2024 Vol. 6, No. 12
Given the challenges presented by drug-resistant strains of tuberculosis (TB) and the rising mobility of the population, achieving the objective of eradicating TB appears uncertain.
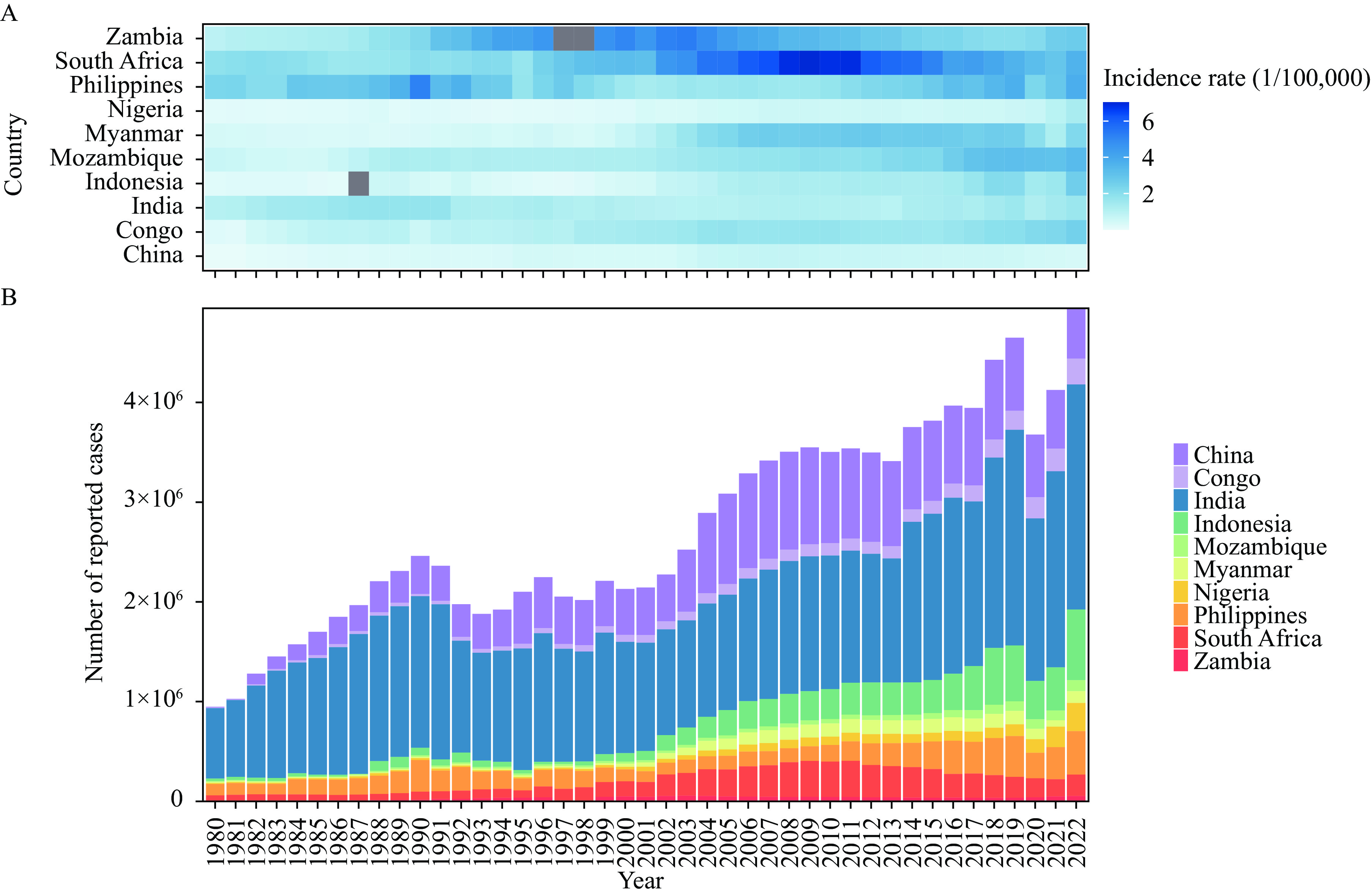
The examination of TB incidence trends in 10 high-burden countries (HBCs) indicated a steady rise in cases, with India and China jointly accounting for nearly 70% of the burden. Projections for the future show diverse trajectories in these countries, with potential difficulties in reaching the TB elimination target, especially in Nigeria, Congo, and South Africa.
The number of TB cases is on the rise. It is crucial to learn from successful strategies to improve TB prevention and control worldwide through collaborative efforts.
Brucellosis, mainly caused by Brucella melitensis (B. melitensis), is regarded as a significant zoonotic disease in China. In Weihai, located at the eastern end of the Shandong Peninsula, brucellosis has been in a low epidemic phase for the past five years.
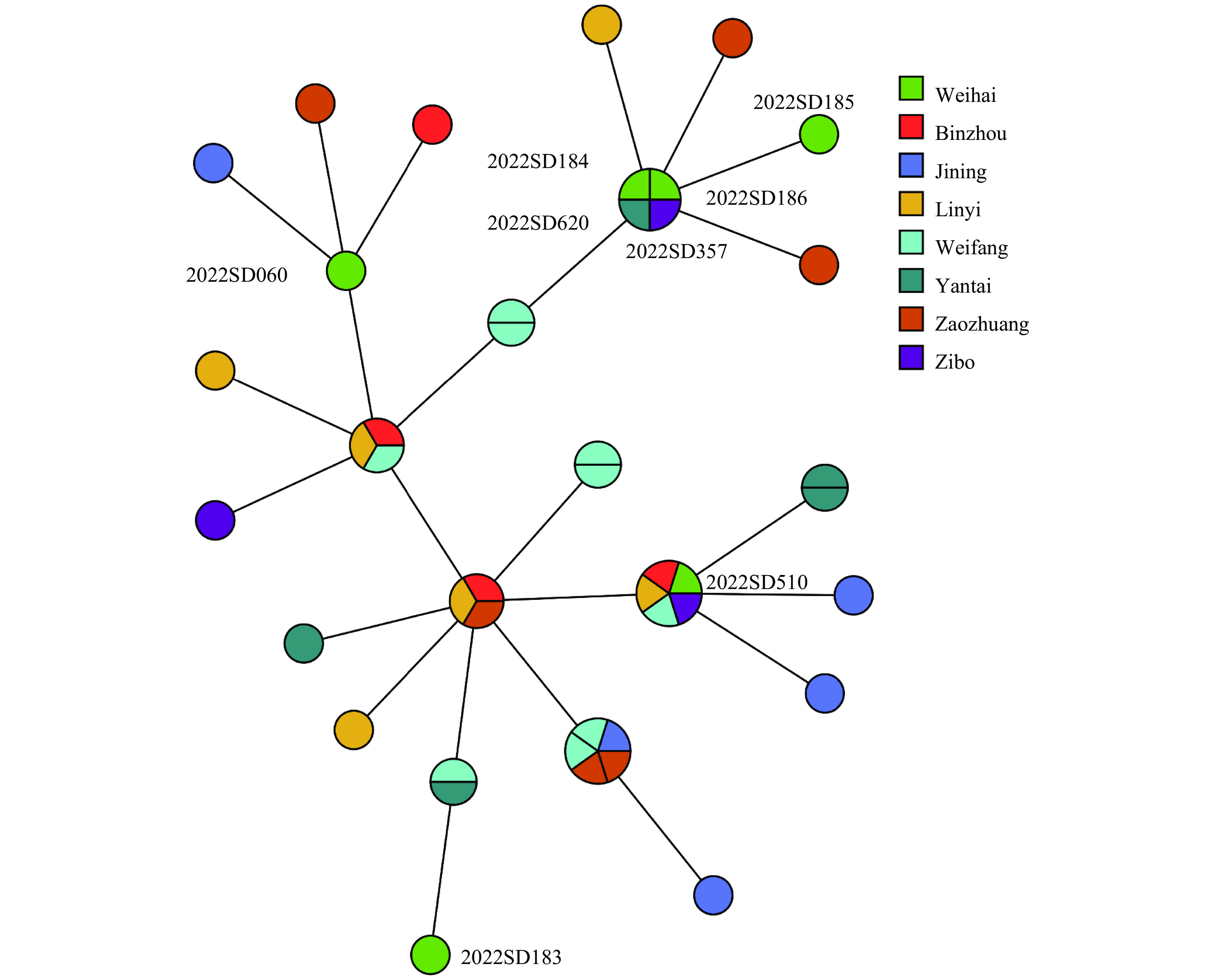
This was the initial report of a brucellosis outbreak in the last five years. Strains of B. melitensis bv. 3 from Weihai and other cities showed a close genetic relationship, suggesting a potential common ancestry.
Epidemiological investigations depend on standardized and effective molecular typing methods and analysis tools for public health laboratories to identify and trace outbreaks. Understanding the circulation patterns of livestock in free-range households in heavily affected areas is essential for controlling the spread of brucellosis.
A retrospective study based on sentinel surveillance was conducted in 10 provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) in China to enhance the understanding of the epidemiological characteristics of human parainfluenza viruses (HPIVs).
From January 2019 to June 2023, respiratory specimens were collected from individuals with acute respiratory infections (ARIs) and screened for four HPIVs serotypes and other common respiratory viruses using multiplex real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). This study analyzed the association of HPIVs infections with seasonal patterns, geographical distribution, demographic profiles, clinical features, and co-infection status.
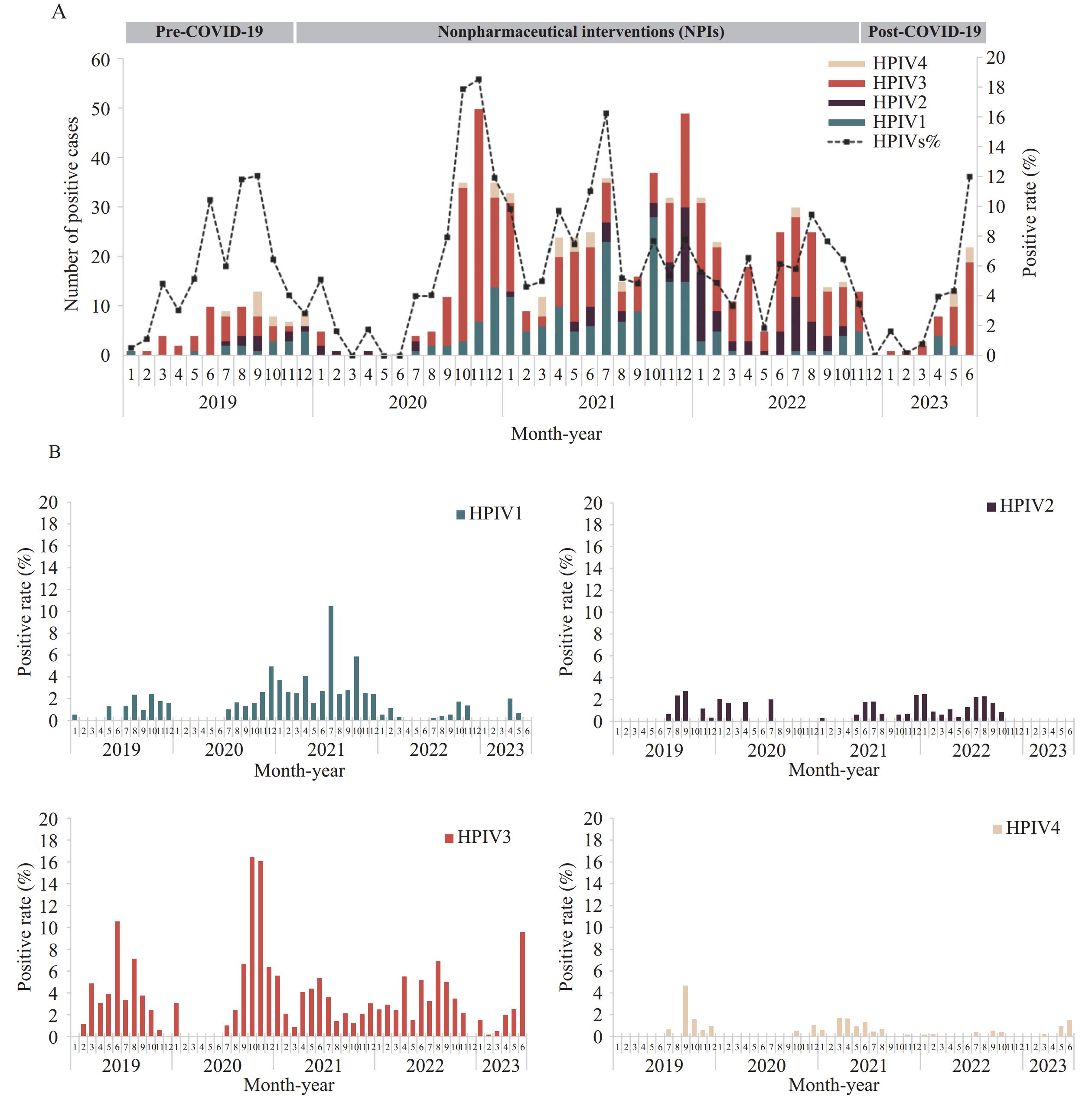
During the study period, a total of 12,866 ARIs were included. The overall detection rate of HPIVs was 6.15%, varying from 5.04% in 2022 to 9.70% in 2020. The median age of HPIVs-infected patients was 3 years. HPIV2 was more prevalent among individuals aged 5–17 years (42.57%), while HPIV4 was more common in those over 65 years (12.24%). HPIV3 (54.16%) and HPIV1 (27.18%) were the predominant serotypes, and their prevalence exhibited significant seasonal fluctuations post- coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. The peak of HPIV3 shifted three months later in 2020 compared to 2019 and returned to a summer peak thereafter. Two peaks of HPIV1 were observed in 2021 following the peak of HPIV3. Additionally, co-infections were frequent in HPIVs cases (overall rate: 22.12%), with human rhinovirus being the most common co-infecting virus.
The prevalence of HPIVs in China was predominantly due to HPIV3 and HPIV1, and their seasonal patterns were altered by pandemic restrictions. Hence, continuous surveillance of HPIVs is essential.
The inclusion of meningococcal vaccines in the National Immunization Program (NIP) over several years has significantly reduced the incidence of meningococcal meningitis in China to historic lows. Worldwide, there has been a diversification of meningococcal serogroups, leading to a shift in dominant serogroups in China from serogroup A to serogroups C and B, accompanied by a rise in reports of serogroups Y and W.
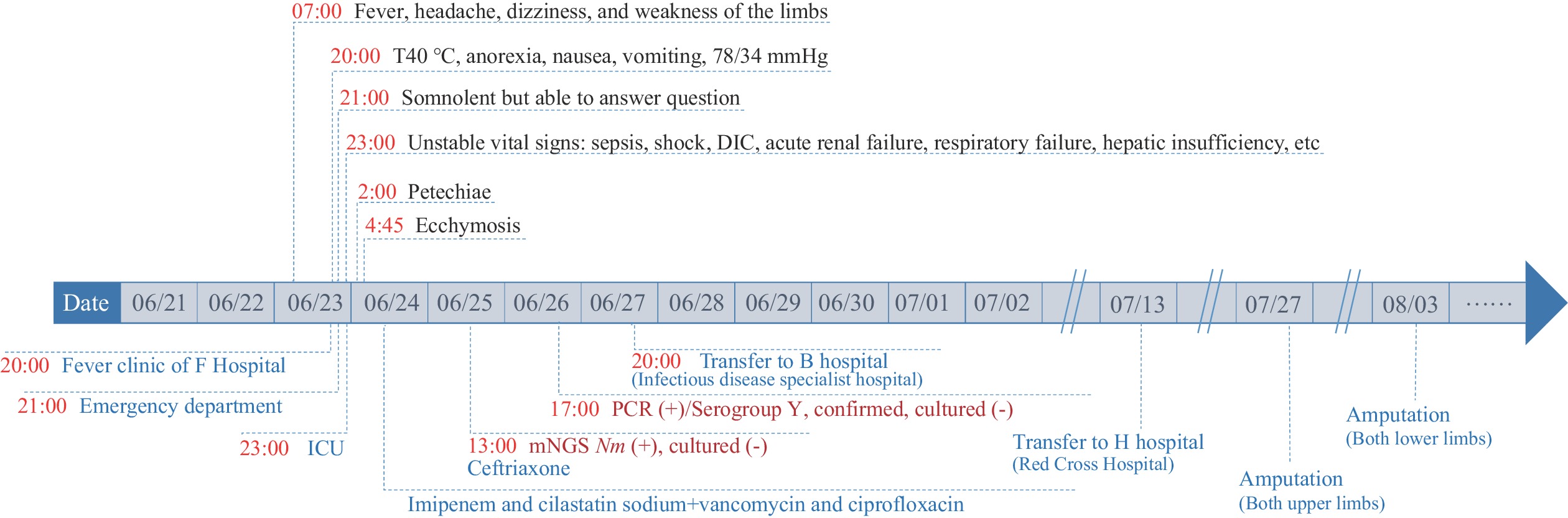
An outbreak of serogroup Y Neisseria meningitidis (Nm) in a secondary vocational school involved a single confirmed severe case and 24 individuals with laboratory-confirmed Nm carriage. Epidemiological investigation revealed that the outbreak was localized to the classroom of the confirmed case. Prolonged close contact within a confined space was identified as a significant risk factor for Nm transmission. The genotype sequence identified was type 1655 (ST-1655), which is categorized under clonal complex 23 (CC-23) and bears resemblance to 8 previously confirmed cases of serogroup Y meningococcal meningitis within Guangdong Province. This suggests that serogroup Y infections continue to sporadically emerge and have become prevalent strains.
This outbreak underscores the critical need to enhance surveillance of meningococcal serogroups and population carrier, and advocate for vaccination with MenY-containing vaccines.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed