-
Introduction Chronic and non-communicable diseases (NCDs) have become an important public health concern in China. We aimed to estimate the incidence, prevalence, and mortality of four major NCDs including cardiovascular disease (CVD), cancer, chronic respiratory diseases (CRD), and diabetes in China during 1990-2017.
Methods The general analytic framework of Global Burden of Diseases Study 2017 (GBD 2017) was applied. Data from Disease Surveillance Point System, censuses, and Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention Cause-of-Death Reporting System were used for mortality estimates. National surveys, cancer registries, and published studies were used for incidence and prevalence estimates.
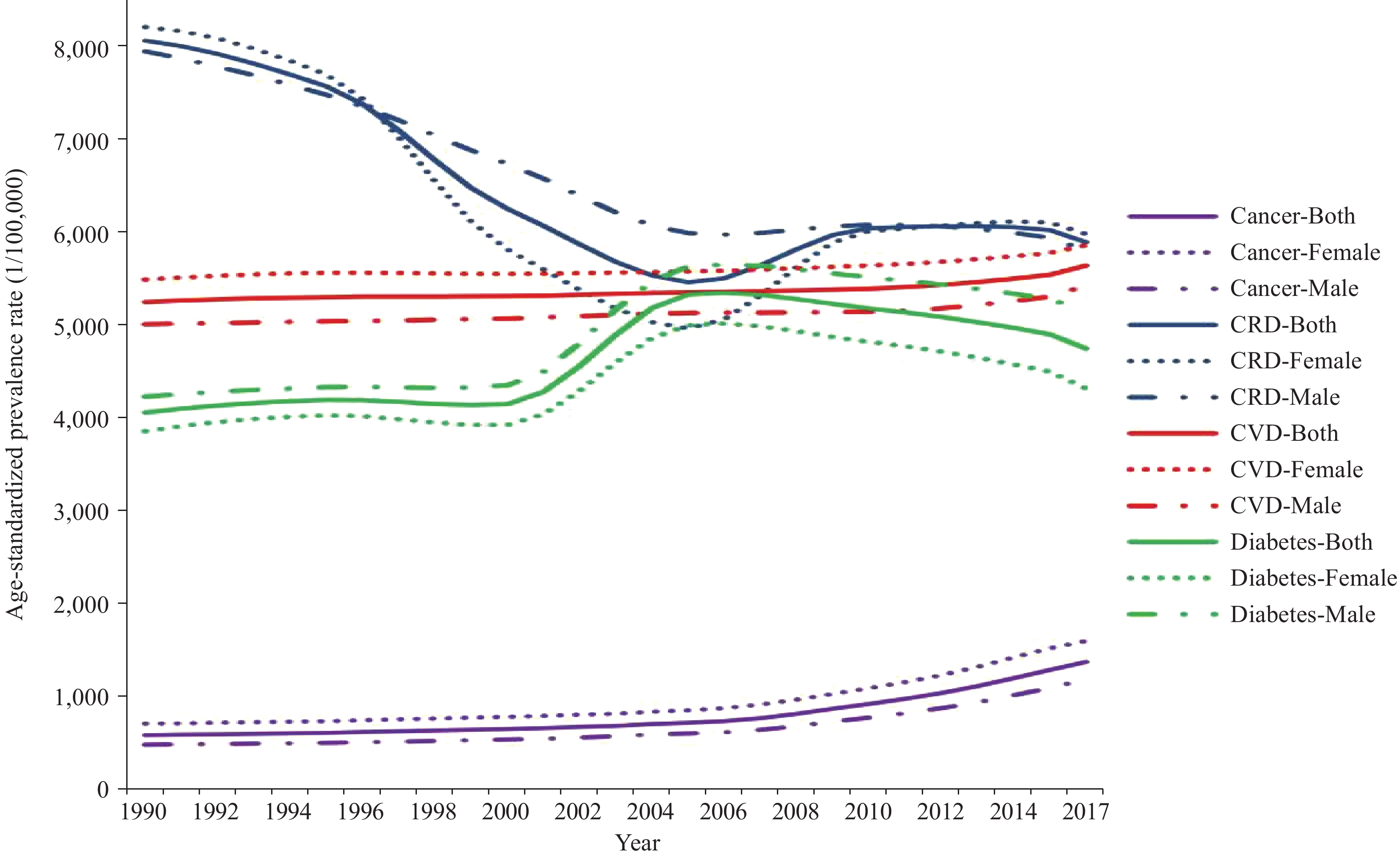
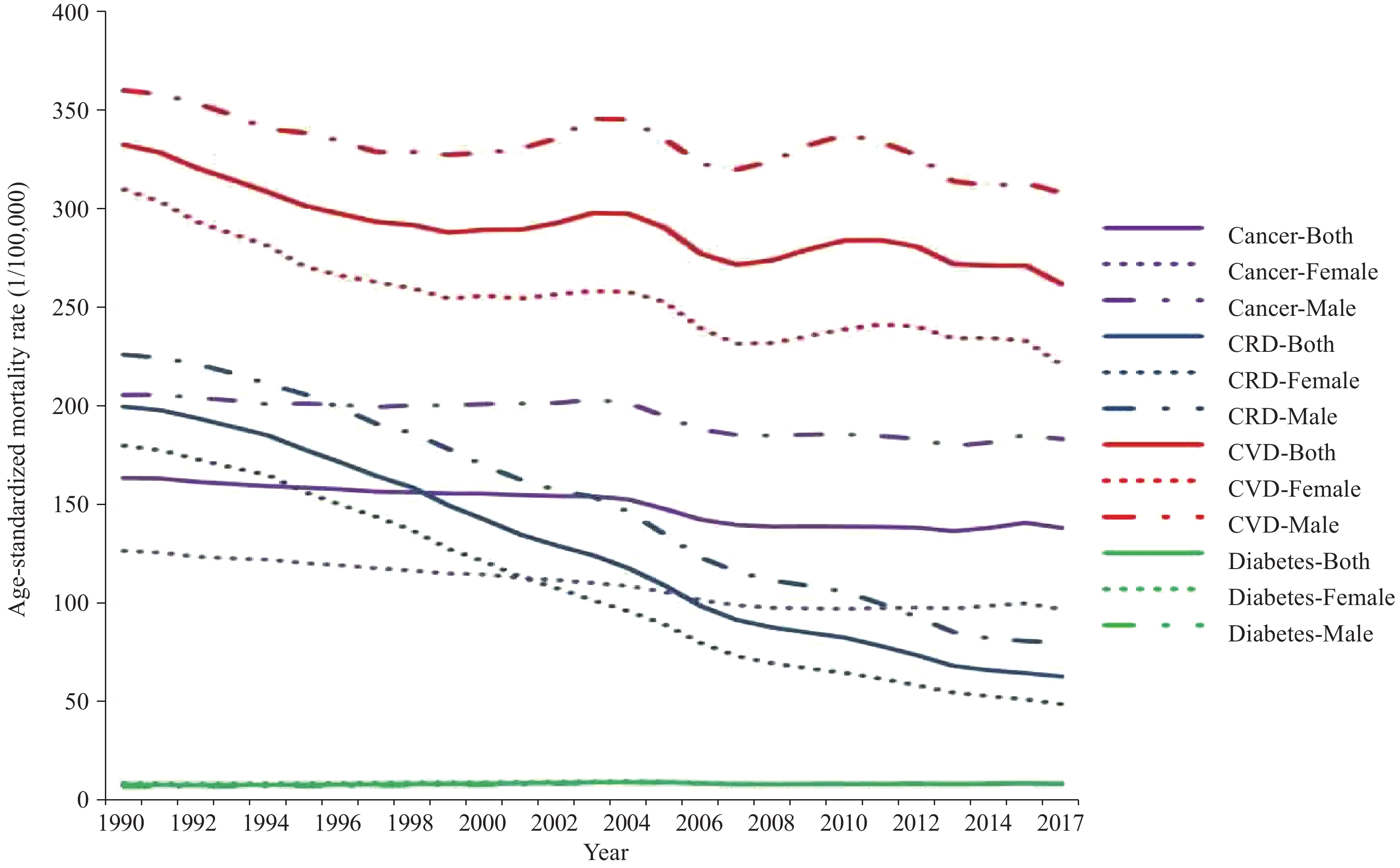
Results In 2017, new cases for CVD, cancer, and diabetes were 13.5, 4.6, and 3.3 million, an increase of 120.4%, 159.7%, and 57.3% respectively compared with 1990. There were 9.6 million incident cases for CRD in 2017, a 4.9% decrease compared with 1990. A total of 8.1 million people died from cancer, CVD, CRD, and diabetes in China in 2017. There was a substantial decline in age-standardized mortality rate for CRD and a steady but slow decline for CVD and cancer. During 1990-2017, the age-standardized prevalence rate increased by 7.4%, 135.2%, and 17.0% for CVD, cancer, and diabetes respectively.
Conclusions and Implications for Public Health Practice The accumulated prevalence of the four major NCDs are increasing but the age-standardized mortality rate for CVD, cancer, and CRD has been on a decline during 1990-2017. More effective intervention strategies should be developed to deal with the continuously increasing burden caused by NCDs in China.
-
Chronic and non-communicable diseases (NCDs) cause a heavy burden globally and have become a major global concern (1-2). In recent decades, China has gone through an epidemiological shift in disease patterns, mainly from infectious and nutritional diseases to NCDs (3). The Chinese government responded quickly to the emerging public health concerns and issued Healthy China 2030 aiming to promote population health with specific goals and targets (4). In order to achieve these goals, clear understanding of the levels and the trends of these NCDs is crucial. In this report, the National Center for Chronic and Noncommunicable Disease Control and Prevention of China CDC used the results of the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2017 (GBD 2017) to investigate the incidence, prevalence, and mortality of four major NCDs including cardiovascular disease (CVD), cancer, chronic respiratory diseases (CRD), and diabetes in China during 1990-2017.
-
Detailed descriptions of the data, quality control measures, and statistical modeling for the GBD 2017 have been reported elsewhere (1,3). Data for all-cause mortality in China were derived primarily from the Disease Surveillance Point System; censuses; surveys including the Annual Survey on Population Change and the Intercensal Survey; the Maternal and Child Health Surveillance System; and the One-Per-Thousand Population Fertility Sample Survey. Cause-specific mortality was estimated primarily with the GBD cause of death ensemble modelling tool, CODEm (1). Prevalence and incidence of non-fatal outcomes were primarily estimated with the Bayesian meta-regression method DisMod-MR 2.1 (5). Data on non-fatal outcomes were derived primarily from published studies, national surveys, cancer registries, the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention cause-of-death reporting system, and hospital inpatient data. World standard population generated by GBD was used to estimate the age-standardized rate for incidence, prevalence, and mortality (6).
-
Table 1 shows the absolute numbers of incidence, prevalence, and mortality of four major NCDs by gender in China. In 2017, the new cases for CVD, cancer, and diabetes were 13.5, 4.6, and 3.3 million, an increase of 120.4%, 159.7%, and 57.3% respectively compared with 1990. There were 9.6 million incident cases for CRD in 2017, 4.9% decrease compared with 1990. There were 106.7, 22.4, 93.9, and 89.5 million prevalence cases for CVD, cancer, CRD and diabetes, respectively, in 2017, increasing by 119.8%, 278.6%, 14.0%, and 114.6% in comparison with 1990.
Incident cases in thousands Prevalent cases in thousands Death numbers in thousands 1990 2017 Percentage change (%) 1990 2017 Percentage change (%) 1990 2017 Percentage change (%) CVD 6,144 (5,918 - 6,396) 13,541(13,003 - 14,120) 120.4 48,538(46,761 - 50,347) 106,670(102,572 - 111,110) 119.8 2,245(2,188 - 2,363) 4,378(4,233 - 4,517) 95.0 Males 3,128(3,018 - 3,256) 6,922(6,650 - 7,214) 121.3 22,868(22,012 - 23,766) 50,357(48,368 - 52,525) 120.2 1,130(1,095 - 1,172) 2,406(2,308 - 2,504) 112.8 Females 3,016(2,899 - 3,145) 6,619(6,348 - 6,917) 119.5 25,670(24,720 - 26,663) 56,314(54,091 - 58,733) 119.4 1,115(1,072 - 1,212) 1,972(1,875 - 2,063) 76.9 Cancer 1,767(1,705 - 1,869) 4,589(4,392 - 4,770) 159.7 5,922(5,745 - 6,247) 22,421(20,842 - 23,751) 278.6 1,418(1,377 - 1,491) 2,607(2,507 - 2,702) 83.9 Males 1,000(958 - 1,039) 2,721(2,586 - 2,865) 172.2 2,291(2,180 - 2,374) 10,245(9,571 - 10,903) 347.1 856(823 - 887) 1,669(1,588 - 1,751) 94.9 Females 767(727 - 857) 1,867(1,736 - 1,979) 143.5 3,630(3,489 - 3,974) 12,176(10,988 - 13,320) 235.4 561(533 - 626) 938(877 - 990) 67.1 CRD 10,162(8,923 - 11,456) 9,665(8,719 - 10,745) -4.9 82,341(76,495 - 89,019) 93,899(86,774 - 100,857) 14.0 1,237(1,070 - 1,285) 1,010(968 - 1,114) -18.4 Males 5,314(4,652 - 6,014) 5,196(4,665 - 5,803) -2.2 40,458(37,506 - 43,777) 45,667(42,116 - 49,359) 12.9 627(604 - 651) 583(555 - 609) -7.1 Females 4,848(4,271 - 5,464) 4,469(4,044 - 4,956) -7.8 41,883(38,915 - 45,159) 48,232(44,430 - 51,865) 15.2 610(431 - 659) 427(394 - 528) -30.0 Diabetes 2,122(1,934 - 2,331) 3,338(3,025 - 3,736) 57.3 41,708(37,392 - 46,543) 89,496(80,957 - 99,786) 114.6 64(61 - 68) 153(148 - 159) 139.9 Males 1,120(1,012 - 1,238) 1,642(1,495 - 1,843) 46.5 22,529(19,981 - 25,381) 48,205(43,307 - 54,000) 114 27(25 - 28) 74(70 - 77) 177.7 Females 1,002(915 - 1,101) 1,696(1,524 - 1,900) 69.3 19,179(17,262 - 21,274) 41,291(37,456 - 45,972) 115.3 37(34 - 41) 80(75 - 84) 113.1 Abbreviation: CVD, Cardiovascular diseases; CRD, Chronic respiratory diseases. Table 1. Incidence, prevalence, and mortality numbers and percentage change of major NCDs in China, 1990 to 2017.
As shown in Table 2, the age-standardized rate for incidence, prevalence, and mortality decreased for CRD with higher declines in females than in males during 1990-2017. The age-standardized prevalence rate increased by 7.4%, 135.2%, and 17.0% for CVD, cancer, and diabetes, respectively. The age-standardized incidence rate per 100,000 was 732, 244, and 199 for CVD, cancer, and diabetes in 2017 in China, which is a 3.3%, 27.9%, and 12.3% increase compared with 1990.
Incidence rate per 100,000 Prevalence rate per 100,000 Death rate per 100,000 1990 2017 Percentage change (%) 1990 2017 Percentage change (%) 1990 2017 Percentage change (%) CVD 708(683 - 737) 732(704 - 760) 3.3 5,241(5,048 - 5,452) 5,632(5,429 - 5,853) 7.4 332(324 - 352) 262(253 - 270) -21.2 Males 742(716 - 771) 771(742 - 800) 3.9 5,000(4,815 - 5,195) 5,414(5,214 - 5,633) 8.3 360(349 - 371) 308(296 - 320) -14.4 Females 681(657 - 709) 697(670 - 726) 2.3 5,484(5,280 - 5,704) 5,847(5,624 - 6,087) 6.6 310(297 - 338) 221(210 - 231) -28.7 Cancer 191(185 - 202) 244(233 - 254) 27.9 582(565 - 613) 1,369(1,244 - 1,502) 135.2 163(159 - 172) 138(133 - 143) -15.5 Males 224(216 - 233) 296(282 - 311) 31.9 478(458 - 493) 1,183(1,095 - 1,274) 147.6 205(198 - 212) 183(175 - 192) -10.9 Females 162(154 - 181) 197(183 - 209) 21.6 704(677 - 771) 1,596(1,390 - 1,870) 126.5 127(120 - 141) 97(91 - 102) -23.3 CRD 930(831 - 1034) 753(641 - 879) -19.0 8,051(7,507 - 8,675) 5,883(5,367 - 6,455) -26.9 200(172 - 207) 63(60 - 69) -68.5 Males 963(862 - 1068) 794(675 - 928) -17.5 7,935(7,409 - 8,528) 5,794(5,270 - 6,394) -27.0 226(218 - 234) 80(76 - 83) -64.6 Females 898(801 - 1001) 709(604 - 826) -21.1 8,198(7,645 - 8,826) 5,970(5,450 - 6,541) -27.2 180(129 - 194) 49(45 - 60) -72.8 Diabetes 177(163 - 195) 199(182 - 219) 12.3 4,052(3,663 - 4,496) 4,740(4,278 - 5,284) 17.0 8(8 - 9) 8(8 - 9) 6.1 Males 177(162 - 194) 203(186 - 226) 15.0 4,222(3,783 - 4,715) 5,145(4,602 - 5,762) 21.9 7(7 - 8) 9(8 - 9) 20.5 Females 178(163 - 196) 193(176 - 214) 8.7 3,851(3,494 - 4,272) 4,311(3,914 - 4,802) 11.9 9(8 - 10) 8(8 - 9) -5.1 Abbreviation: CVD, Cardiovascular diseases; CRD, Chronic respiratory diseases. Table 2. The age-standardized incidence, prevalence, and mortality rates and percentage change of major NCDs in China, 1990 to 2017.
Figure 1 shows the trend of the age-standardized incidence rate for four major NCDs during 1990-2017. There was a steady but slow rise in age-standardized incidence rate for cancer, especially in the past 10 years. As shown in Figure 2, the age-standardized prevalence rate decreased significantly for CRD while increasing significantly for cancer. Figure 3 showed a substantial decline in age-standardized mortality rate for CRD. The age-standardized mortality rate for diabetes, however, remained relatively stable during the study period.
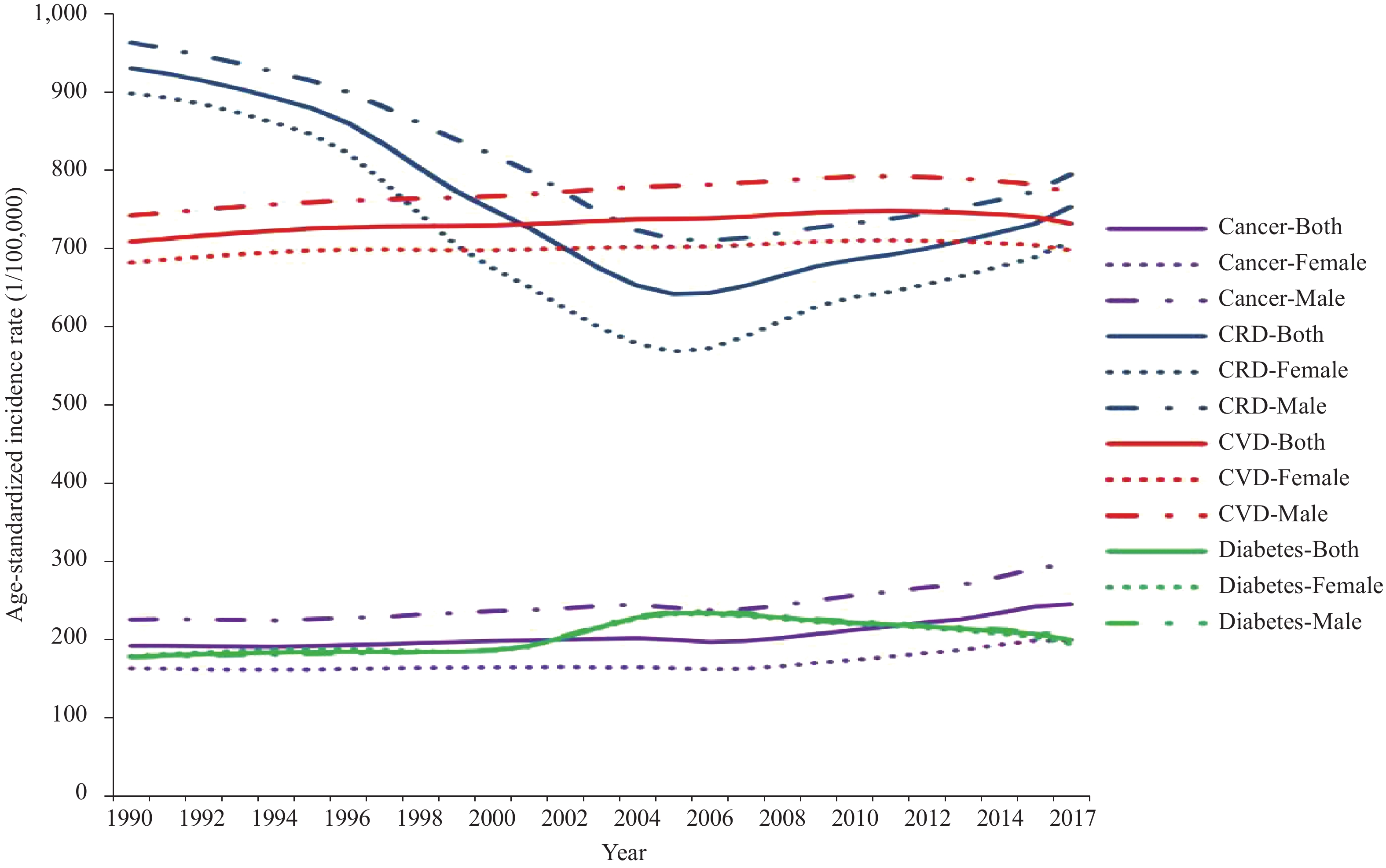 Figure 1.
Figure 1.Age-standardized incidence rates (1/100,000) for CVD, cancer, CRD, and diabetes in China, 1990-2017.
Note: “Both” represents the total population; Abbreviation: CVD, cardiovascular diseases; CRD, chronic respiratory diseases. -
Our study found that a total of 8.1 million people died from cancer, CVD, CRD, and diabetes in China in 2017. These diseases place heavy burdens on the economic and social development in China and have become a huge challenge for the Chinese government.
China has made great achievements towards reducing the burden of communicable, maternal, neonatal, and nutritional conditions. The overall improvement in healthcare among the Chinese population can also be reflected by the observed decline of mortality rate for CVD, cancer, and CRD in this study. Better access to medical services, wider coverage of health insurance in both urban and rural areas, and improvement of diagnosis and treatment of many diseases have contributed to the decline in mortality rate. On the other hand, longer life expectancy, population aging, and more westernized lifestyles have resulted in the increasing number of cases and deaths due to NCDs, which poses challenges to society and the government.
These NCDs have common risk factors including tobacco smoking, alcohol drinking, physical inactivity, and unbalanced dietary habits. Previous studies showed that modifiable risk factors explained nearly 60% of cancer deaths in China, with tobacco smoking accounting for 22.6% of cancer deaths (7). The burden will continue to grow with high smoking prevalence in Chinese men and the high level of indoor air pollution from cooking and heating with coal and other biomass fuels in rural areas (8).
Our results showed that both the absolute numbers and the age-standardized rates for incidence, prevalence, and mortality for diabetes increased from 1990 to 2017. A large cross-sectional survey in 2010 showed the estimated diabetes prevalence of Chinese adults was 11.6% and the prevalence of pre-diabetes was 50.1%, representing 113.9 million Chinese adults with diabetes and 493.4 million with pre-diabetes (9). Along with the striking number of people with diabetes, the significant increasing trend of diabetes prevalence and mortality indicated the importance of diabetes as one of the emerging public health challenges in China during the last two decades.
Accordingly, the Chinese government has recognized and paid more attention to the importance of prevention and control of NCDs. Many efforts have been made to tackle the problem with focuses on surveillance, monitoring, and intervention. In addition, intervention efforts tailored to individuals and high-risk populations were also made at the national, provincial, and city levels. The National Healthy Lifestyle for All Campaign was launched in 2009 and included a broad range of focuses such as promoting physical activity, improving community exercise facilities, establishing demonstration areas including restaurants, schools, and factories, and increasing health related awareness such as providing community members with salt reduction spoons, oil control jars, etc. These health-promotion interventions have been shown to play an important role in addressing NCDs in China (10). Building upon the Healthy China 2030, the Chinese central government recently issued the Healthy China Action 2019-2030 and specified 15 major areas for action (11). The effective implementations of this plan is anticipated to halt the increasing burden from NCDs among Chinese population.
The findings in this report are subject to some limitations. GBD 2017’s limitations are also applied to this study. First, for the estimation of all-cause mortality in China, death distribution methods were used to evaluate the completeness of the Disease Surveillance Point System, but these methods have a wide range of uncertainty. Second, the current DisMod-MR 2.1 tool does not capture the cohort nature of some diseases such as lung cancer. Third, the lack of more robust cause-specific mortality data from some western provinces affects the precision of our estimates.
NCDs have become a serious public health problem and pose significant challenges to society. In the battle of dealing with NCDs, Chinese government needs to place more effort in the continued surveillance of the levels and trends of chronic diseases and relevant risk factors. Prevention strategies including controlling common risk factors are urgently needed.
HTML
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download: