2024 Vol. 6, No. 2
Endemic fluorosis, caused by high fluoride levels in drinking water, has been a significant health issue in rural areas of China for many decades.
There has been a notable decline in the detection rate of dental fluorosis in children aged 8–12 years in drinking water fluorosis areas across the country from 2009 to 2022. While 14 provincial-level administrative divisions are classified as low-probability clusters, Tianjin remains classified as a high-probability cluster.
The current policy for preventing and controlling endemic fluorosis in China needs adjustment. Rather than focusing solely on regions with high incidence, there should be a shift towards monitoring and early warning of fluoride exposure. Additionally, local containment measures should be intensified.
Studies have extensively documented the separate and independent effects of extreme temperature and ozone on morbidity and mortality associated with respiratory and circulatory diseases.
The study revealed a significant association between elevated temperature, ozone pollution, and the combined effect of high temperature and ozone pollution with an increased risk of all-cause medical emergency calls (MECs) and MECs specifically related to neurological diseases.
Interventional measures should be implemented to mitigate exposure to high temperatures and ozone levels. Specifically, during the warm season, it is crucial for relevant authorities to focus on disseminating scientific information regarding the health impacts of elevated temperatures and ozone pollution. Additionally, timely public health advisories should be issued to alert the public effectively.
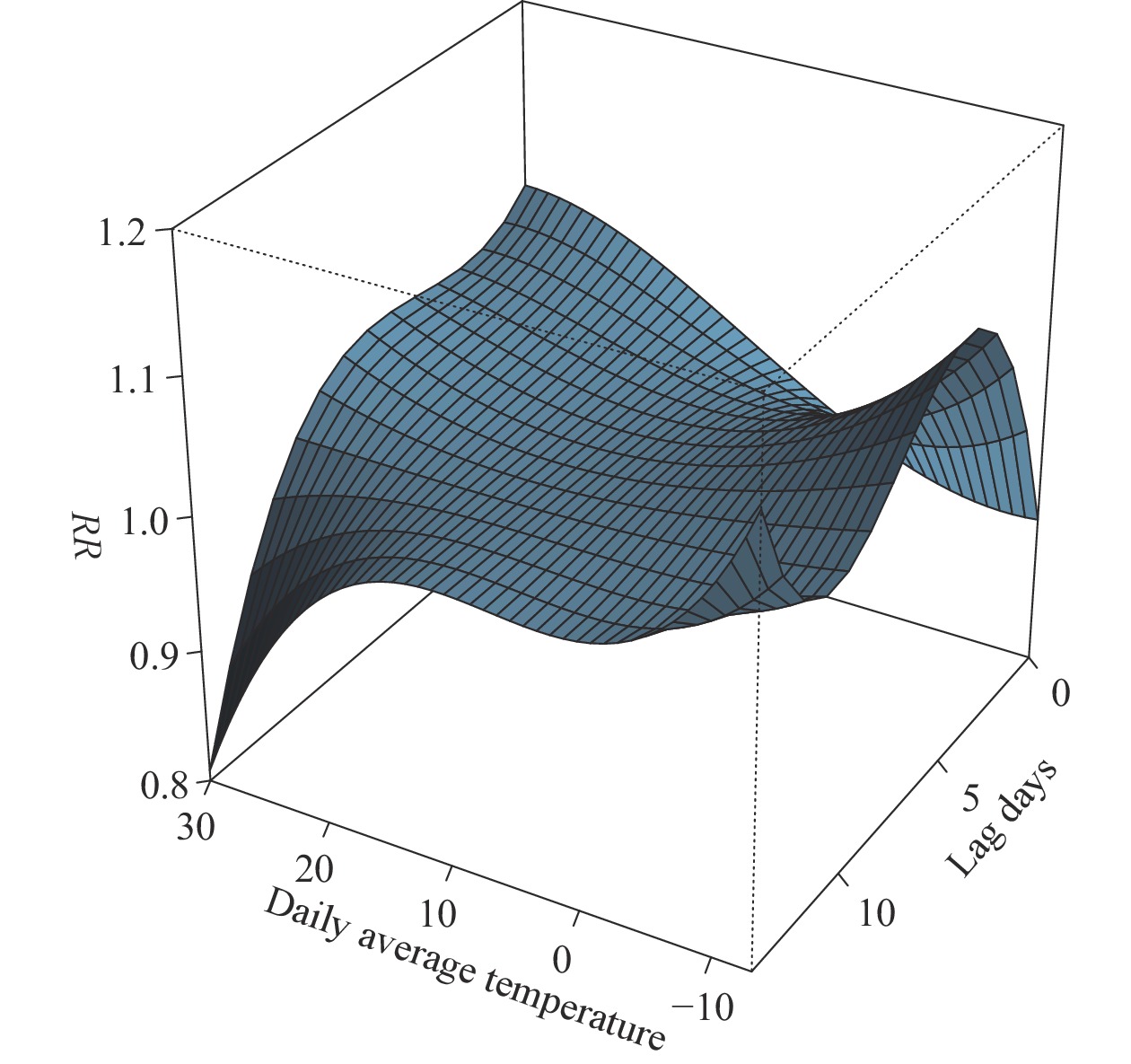
The impact of air temperature on varicella has been studied, but there is limited research exploring its effect on varicella by gender and age group.
We conducted a time series analysis to examine the differential effects of air temperature on varicella infection across different demographic groups. Our findings indicate that lower temperatures have a more pronounced influence on varicella incidence among males and children compared to females and adults.
These findings can assist in identifying populations that are vulnerable to temperature-related varicella and in guiding the implementation of effective measures for varicella control.
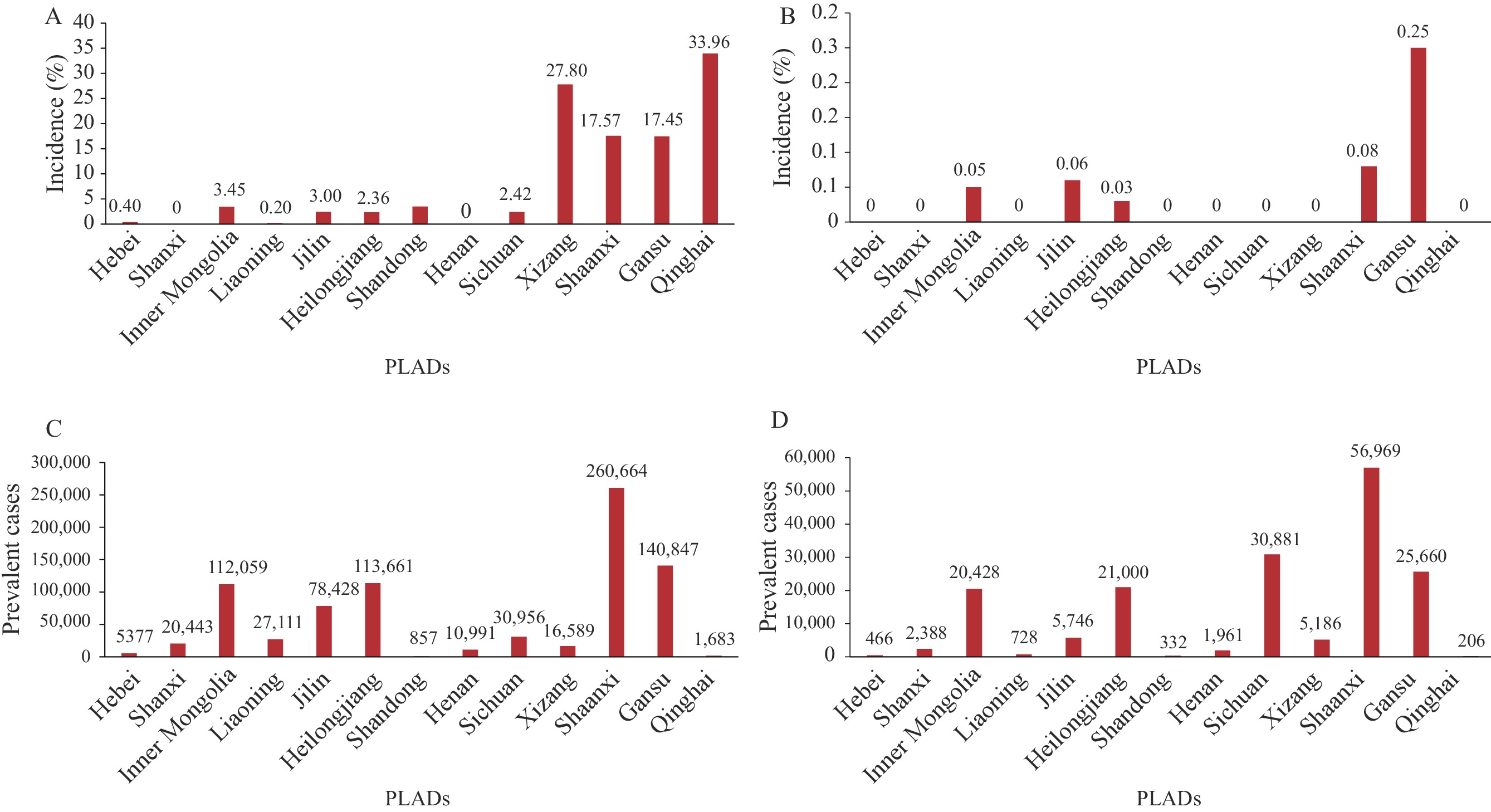
Kashin-Beck disease (KBD) is a chronic and degenerative osteoarthropathy characterized by cartilage degeneration. It is an endemic disease that is highly prevalent among the Chinese population and poses a significant health risk.
This is the first national report on the economic burden of KBD in China. According to the data from 2021, KBD has caused significant disease and economic burdens. The most substantial reduction in healthy life expectancy was observed among patients with degree II severity and those aged 60 years and older, resulting in a total indirect economic burden of 112.74 million Chinese Yuan (CNY).
The results of this study will contribute to informing the development of tailored prevention and control strategies by the government. These strategies will include targeted policies and recommendations for appropriate healthcare and financial subsidies, which will be based on the demographic characteristics of the endemic areas.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed