2021 Vol. 3, No. 13
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women in China and around the world. By 2019, 121 countries have instituted a national screening program as a secondary prevention measure for breast cancer.
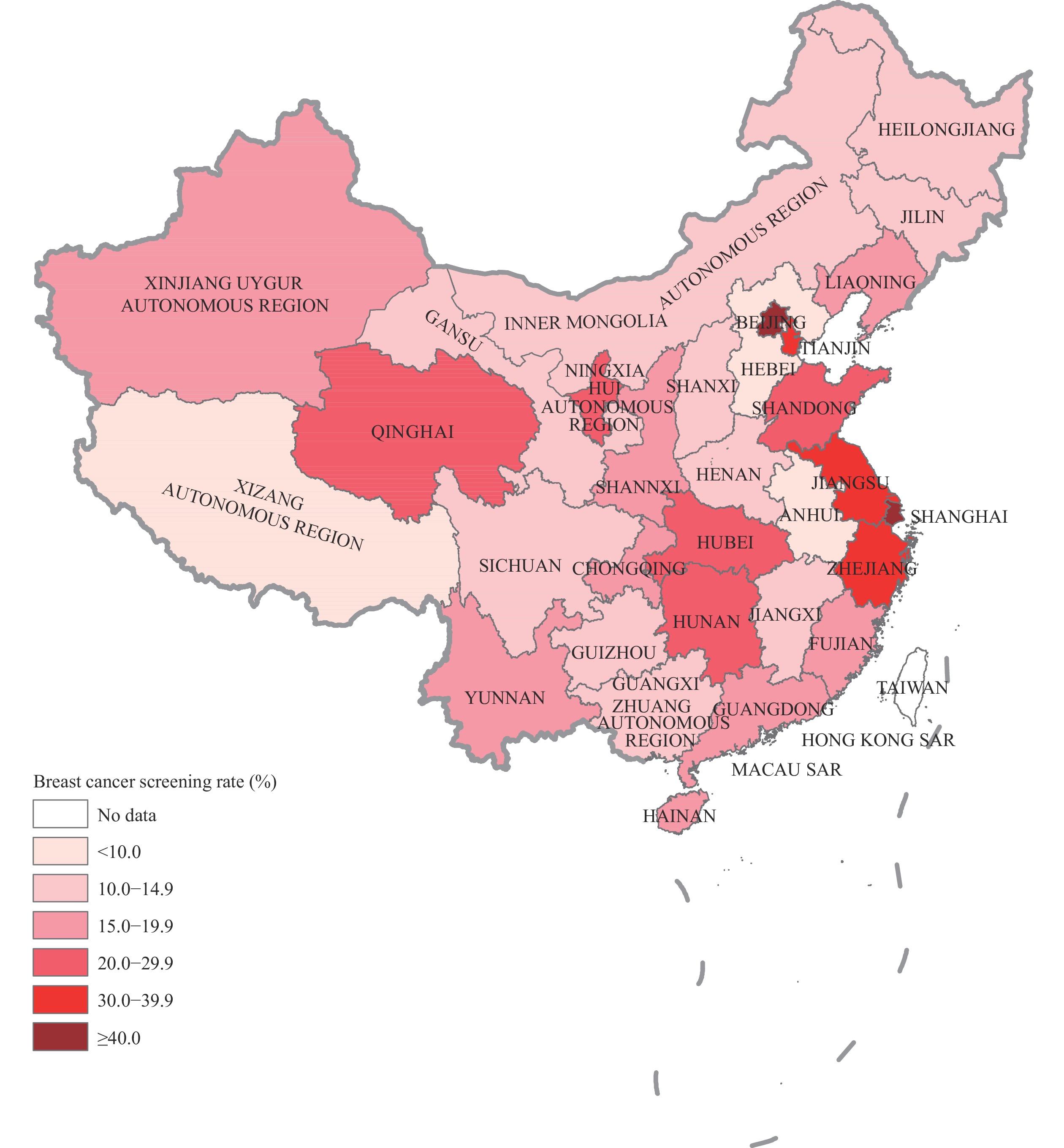
Breast cancer screening rates in China were 18.9% in women aged 20 years and above, and 25.7% in women aged 35–64 years in 2015. The screening rate for women aged 20 years and above was significantly higher in urban areas than in rural areas (24.6% vs. 15.0%), and in the eastern region than in the central and western regions (24.0% vs. 15.1% and 15.3%).
Continued efforts should be made to strengthen national and local policy initiatives and financial support for population-based, organized screening programs for breast cancer. Health education and accessibility of screening services to women across the country should be strengthened, especially for women aged 50 years and above.
What is already known about this topic?
A new tuberculosis (TB) treatment service model called “trinity model” has been adopted in China since 2010 but the implementation coverage is still unknown.
What is added by this report?
In 2020, more than one-third (36.5%) of health facilities diagnosed less than 100 TB cases, about one-fourth (25.5%) diagnosed 100 to 200 cases, and 94 health facilities diagnosed more than 800 cases. Among 2,960 county-level TB management areas, 157 (5.3%) counties were dominated by CDCs, 364 (12.3%) were dominated by TB/infectious diseases-specific hospitals, 370 (12.5%) independent TB dispensaries (or chronic disease stations), and 2,069 (69.9%) general hospitals.
What are the implications for public health practice?
The National TB Program (NTP) needs to explore more suitable treatment reimbursement mechanisms and help treatment facilities build an efficient referral system to provide quality treatment services for TB patients.
Beverage consumption has become a problematic dietary behavior in children and adolescents. Excessive drinking of beverages, especially sugary beverages, can increase the risk of chronic diseases such as obesity, dental cavities, and diabetes.
This report revealed the beverage consumption rate was higher in males, in urban areas, and adolescents aged 12–17 years. The top three beverages by consumption rate were carbonated beverages (33.2%), milk-containing beverages (25.0%), and non-100% fruit and vegetable beverages (23.5%). Children and adolescents in China consumed beverages at a primary frequency rate of 1–3 times/week. Among children and adolescents aged 6–17 years who consumed beverages, the average amount was 193.8 g/d, and was higher in males (210.6 g/d), those in urban areas (204.7 g/d), and adolescents aged 12–17 years (259.0 g/d).
Children and adolescents are key periods of life to develop healthy dietary behaviors for individuals. The consumption of beverages by Chinese children and adolescents has shown to increase year over year. Parents, schools, and governments need to prioritize promoting health consumption of beverasges.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed