2021 Vol. 3, No. 40
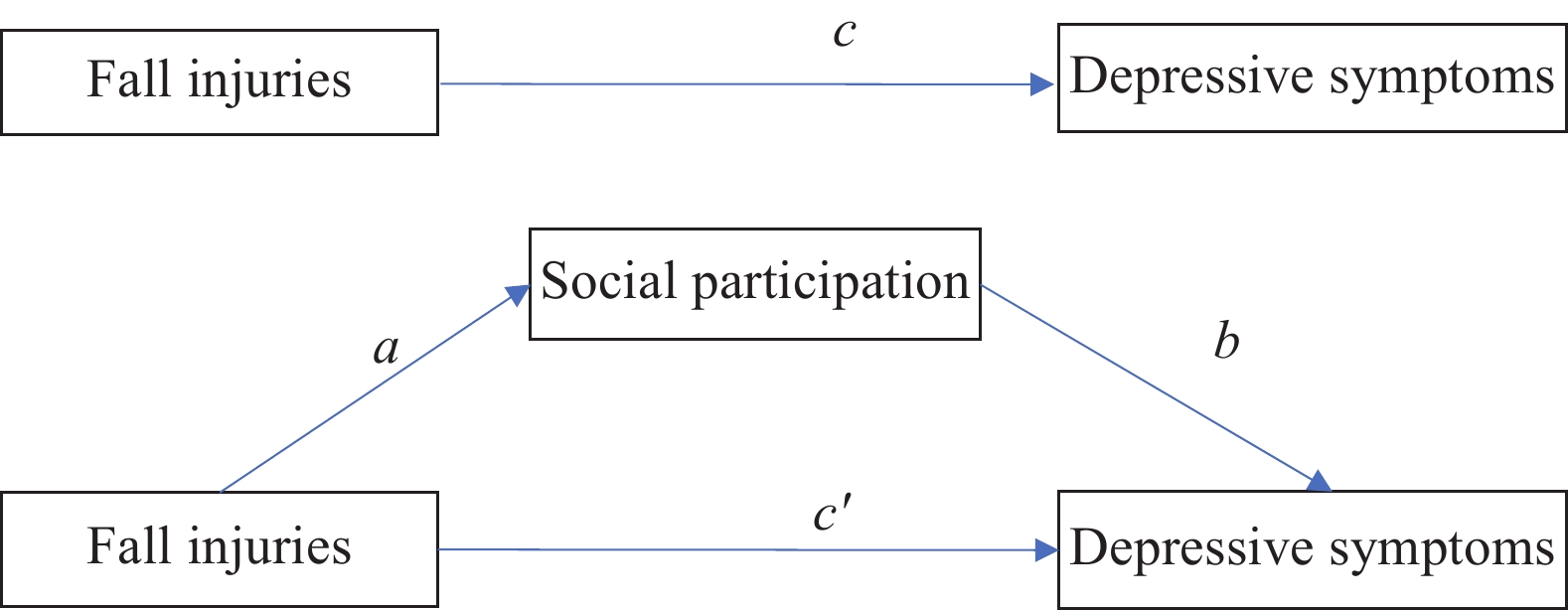
Prior studies found that fall events were associated with a higher level of depressive symptoms and a lower level of social functioning and social participation. In addition, social participation has also been significantly associated with better conditions of depressive symptoms.
This article implemented the literature in three ways. First, it examined the mechanisms of social participation in the association between fall injuries and depressive symptoms among older adults in China. Second, it specified the fall-injured older adults group from those who merely experienced fall events. Third, it compared the results between rural and urban China and discussed policy implications for both groups.
Based on the findings of this study, future policies could consider boosting social participation at both the household and community level while taking into account the challenges of mobilities and social capabilities after fall injuries. Meanwhile, it is essential to accelerate the construction of aging-friendly communities to improve the accessibility of social participation and broaden social services to health management and monitoring.
Previous studies on the importance of oral health in later life have mainly focused on nutritional and physical health indicators, while the effects of oral status on the mental health of older people, especially on depression, need to be further explored.
Longitudinal results show tooth loss was positively associated with depressive symptoms among older adults in the mainland of China, while denture use was associated with a decreased risk of depression. Effect modification by denture use was observed (P for interaction <0.001).
Measures should be taken to help Chinese older adults promote oral health and strengthen the care of dentures by expanding basic health insurance coverage to include dental prosthodontics or providing affordable dental insurance for seniors.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed