2024 Vol. 6, No. 14
The mortality rate and disease burden associated with falls among the elderly in China are on the rise. Interventions can play a crucial role in preventing and managing falls.
The application of the “5E” injury prevention strategy led to a decrease in both the occurrence of falls and the likelihood of subsequent falls. Regular physical activity and maintaining a positive outlook were identified as protective measures against falls, while sleep issues and hearing impairment were found to increase the risk of falling.
The group-based comprehensive intervention strategy is crucial as it offers an innovative intervention model and empirical evidence for decreasing fall rates among elderly individuals living in rural areas.
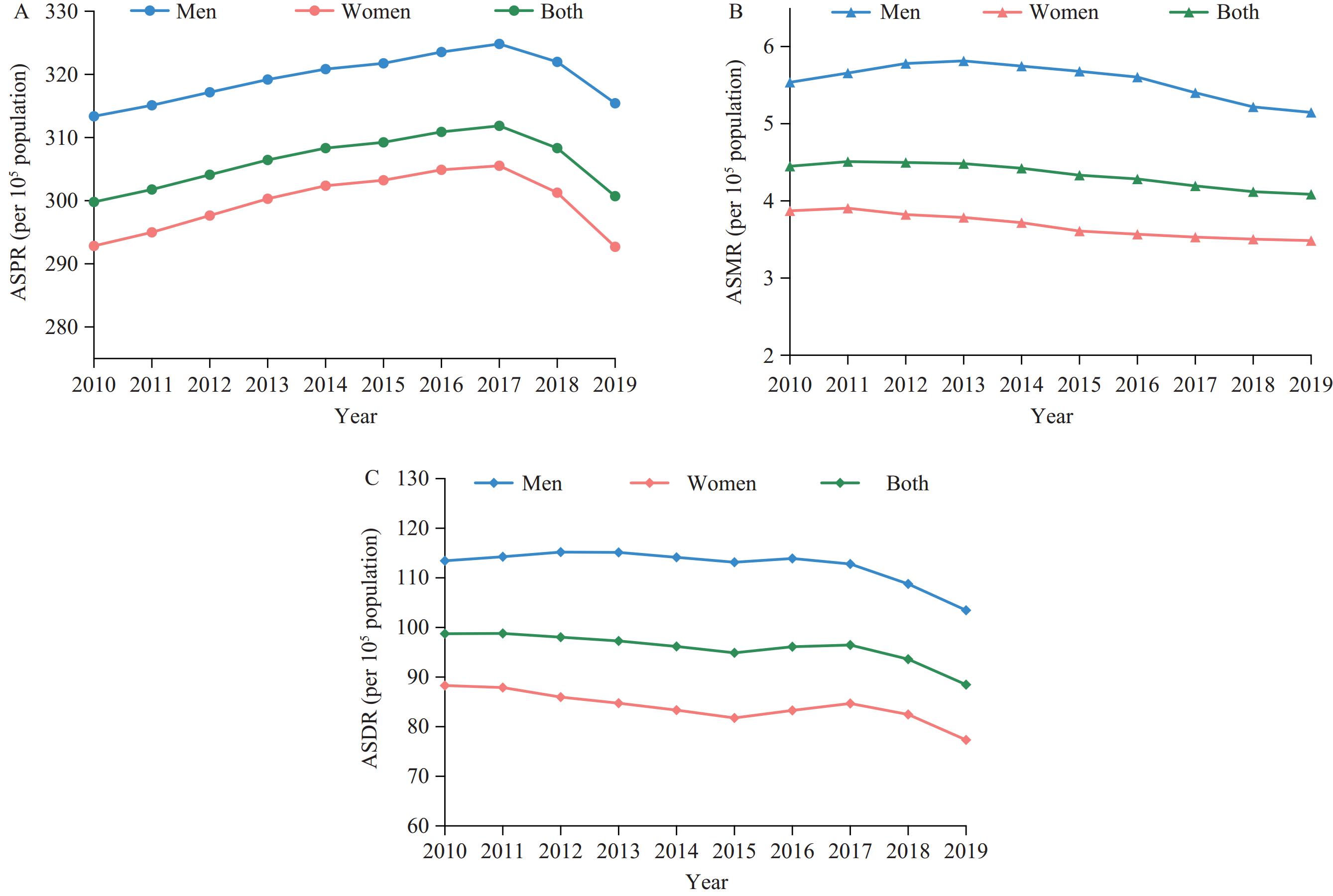
The global burden of chronic kidney disease (CKD) is on the rise.
In 2019, 5.58 million individuals in China were affected by CKD related to hypertension, leading to 70,260 fatalities and 1.69 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). The most affected groups were men, older individuals, and residents of western China. Over the period from 2010–2019, the age-standardized prevalence rate (ASPR) remained constant, and the age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) and age-standardized DALY rate (ASDR) showed a decreasing trend. However, there was an increase in the number of cases, deaths, and DALYs associated with this condition.
Hypertension significantly contributes to the burden of CKD; therefore, raising awareness and implementing early screening measures are essential.
To protect the health of young people from the harmful impacts of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes), China has enacted various policies and regulations since 2018. As of October 1, 2022, the Electronic Cigarette Management Measures were put into action. They prohibited the sale of flavored e-cigarettes, permitting only those of plain tobacco flavor to be sold.
The illegal market for flavored e-cigarettes, often disguised as milk tea cups, cola cans, and violent bear images, continues to flourish. There is an increased need to bolster support for the prohibition of flavored e-cigarettes and enhance public awareness of associated regulations.
To advance the health of China’s youth, it is crucial to improve the implementation and understanding of e-cigarette policies and guidelines.
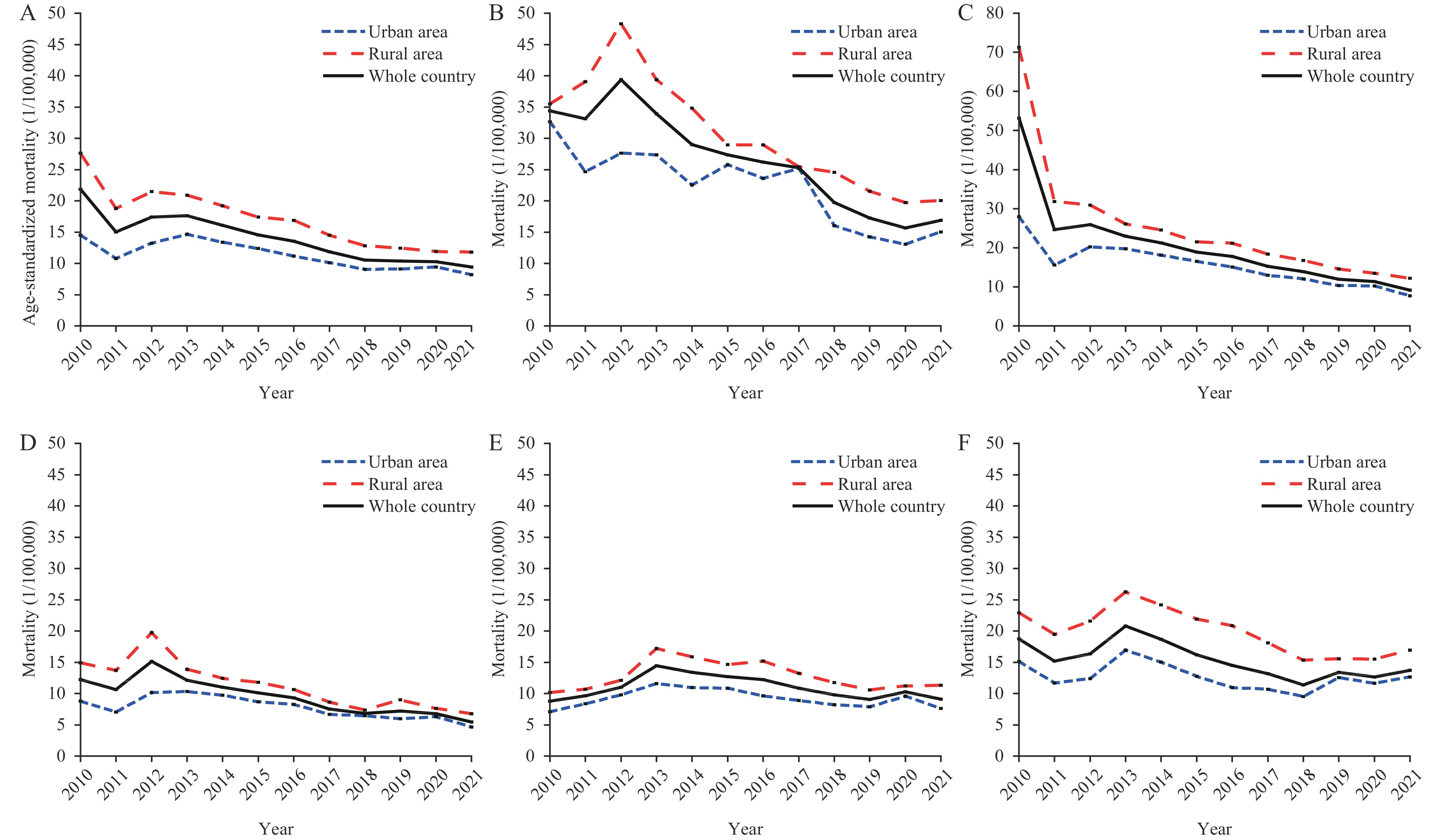
To examine the recent trends in child injury mortality in China.
Injury mortality data of 2010–2021 for children and adolescents aged 0–19 years were from the China Health Statistics Yearbook. Injury mortality disparities across urban vs. rural locations, gender, and age groups were scrutinized. Annual percent change (APC), average annual percent change (AAPC), and their 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were estiamted usimg Joinpoint regression models.
The age-standardized injury mortality significantly dropped from 21.87 to 9.41 per 100,000 population among children and youth aged 0–19 years during 2010–2021, with an AAPC of −6.7% (95% CI: −8.2%, −5.2%). The urban-rural disparity and gender gap in injury mortality reduced gradually. In 2021, drowning and road traffic crashes were the top two causes of child injury deaths, explaing 31.1% and 27.9% of total injury deaths, respectively. Suffocation accounted for 62.3% of injury deaths among infants younger than a year. Alarmingly, the suicide mortality rate rose from 2.16 to 3.42 per 100,000 population between 2010 and 2021 among teenagers aged 15–19 years. Subgroup analyses yielded similar results.
During 2010–2021, the injury mortality decreased significantly among Chinese children and adolescents, and the responding urban-rural disparities narrowed.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed