2024 Vol. 6, No. 3
Approximately 80% of newly diagnosed human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) cases among individuals aged 15–24 years in China are attributed to out-of-school youth.
This study presents findings on HIV prevalence and comprehensive insights into HIV service utilization, risky behaviors, and prevention knowledge among young out-of-school men who have sex with men (MSM) aged 16–24 years in China. This population exhibits a disproportionately high burden of HIV, with only 51.6% of HIV cases previously diagnosed.
HIV services should be expanded to include these key populations. Tailored interventions are needed to remove barriers to regular HIV services faced by young key populations.
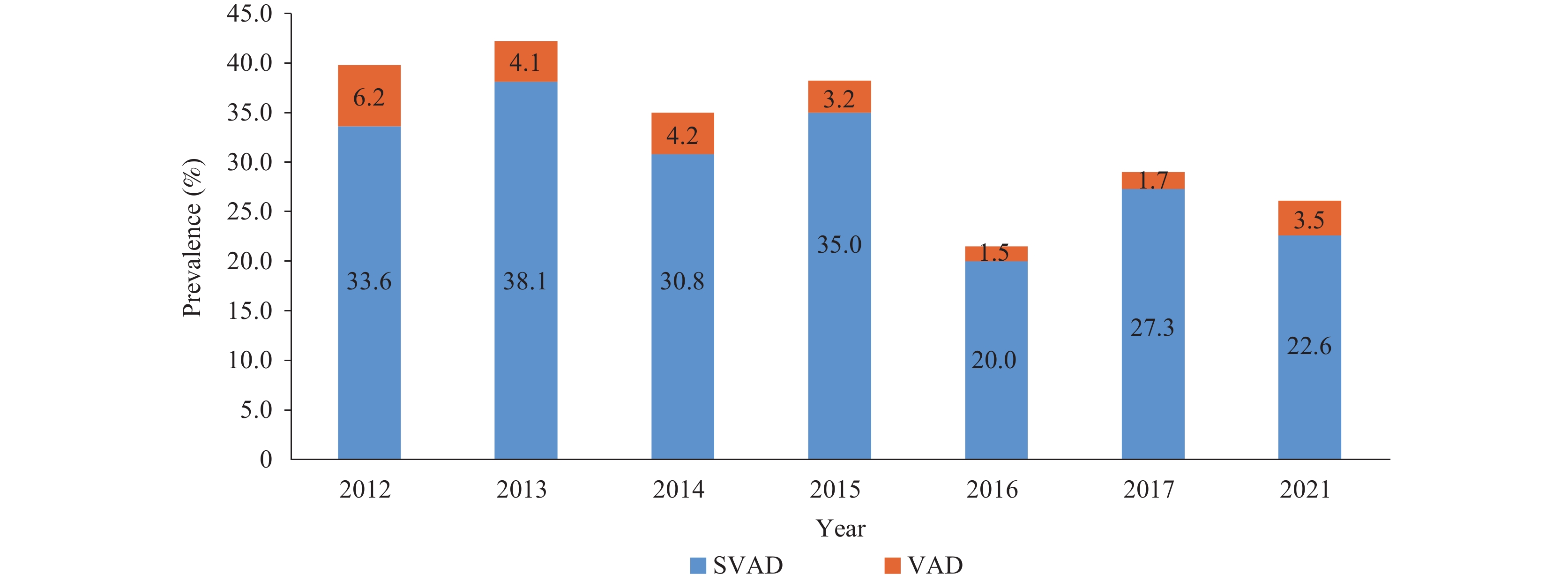
Vitamin A deficiency (VAD) is a leading global nutritional concern, ranking among the top four major nutritional deficiencies worldwide. The prevalence of VAD is unevenly distributed across various regions, both within China and globally.
The report adds valuable insights into the vitamin A nutritional status of rural students aged 6–17 years who participated in the Nutrition Improvement Programme for Rural Compulsory Education Students (NIPRCES). Over the decade from 2012 to 2021, there was a modest improvement in vitamin A status. The prevalence of VAD and sub-clinical VAD (SVAD) declined as the students aged. Throughout the majority of the survey years, the incidence of VAD was higher among males and western regions compared to females and central regions, respectively.
A comprehensive approach, incorporating dietary diversification, nutrition education, and food fortification, should be implemented to prevent VAD and SVAD especially in males, younger children and children in western areas.
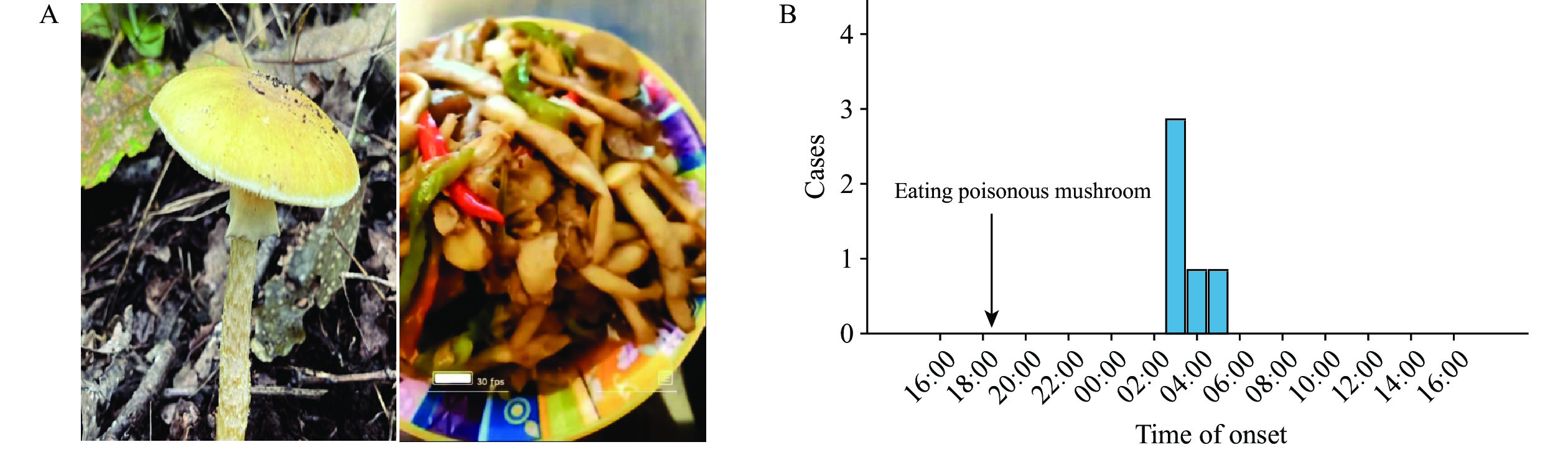
Fatal poisonings caused by wild mushrooms containing amanita toxins pose a significant threat in the southern regions of China. These toxins primarily induce gastrointestinal symptoms initially, which are then followed by potentially life-threatening acute liver damage.
This report contributes to the existing knowledge on these cases of poisoning by documenting the second occurrences in Hebei Province and the first occurrences in Xingtai City. Five individuals reported consuming wild mushrooms from the same origin, and laboratory tests confirmed the presence of α-amanitin in their blood samples.
This underscores the risk associated with the collection and consumption of amanita toxin-containing mushrooms in Hebei. It is important to note that the identification of toxic and non-toxic mushrooms should not solely rely on personal experience or appearance.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed