2024 Vol. 6, No. 6
Echinococcosis is classified as a Class C infectious disease in China. It is endemic in 370 counties located in the agricultural and pastoral regions of western China.
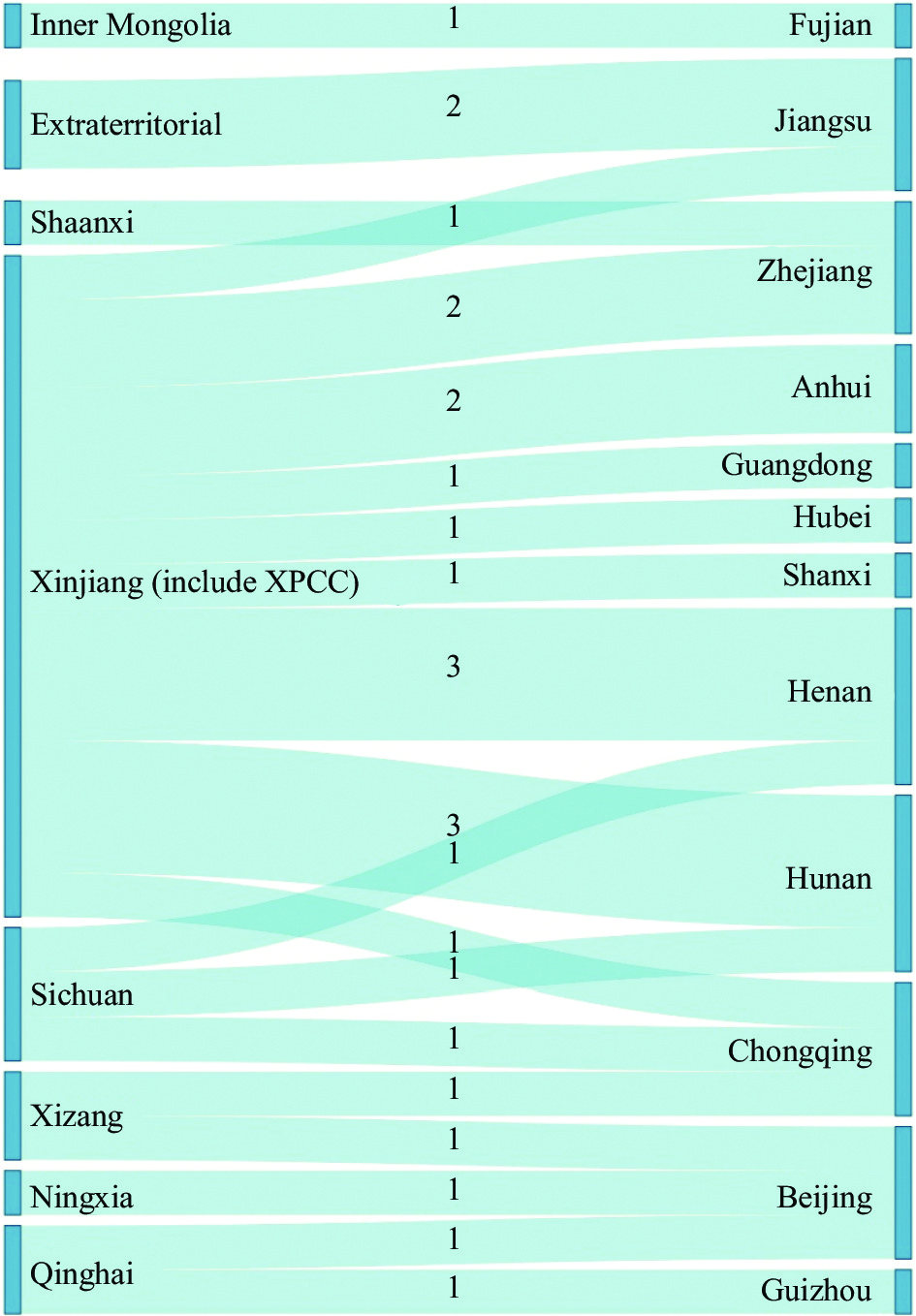
This report provides a comprehensive overview of the cases of echinococcosis reported in China in 2022. Following a thorough evaluation conducted by provincial CDCs, it was identified that 105 new cases were not reported through the National Notifiable Disease Reporting System. Furthermore, there were 1,051 cases that were reported among patients who had been previously diagnosed with echinococcosis.
The reported cases of echinococcosis in non-endemic counties of provincial-level administrative divisions where the disease is endemic need to be given more attention, as there is a potential risk of it spreading within the non-endemic areas. Inadequate reporting practices by clinical medical institutions are hindering the subsequent investigations carried out by CDCs. It is important to implement enhanced health promotion efforts that focus on high-risk populations to address unhealthy lifestyles.
Anopheles sinensis (An. sinensis) is the predominant malaria vector in China. The impact of S-methoprene on the emergence process of mosquito larvae suggests its potential as a control method for vector mosquitoes. However, the efficacy of S-methoprene in controlling An. sinensis has not yet been demonstrated.
The effectiveness of S-methoprene against An. sinensis was assessed in laboratory and semi-field conditions in Yunnan Province.
These results offer valuable options and guidance for utilizing S-methoprene products in malaria reimportation prevention areas within Yunnan Province.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed