2020 Vol. 2, No. 11
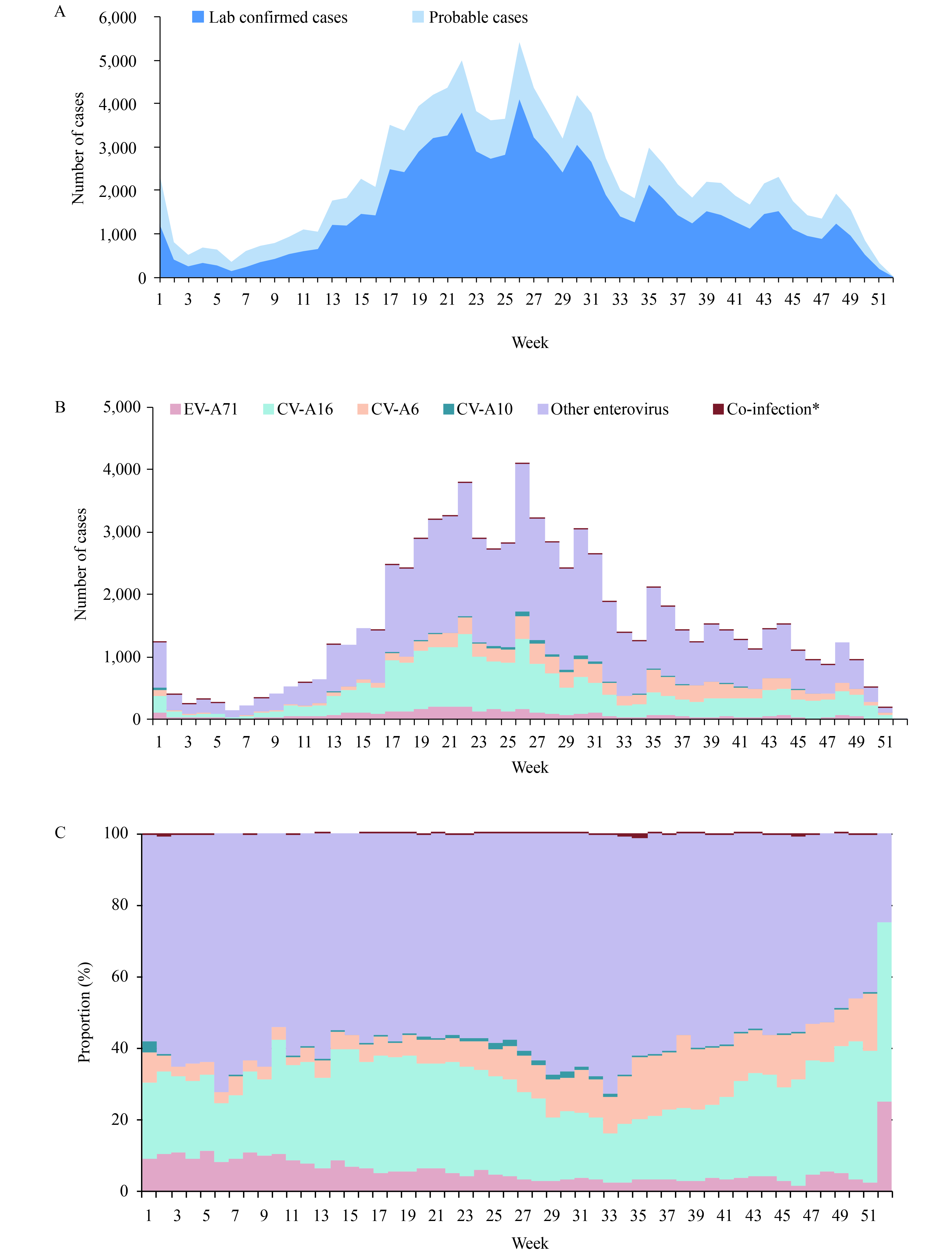
Enterovirus 71 (EV-A71) is the main causative pathogen for severe and fatal patients with Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) in mainland China from 2008 to 2017. Non-EV-A71 and non-CV-A16 (other enterovirus) serotypes were the major causative-serotypes for mild HFMD in years of 2013, 2015, and 2017.
In 2018, other enterovirus serotypes replaced EV-A71 for the first time as the major cause of severe HFMD with a proportion of 70.7%. However, at the national level, only a small proportion of the other enterovirus serotypes were further identified as CV-A6 and CV-A10.
Further identification of other enterovirus serotypes is highly recommended for provincial CDCs, especially for severe HFMD. Studies contributing to a multivalent vaccine for HFMD should be prioritized.
After the type 2 strain of the live, attenuated poliovirus vaccine was withdrawn globally in 2016, any identification of a type 2 poliovirus is a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. A vaccine-derived type 2 poliovirus (VDPV2) was identified in Sichuan, prompting an urgent, comprehensive investigation and response.
Type 2 monovalent, live, attenuated oral poliovirus vaccine (mOPV2) is being used to respond to the numerous VDPV2 outbreaks seen around the world. In contrast, the response in Sichuan used Sabin strain inactivated poliovirus (sIPV) to stop circulation of the VDPV2. In the 6 months following the vaccination response, there have been no VDPV2s detected in Sichuan, despite extensive search.
Further search for the VDPV2 must continue in order to determine whether transmission has been stopped. The ongoing investigation and response to the Sichuan VDPV2 is providing evidence to the Global Polio Eradication Initiative on managing VDPV2 outbreaks.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed