-
With the increasing number of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases and worldwide vaccination coverage, ‘vaccination passports’ (vaccination certificates) may become a required permit for global travel, thereby supporting economic recovery. On March 7, 2021, Wang Yi, State Councilor and Foreign Minister of China, announced the launch of the Chinese version of an ‘international travel health certificate’ at a press conference of the National People’s Congress and the Chinese Political Consultative Conference. He proposed a feasible ‘Chinese solution’ for promoting the recovery of the global economy and the facilitation of cross-border travel, and hoped that the international travel health certificate and vaccination passport can be mutually authenticated. The Israeli government issued a vaccination certificate or ‘green passport’ to vaccinees via a smartphone application and the government website, which must be presented when entering places with a high risk of infection such as restaurants and cultural facilities. The European Union (EU) plans to introduce an EU vaccination certificate by the summer of 2021 that includes vaccination records and nucleic acid test results. The government of the Republic of Korea is exploring the implementation of a COVID-19 vaccination passport by issuing vaccination passports to Korean citizens and exempting arriving foreigners with vaccination passports from quarantine.
Mutual trust of electronic vaccination certificates is important to promote the implementation of vaccination passports. The World Health Organization (WHO) issued interim guidance for developing a smart vaccination certificate (hereafter referred to as the guidance) in March 2021 (1), and created the concept of digital vaccination certificates (DVCs) or ‘smart vaccination certificates’ (SVCs). The purpose of SVCs is to provide a mechanism for individuals to submit documents proving that they have been vaccinated, and the certificate can be encrypted and verified by the authorities. SVCs are considered superior to paper vaccination certificates that may be defrauded, lost, damaged, or difficult to read due to illegible handwriting. SVCs were designed for COVID-19 vaccines, but the aim is to establish a basic consensus mechanism applicable to other vaccines in the future. Following the guidance, in this work we propose a technical route for the application of blockchain, the underlying technology of Bitcoin, in trusted DVCs.
-
Inconsistent development in the digitalization of immunization programs in different countries poses problems and challenges to existing vaccination information systems, as follows: 1) Information on vaccine production is usually generated unilaterally by vaccine license holders using traditional information technology; it is difficult to verify the authenticity of sources and the integrity of content, and there is a risk of tampering and fabrication; 2) Cold-chain distribution of vaccines is mainly self-monitored by logistics enterprises with insufficient external supervision, lacking automated collection and certification of information on personnel, equipment, temperature, and time spent in the transportation process; 3) The lack of a mechanism by which records are made by persons in charge during the circulation and use of vaccines makes it difficult to verify the authenticity of information; and 4) traditional centralized vaccine management information systems suffer from poor data access and vulnerability to single point failures, which makes it difficult to ensure information sharing and the availability of third-party inquiry services.
-
In recent years, blockchain has gained worldwide attention and is widely used in digital currency, financial credit reporting, and supply chain management. Blockchain employs a distributed storage system to ensure the authenticity and integrity of information, uses consensus algorithms to establish fault-tolerant mechanisms, deploys and validates smart contracts to avoid transaction risks, and issues workload certificates to encourage user participation. Blockchain has great potential for application in vaccine tracking. Making full use of blockchain technology allows decentralization of immunization program information systems, better protection of vaccine safety and vaccination data, and tracking/managing the whole process of vaccine deployment. The combination of blockchain, the internet of things, and artificial intelligence in DVC systems provides the technical means to promote the recovery of the global economy and to facilitate the cross-border movement of people. The practical significances of trusted DVCs or SVCs based on blockchain technology are shown in the following paragraphs (2).
The first is authentic and valid data storage. Distributed data storage with blockchain is characterized by tamper-proof data and non-repudiation. Asymmetric encryption can be used to achieve mutual trust of vaccination information between nodes. Meanwhile, signature/verification mechanisms make vaccination information undeniable. Based on the consensus among blockchain nodes and cryptographic principles, a tamper-proof record of malicious acts in a node is created and broadcast throughout the network.
The second is safe and reliable information transmission. The cross-border authentication of DVCs or SVCs is prone to frequent disruption of information transmission. The consensus mechanism of blockchain can be used to obtain authentic and valid information. As long as the destruction is controlled to some extent (less than 50% of the computing power of the entire network), cross-validation between user nodes can be carried out based on the consensus mechanism to achieve the verification and accurate transmission of information and to improve the reliability of network information.
The third is autonomous and flexible application mechanisms. Blockchain shortens the delay of intermediate processes and increases the speed of response through fast network computing. With the application of DVCs or SVCs, artificial intelligence will also be widely used in verification systems. Consensus algorithms can be combined with swarm intelligence to create application modes suitable for the specific conditions of various countries.
The fourth is trusted and interconnected network architectures. In the guidance, the WHO proposed the construction of a trust framework consisting of technical specifications, interoperability standards, and related governance mechanisms to establish a consensus mechanism agreed upon by multiple entities (countries or regions), and to build a stable and reliable blockchain network as a key factor to ensure the implementation of this trust framework. The trust framework of global DVCs or SVCs consortium blockchain established by the WHO aims to provide a consensus mechanism at the technical level. Based on the consensus, any member country can trust that DVCs or SVCs issued by another member country are authentic and tamper-proof. Meanwhile, the WHO has developed and provided worldwide cross-chain relay services (3).
-
The first scenario is control and protection of key information. DVCs represent a basic component of vaccination tracking. Combining digital and traditional management of vaccines and vaccination and maintaining the integrity of vaccination certificates are essential to the functioning of DVCs. The control and protection of key information are mainly reflected in two application scenarios: 1) continuity of vaccination: a vaccination record is a dynamic documentation of vaccination and an important part of individual medical records that provides vaccination information to healthcare workers as part of individual health records; 2) certificate of vaccination: the certificate of vaccination is a document that records and proves individual vaccination. DVCs are typically deployed and operated on regional digital health information platforms. Centralized data in DVC systems are vulnerable to attacks. The security level of original data recorded in DVC systems can be elevated by adopting blockchain technology. This ensures that all information is accurate, valid, tamper-proof, and largely isolated from external threats (4). Meanwhile, cryptographic technologies used in blockchain can automate the safe storage and transmission of key data and reduce the cost of safety regulation and communication networks connecting organizations and institutions (5). The process of vaccination data transmission based on blockchain technology is shown in Figure 1.
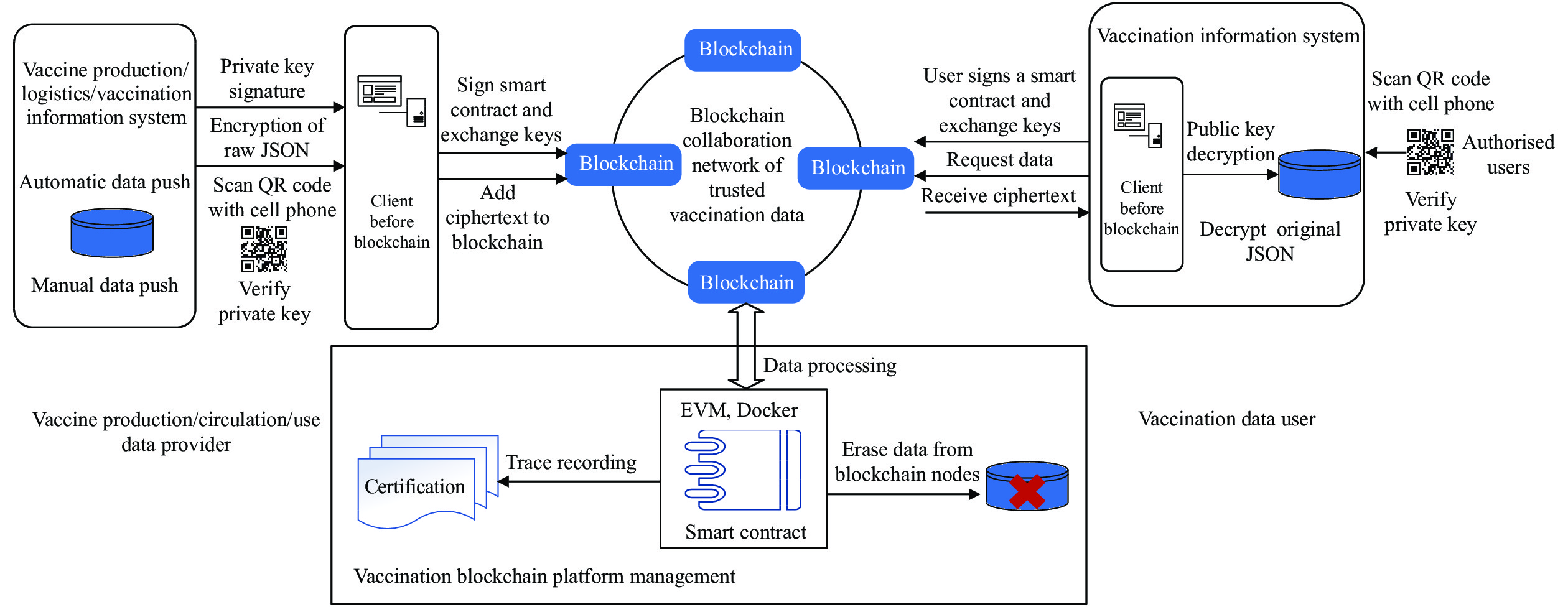 Figure 1.
Figure 1.Blockchain-based vaccination data transmission.
Abbreviations: JSON=JavaScript Object Notation; QR code=Quick Response Code; EVM=Ethereum Virtual Machine.The second scenario is collaborative recording of vaccination certificate information. Traditional vaccination certificate information is usually recorded separately (production code, cold-chain storage, cold-chain transportation, and vaccination), then uploaded to different information management systems. Information on vaccine production, circulation, and use is isolated, and management nodes control information from independent systems, making it difficult to achieve zero trust for tamper-proof information. The decentralized, distributed ledger of blockchain publicly records all key information for vaccines in a distributed ledger through encryption, which greatly increases the cost of information tampering and makes it suitable for guaranteeing the authenticity and credibility of data from the whole process of vaccine deployment. Tracking DVCs is supported by consortium blockchain technology that provides traceable and tamper-proof data storage, smart contracts that can be developed and called on demand, a non-repudiable signature mechanism based on asymmetric cryptography, and decentralized system architecture. Blockchain can provide a basis for the interaction and intelligent coordination of vaccine planning and distribution, cold-chain logistics monitoring, stock-in/stock-out management, and vaccination information recording. The principles of collaboration in trusted vaccination certificate information based on smart contracts is shown in Figure 2.
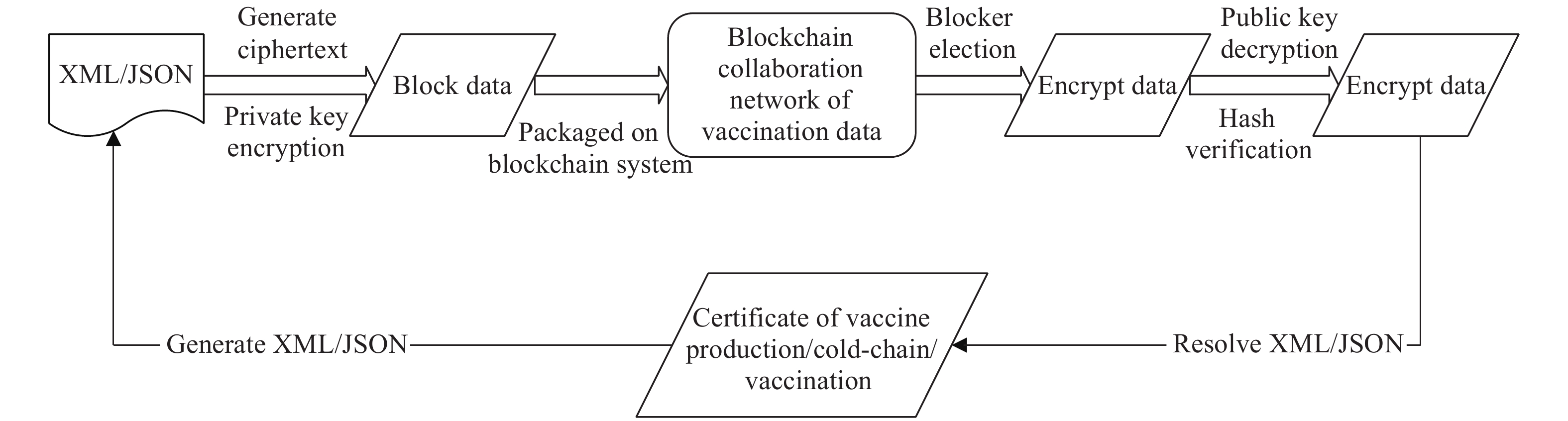 Figure 2.
Figure 2.Principles of collaboration in trusted vaccination certificate information based on smart contracts. Abbreviations: XML=EXtensible Markup Language; JSON=JavaScript Object Notation.
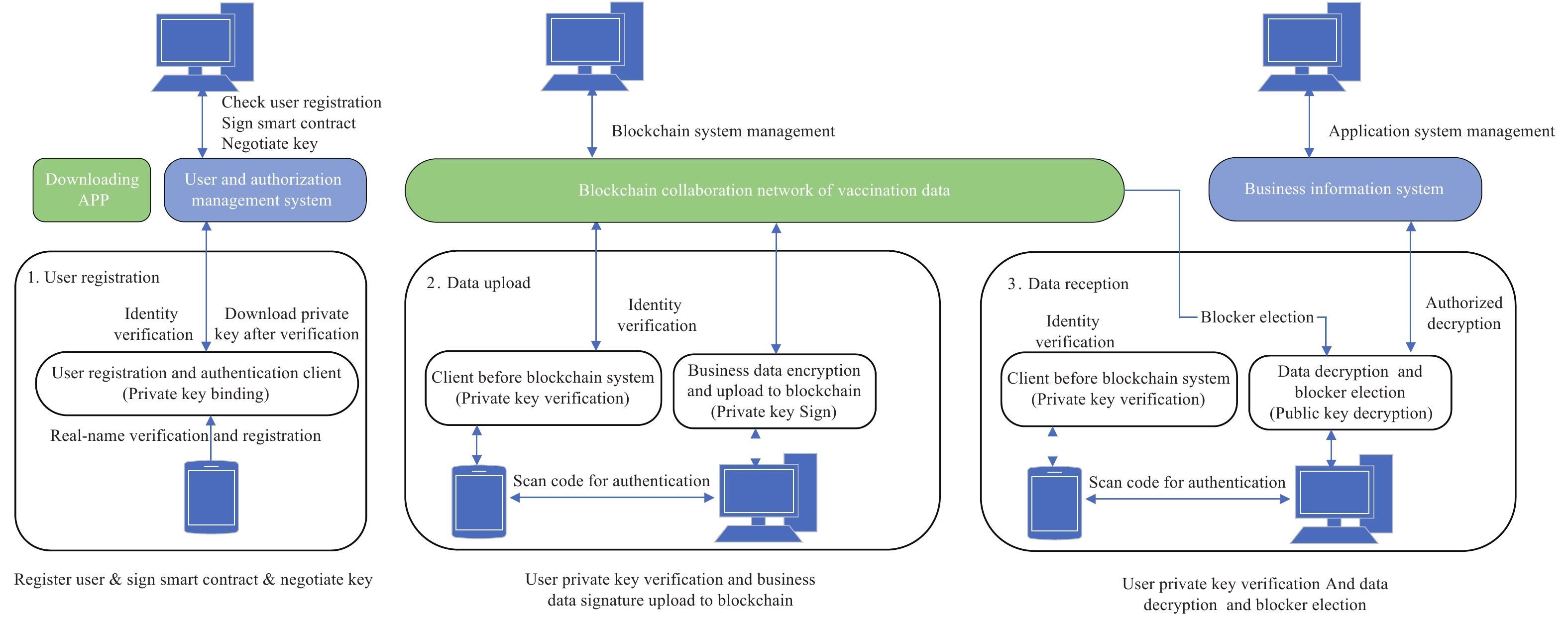
The third scenario is cross-domain user digital identity authentication. Digital identity authentication based on the smart contract of blockchain provides digital identity authentication with a private key and encryption with a public key for all participating entities (i.e., all cross-domain users involved in the collaboration or verification of the entire process of vaccination). An unclassified world wide web consortium (W3C) decentralized identifier (DID) is assigned to each participating entity (6) via blockchain-enabled self-generated identity keys, bound to public keys and other unencrypted metadata in shared documents, and kept unchanged. The key is distributed across all participating user network nodes through blockchain ledger without the use of a third-party digital certificate authority (CA), which provides a common, domain-wide root of trust for digital identity and public key encryption (PKE). All user entities have service terminal nodes on the blockchain collaboration network of trusted vaccination data. The vaccine production data, cold-chain logistics monitoring data, vaccination data and adverse events following immunization (AEFI) data are asymmetrically encrypted and added to blockchain for distribution through cross-domain client application software. In addition, encrypted documents for collaborative transactions can be accessed from blockchain via client application software. The digital identity verification process based on blockchain smart contracts is shown in Figure 3.
-
Due to the special requirement of vaccination data security, most vaccination information has different levels of protection. Therefore, information storage encryption must be strictly controlled by blockchain. To address this challenge, the peer-to-peer nature of nodes can be partly sacrificed to construct a polycentric rather than peer-to-peer blockchain, network nodes can be appropriately managed in a hierarchical manner, and the level of vaccination information protection can be matched with the level of confidentiality of information stored in the blockchain. The WHO should be driven to establish a globally trusted SVC consortium blockchain to achieve polycentric trust and consensus.
Blockchain has a distributed network structure with frequent information exchange and requires high communication bandwidth between nodes, which might not be met by traditional communication approaches. The nodes also have high demand for hardware, such as large-capacity memory and high-performance central processing units (CPUs), to ensure efficient information transfer. Balancing performance and cost requires powerful communication equipment where possible. It is possible to reduce the overall pressure on network communication by designing super nodes as communication agents for ordinary nodes and concentrating a large amount of communication traffic on a small number of links, but this will inevitably compromise the robustness of the network structure.
Large node size delays smart contract processing, reduces the overall performance of the network, and affects the efficiency of information exchange. Since collaborative vaccination information verification requires real-time information transmission, processing speed and throughput are two factors limiting the performance of blockchain. This can be addressed by using 5G network mobile process calculi, which splits a transaction into problem sets in the case of frequent out-block operations of on-chain data, and each node handles only one small fragment transaction related to its specific needs. Small fragments are assembled to larger fragments and eventually a complete transaction.
In summary, combining blockchain with DVCs has great potential for a range of applications, but defense against malicious cyberattack is a key concern. It is necessary to strengthen the development and supervision of technologies underpinning blockchain so that the performance can meet global application standards. In addition, through deep integration with other information technologies, the operation efficiency of the whole system can be improved while overcoming the shortcomings of blockchain. Implementation of WHO guidance in China requires the development and publication of unified data element standards and format standards for DVCs and SVCs as soon as possible, as well as further clarification of the public key application technical standards and open-source software development kit (SDK) based on blockchain technology, and detailed technical guidelines for implementation. Countries should be encouraged to adopt international open-source blockchain and networking technologies. The WHO should be driven to select appropriate regions or countries to set up cross-chain relay service sites, to establish globally trusted consortium blockchain processes, to unify encryption algorithms, and to establish smart contracts to add DVCs to blockchain for certification and mutual trust/consensus.
-
No conflicts of interest reported.
-
All participants of the standard “Baseline for vaccine traceability blockchain application”.
HTML
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download: