2021 Vol. 3, No. 10
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic potentially affected prenatal care quality and maternal and fetal outcomes globally.
During COVID-19 pandemic period, the rates of caesarean sections (CS) and preterm birth for uninfected pregnant women increased slightly in areas that were relatively severely impacted by the pandemic in China. The overall number of prenatal examinations did not dramatically decrease, while the eligible examinations significantly decreased in Hubei Province.
Routine prenatal examinations had been well maintained during the pandemic period in China. In the future, in-time prenatal examinations should be provided to improve the quality of screening and management of high-risk pregnancy under pandemic-affected circumstances. Psychological counseling and transfer treatment channels should be strengthened for pregnant women during lockdown period.
A passenger who was from the United States was taken to the hotel for the required isolation on November 13, 2020. During the quarantine she was diagnosed as the COVID-19 patient on November 15, 2020. Controlling the importation of COVID-19 remains a major challenge.
In this study, an epidemiological investigation was conducted for a confirmed case of COVID-19, including the treatment records in the hospital and 14-day travel trajectory before the onset of disease.
This study described an epidemiological investigation and management process on an imported case of COVID-19 and analyzed the test results, aiming to provide useful warnings to strengthen the capacity of public health system in response to the importation.
What is already known on this topic?
Clusters of COVID-19 cases often happened in small settings (e.g., families, offices, school, or workplaces) that facilitate person-to-person virus transmission, especially from a common exposure.
What is added by this report?
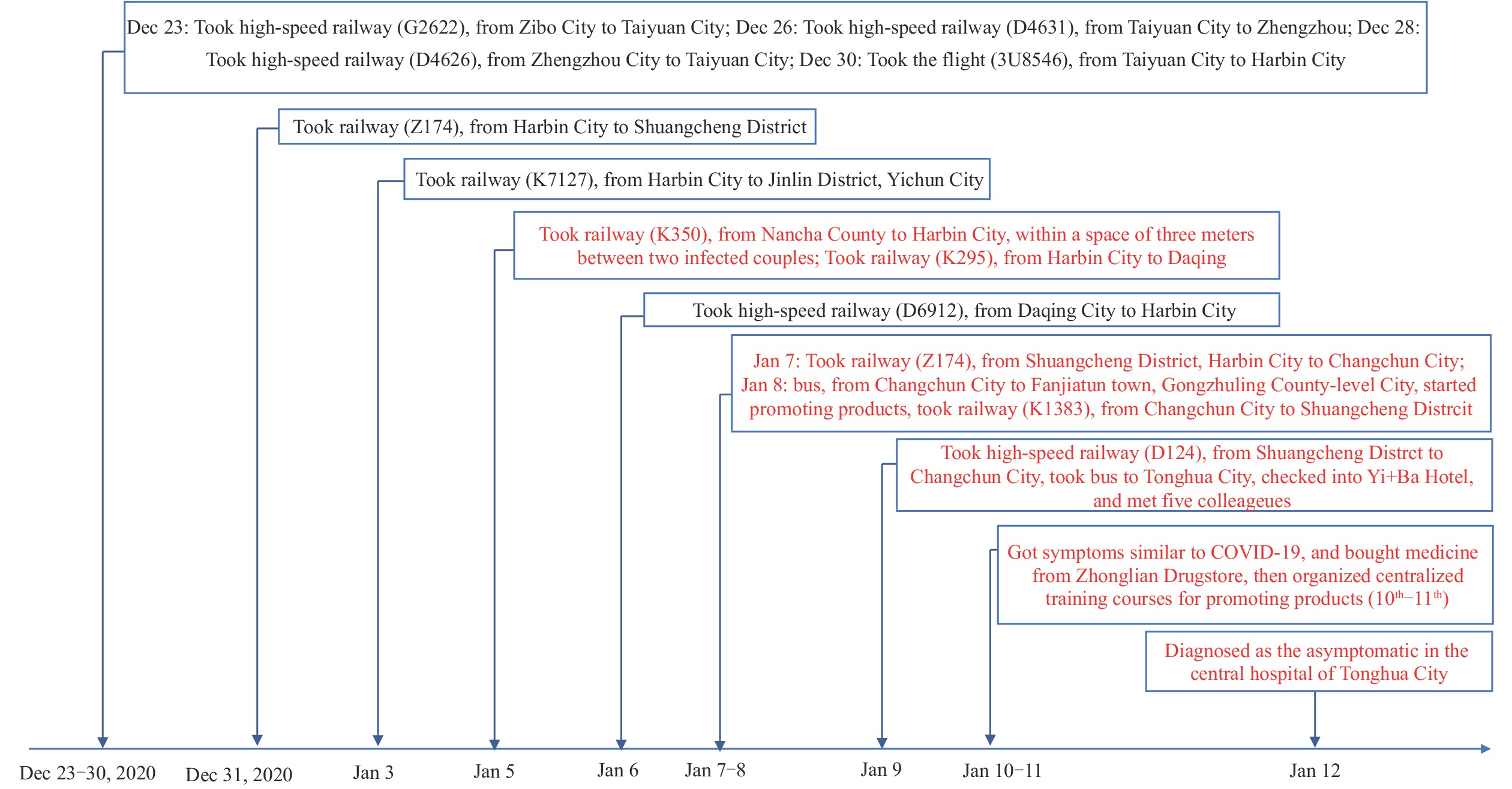
On January 10 and 11, 2021, an individual gave three product promotional lectures in Tonghua City, Jilin Province, that ultimately led to a 74-case cluster of COVID-19. Our investigation determined the outbreak to be an import-related COVID-19 superspreading cluster event in which elderly, retired people were exposed to the infected individual during his promotional lectures, which were delivered in a confined space and lasted several hours.
What are the implications for public health practice?
Routine activities, such as attending a lecture in a classroom, can provide an environment conducive to COVID-19 superspreading events because respiratory viruses can spread easily and widely. We suggest local government to strengthen infection control management, reduce unnecessary indoor large gathering activities, and promote wearing of masks, especially during wintertime in the north of China. Health education for elderly people should promote use of effective personal protection and emphasize the importance of wearing masks.
What is known about this topic?
Patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection can be categorized by severity: asymptomatic infection, mild illness, moderate illness, severe illness, and critical illness. The rate of transmission to a specific group of contacts (the secondary attack rate) may be 3–25 times lower from people who are asymptomatically infected than from those with symptoms. The incubation period is 2–14 days.
What is added by this report?
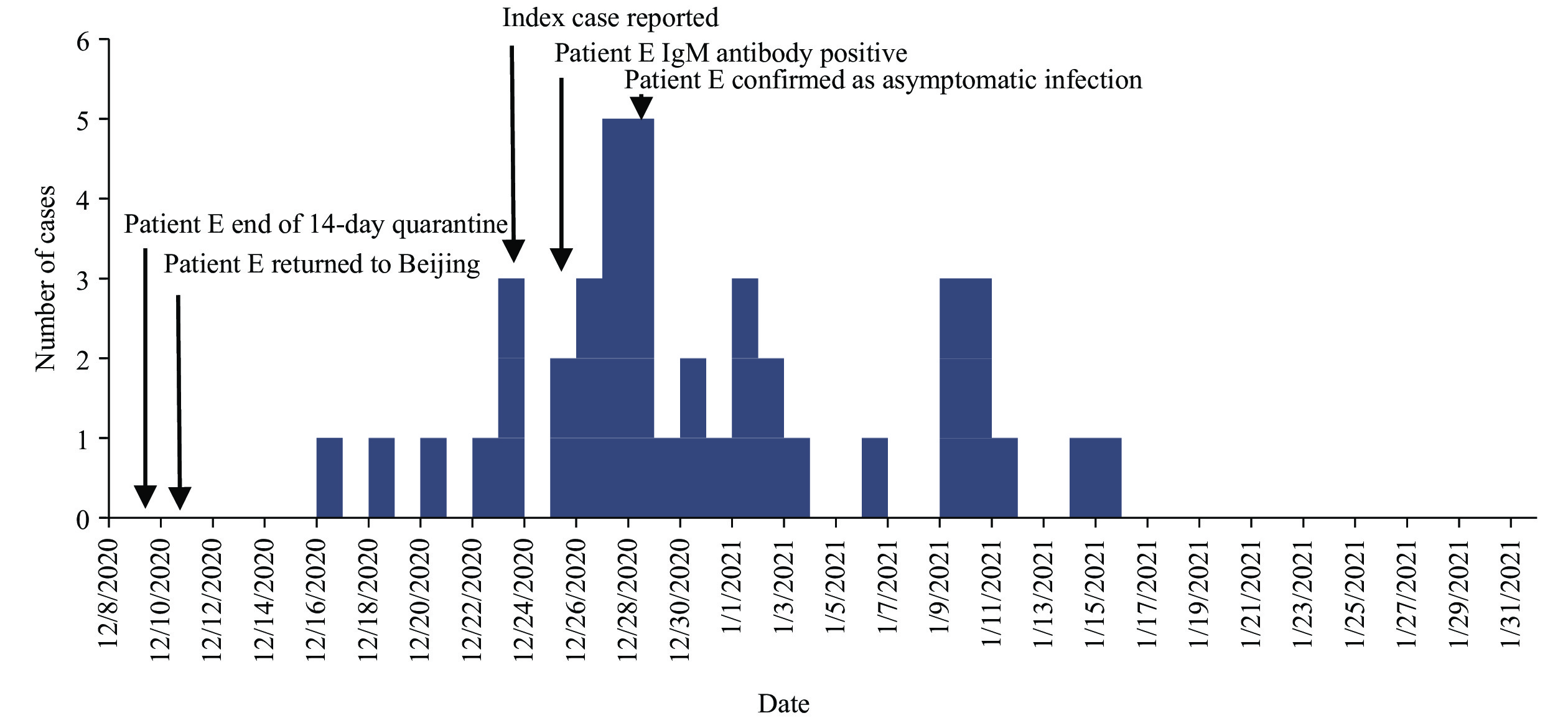
An individual with asymptomatic infection shed live virus that started a 42-case outbreak in Shunyi District of Beijing in December 2020. The individual had been quarantined for 14 days in a designated quarantine hotel in Fuzhou after entering China from Indonesia. During quarantine, he had 5 negative throat swab tests and 2 negative IgM serum tests. The investigation team determined that the incubation periods of 31 confirmed cases ranged from 2 to 23 days.
What are the implications for public health practice?
The frequency of nucleic acid testing should be increased for international entrants and people who are close contacts of confirmed COVID-19 cases. The investigation team recommend expanding sample types for nucleic acid testing to include anal swabs and residential environmental sampling; serum antibody testing can be used as a reference indicator. Parallel testing by two institutions at key points in time, such as the end of isolation, should be implemented.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed