2024 Vol. 6, No. 11
There is mounting evidence indicating that the aging process initiates during early life stages, with in utero the individual’s environment playing a significant role. Consequently, it is crucial to comprehend the enduring effects of early life circumstances on health in old age.
In this study, we conducted a meta-analysis to examine the effects of the Chinese Famine (1959–1961) on the health of older adults. We also explored potential mechanisms underlying these effects.
The complex interplay between early life circumstances, multiple health-related sectors, and healthy aging necessitates a comprehensive life-course approach and strategic interventions to enhance public health in an aging society.
Addressing health disparities is a worldwide priority, with a well-established acknowledgment of the influence of childhood circumstances on these discrepancies. In China, particularly among the elderly, health inequalities are a notable concern.
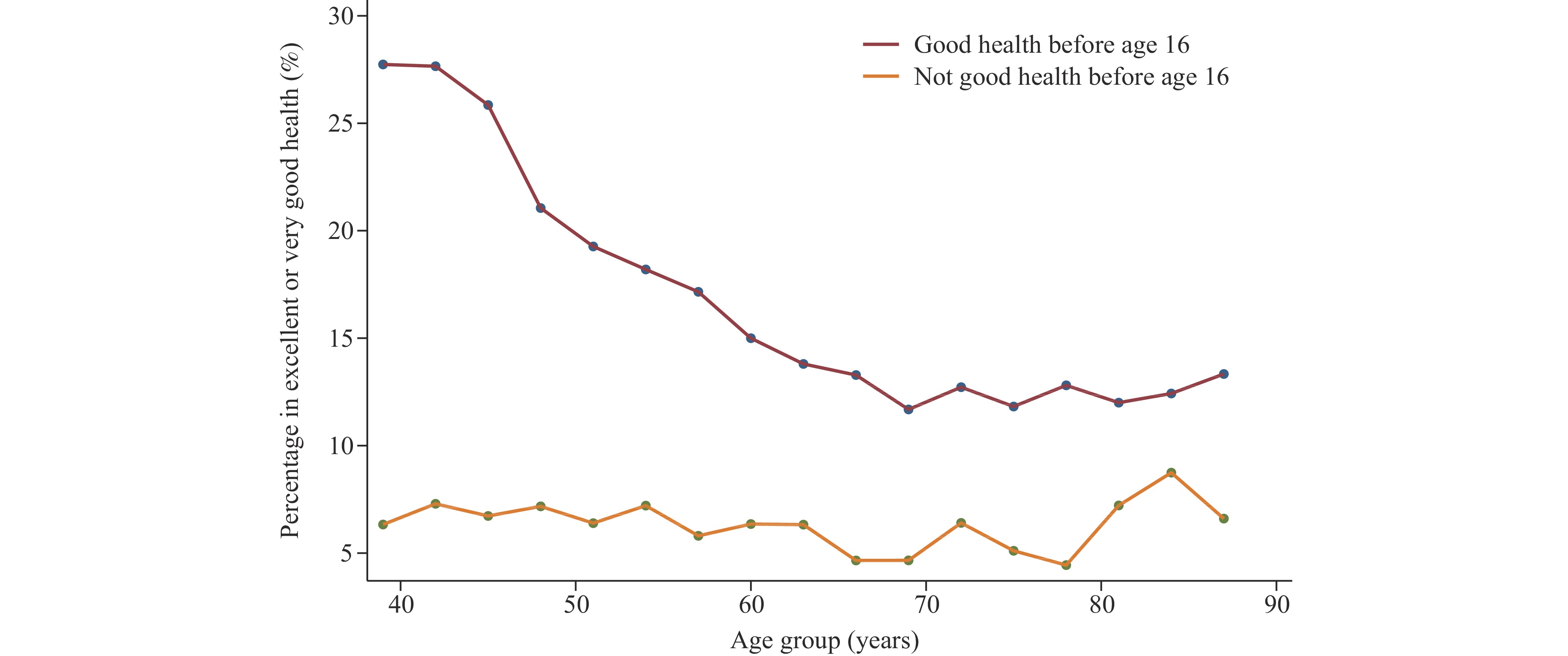
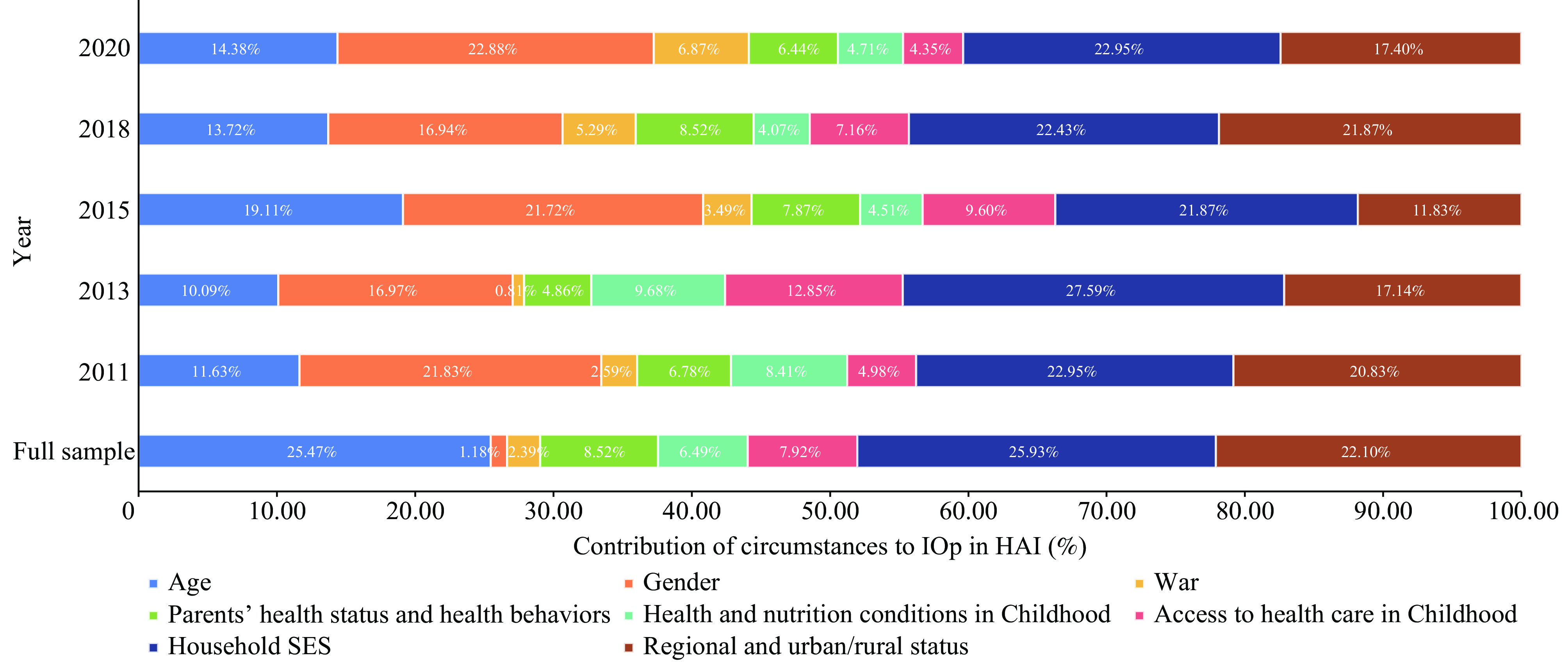
The inequality in healthy aging has increased from 2011 to 2020, both in general and concerning childhood factors. Nevertheless, the impact of early-life healthcare access and parental health behaviors on healthy aging gaps has reduced among older adults in better health within the top segment of healthy aging.
Efforts towards reducing regional health disparities and improving healthcare access for children, along with promoting the health and well-being of parents, especially in economically disadvantaged households, are crucial policy considerations.
Childhood circumstances impact senior health, prompting the introduction of machine learning methods to assess their individual and collective contributions to senior health.
Using health and retirement study (HRS) and China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS), we analyzed 2,434 American and 5,612 Chinese participants aged 60 and above. Conditional inference trees and forests were employed to estimate the influence of childhood circumstances on self-rated health (SRH).
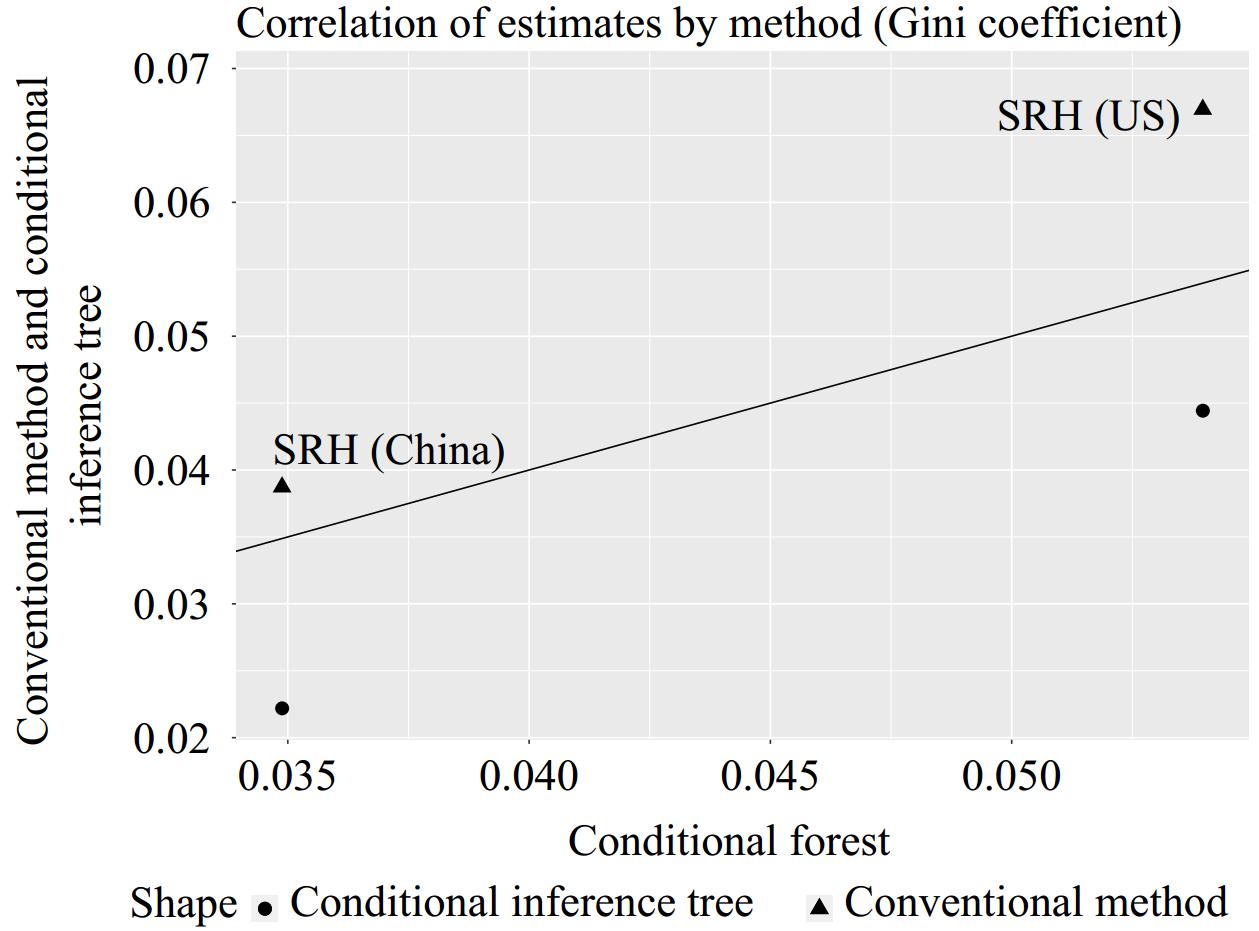
The conventional method estimated higher inequality of opportunity (IOP) values in both China (0.039, accounting for 22.67% of the total Gini coefficient 0.172) and the US (0.067, accounting for 35.08% of the total Gini coefficient 0.191). In contrast, the conditional inference tree yielded lower estimates (China: 0.022, accounting for 12.79% of 0.172; US: 0.044, accounting for 23.04% of 0.191), as did the forest (China: 0.035, accounting for 20.35% of 0.172; US: 0.054, accounting for 28.27% of 0.191). Childhood health, financial status, and regional differences were key determinants of senior health. The conditional inference forest consistently outperformed others in predictive accuracy, as demonstrated by lower out-of-sample mean squared error (MSE).
The findings emphasize the need for early-life interventions to promote health equity in aging populations. Machine learning showcases the potential in identifying contributing factors.
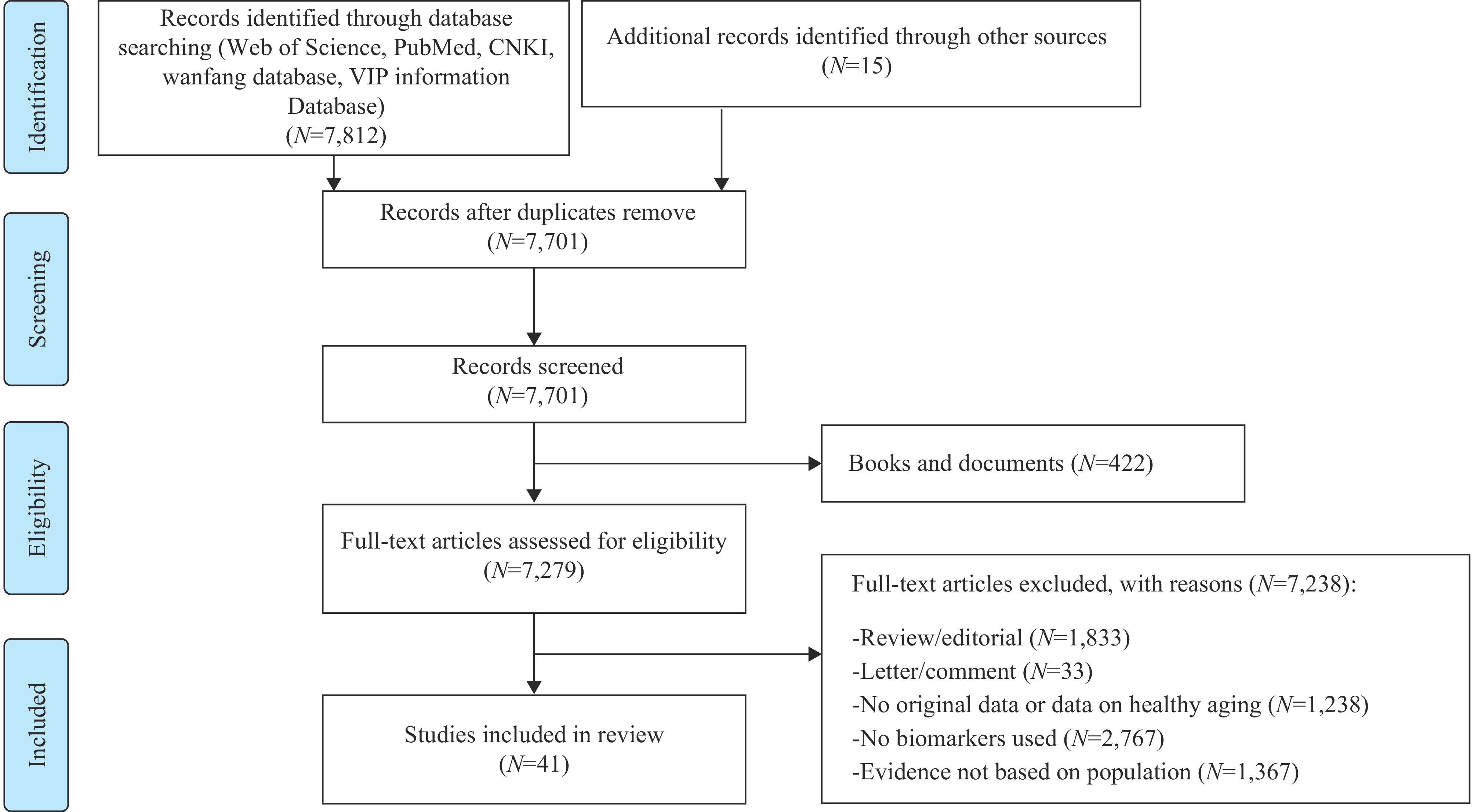
Assessing individual risks of healthy aging using biomarkers and identifying associated factors have become important areas of research. In this study, we conducted a literature review of relevant publications between 2018 and 2023 in both Chinese and English databases. Previous studies have predominantly used single biomarkers, such as C-reactive protein, or focused on specific life course stages and factors such as socioeconomic status, mental health, educational levels, and unhealthy lifestyles. By summarizing the progress in this field, our study provides valuable insights and future directions for promoting healthy aging from a life course perspective.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed