2024 Vol. 6, No. 8
Acute respiratory infections (ARIs) are a significant contributor to illness and death in children. There has been a notable rise in the occurrence of ARIs and the associated pathogens in China, which has garnered worldwide attention.
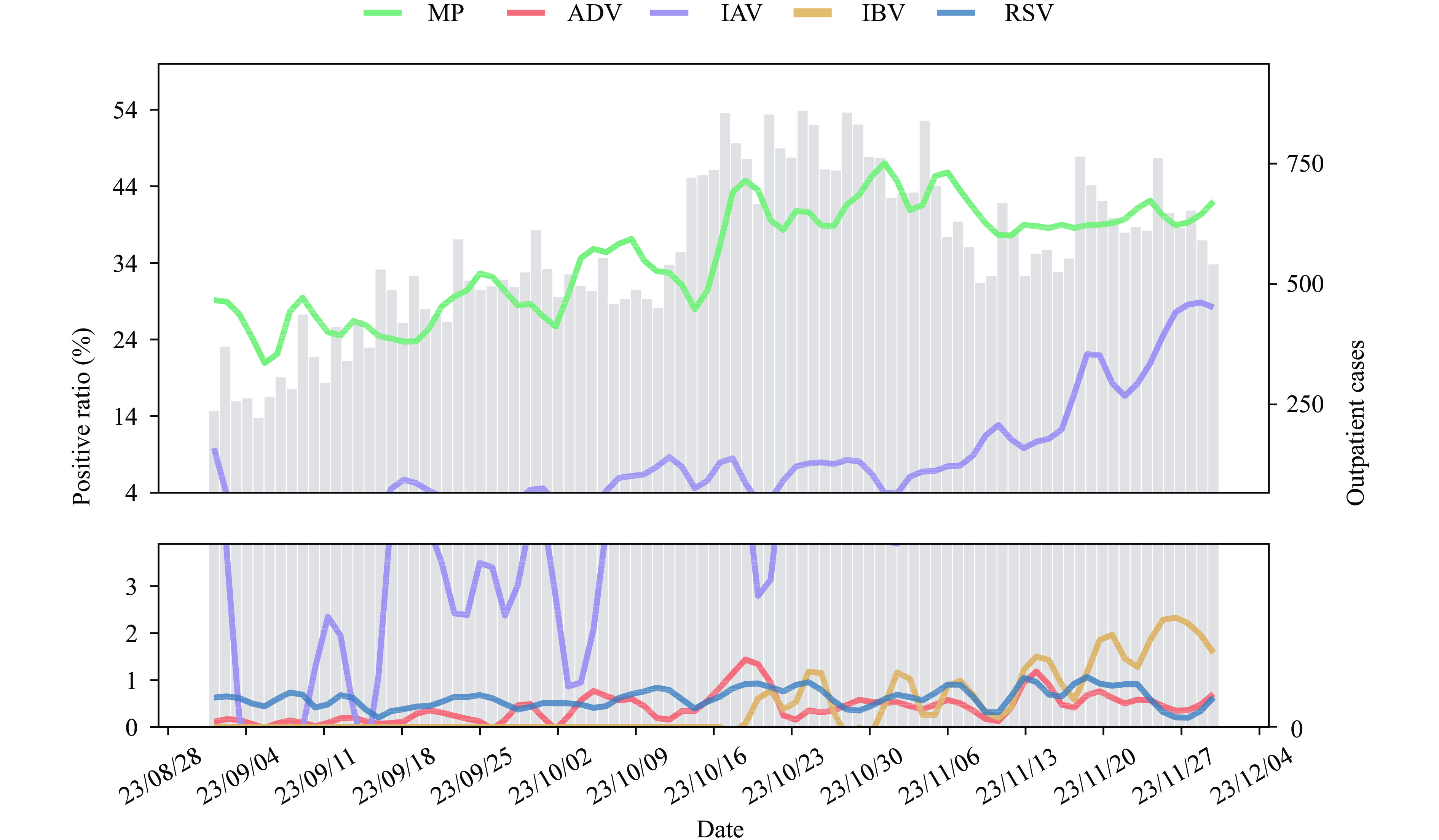
This study conducted a retrospective analysis of the clinical characteristics of children with ARIs in Wuhan City from September to November 2023. The study evaluated the epidemiological patterns of common respiratory viruses and Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP), revealing a continued prevalence of MP and a growing trend of influenza. Our findings emphasize that the circulation of respiratory viruses and MP has not returned to pre-pandemic levels, underscoring the importance of enhancing surveillance for respiratory pathogens.
The epidemiology of ARIs and the pathogens involved need to be emphasized. This highlights the importance of developing policies to protect children from respiratory pathogens such as MP, influenza, and respiratory syncytial virus.
Respiratory infections pose a significant burden on public health. Despite recent outbreaks occurring in various locations, there is limited information available on the prevalence trends of multiple common respiratory pathogens in China beyond 2022.
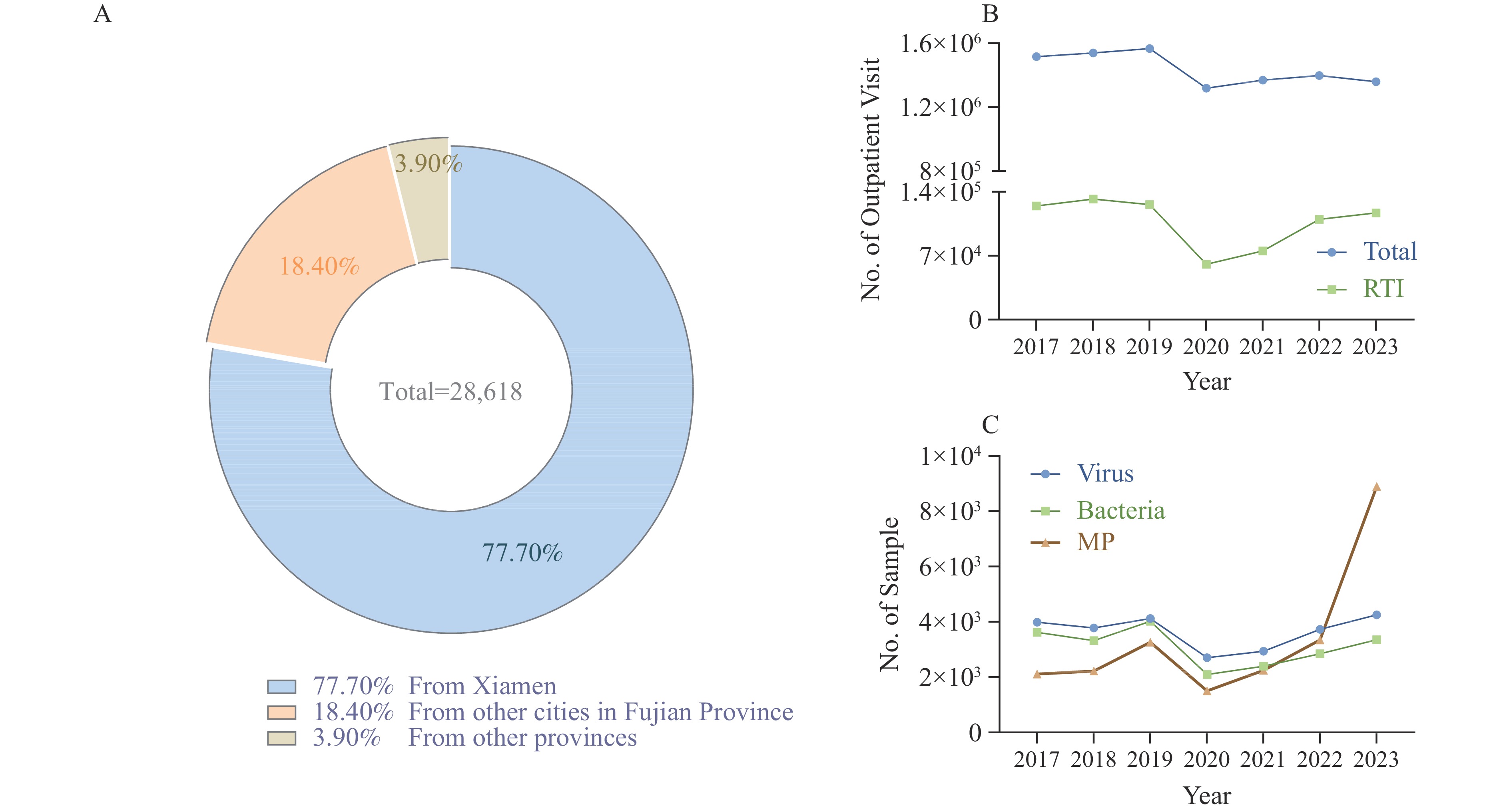
A retrospective analysis was conducted on respiratory pathogen infections in a Xiamen hospital over a seven-year period. The analysis revealed fluctuating trends, with the number of infections for certain viruses initially decreasing after 2019, only to rebound to previous or higher levels. Recently, there has been an observed collective increase in positive cases for certain pathogens.
The study improves understanding of respiratory pathogens, primarily in Xiamen, with potential implications for the improvement of strategies for the prevention and management of respiratory infectious diseases.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed