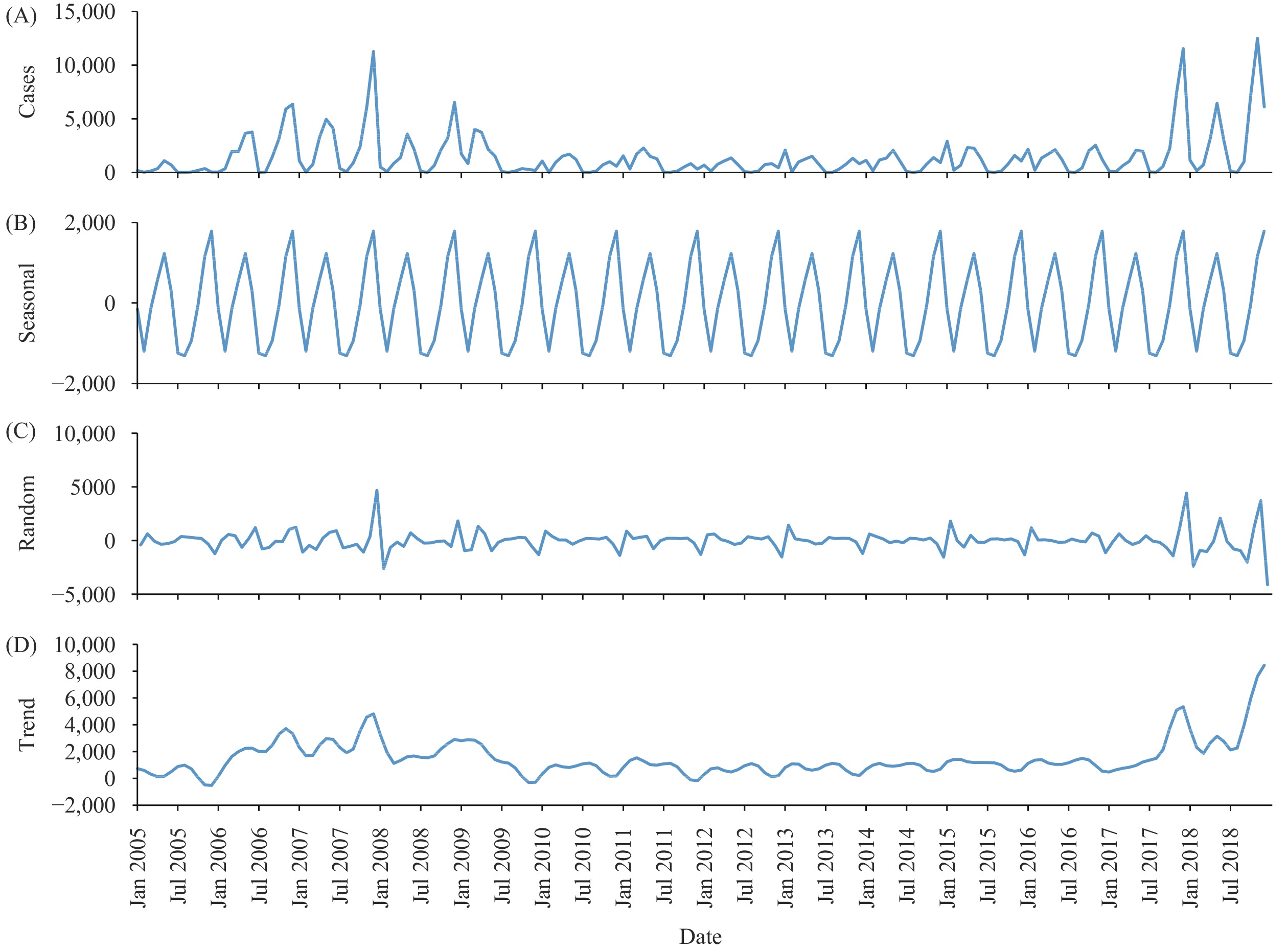
Varicella, a prevalent respiratory infection among children, has become an escalating public health issue in China. The potential to considerably mitigate and control these outbreaks lies in surveillance-based early warning systems. This research employed an autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model with the objective of predicting future varicella outbreaks in the country.
An ARIMA model was developed and fine-tuned using historical data on the monthly instances of varicella outbreaks reported in China from 2005 to 2018. To determine statistically significant models, parameter and Ljung-Box tests were employed. The coefficients of determination (R2) and the normalized Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) were compared to selecting an optimal model. This chosen model was subsequently utilized to forecast varicella outbreak cases for the year 2019.
Four models passed parameter (all P<0.05) and Ljung-Box tests (all P>0.05). ARIMA (1, 1, 1)×(0, 1, 1)12 was determined to be the optimal model based on its coefficient of determination R2 (0.271) and standardized BIC (14.970). Fitted values made by the ARIMA (1, 1, 1)×(0, 1, 1)12 model closely followed the values observed in 2019, the average relative error between the actual value and the predicted value is 15.2%.
The ARIMA model can be employed to predict impending trends in varicella outbreaks. This serves to offer a scientific benchmark for strategies concerning varicella prevention and control.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed