2023 Vol. 5, No. 52
Bacterial resistance surveillance is crucial for monitoring and understanding the trends and spread of drug-resistant bacteria.
The number of strains collected in 2022 increased compared to 2021. The top five bacteria, including Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter baumannii, remained largely unchanged. The detection rate of methicillin-resistant strains continued to decrease. Among clinical Enterobacterales isolates, the resistance rate to carbapenems was generally below 13%, except for Klebsiella spp., which had a resistance range of 20.4% to 21.9%. Most clinical Enterobacterales isolates were highly susceptible to tigecycline, colistin, and polymyxin B, with resistance rates ranging from 0.1% to 12.6%. The detection rate of meropenem-resistant P. aeruginosa and meropenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii showed a decreasing trend for the fourth consecutive year.
Multidrug-resistant bacteria remain a significant public health challenge in clinical antimicrobial treatment. To effectively address bacterial resistance, it is essential to enhance both bacterial resistance surveillance and the prudent use of antimicrobial agents.
Varicella outbreaks significantly disrupt schools and other child-centered institutions. This study aimed to identify patterns and epidemiological features of varicella outbreaks in China from 2006 to 2022.
Data were extracted from outbreak reports submitted to the Public Health Emergency Reporting Management Information System within the specified timeframe. Analytical methods included Spearman correlation tests and the Mann-Kendall trend tests, conducted using R software to analyze and summarize reported data. Additionally, statistical analyses of trends and epidemiological characteristics were performed using SPSS software.
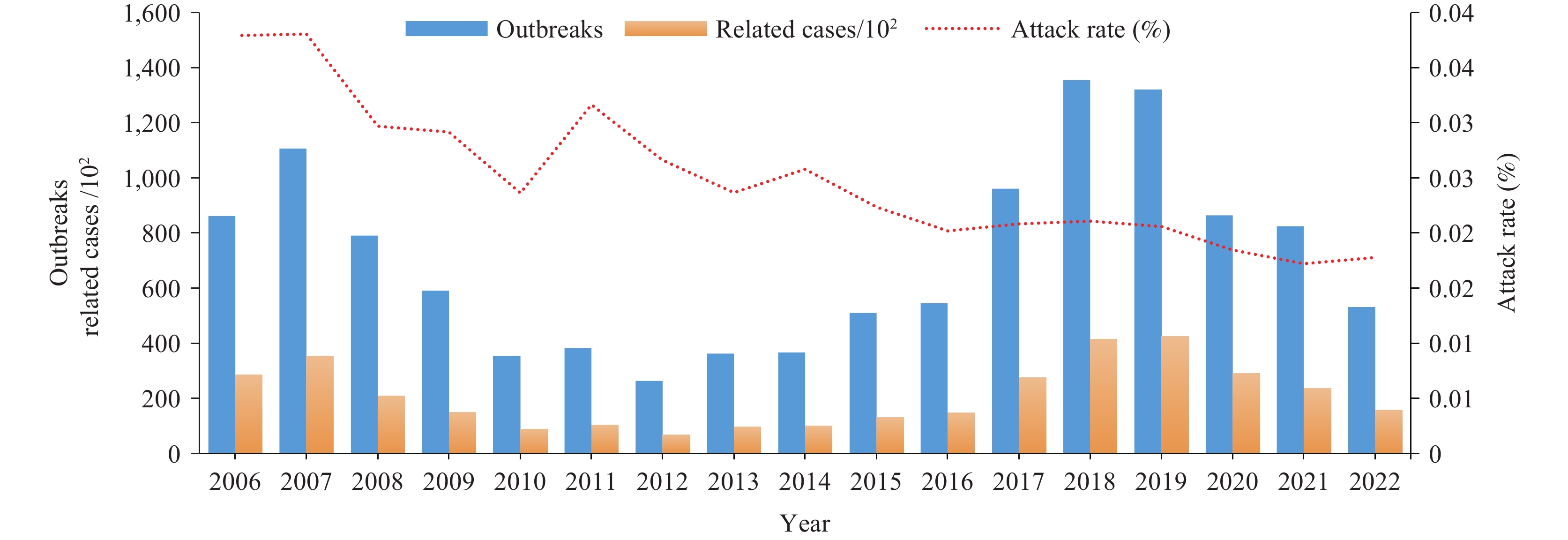
Between 2006 and 2022, a total of 11,990 varicella outbreaks were reported in China, resulting in 354,082 cases. The attack rates showed a decreasing trend over the years (Z=−4.49, P<0.05). These outbreaks occurred in two peaks annually. The eastern region accounted for the highest number of outbreaks (31.53%), followed by the southwestern (24.22%) and southern (17.93%) regions. Varicella outbreaks were most common in elementary schools. Most of the outbreaks (60.43%) were classified as Grade IV (general) severity, with 86.41% of the outbreaks having 10–49 cases. The median and inter-quartile ranges (IQR) of the duration of outbreaks, response time, and case counts were 21 (10, 39) days, 4 (0, 12) days, and 23 (16, 35) cases, respectively. These variables showed a positive correlation (P<0.001).
Varicella outbreaks exhibited fluctuating trends, initially decreasing until 2012, followed by an increase, reaching the highest peak in 2018–2019. Continual monitoring of varicella epidemiology is necessary to assess the burden of the disease and formulate evidence-based strategies and policies for its prevention and control.
Campylobacter is a significant foodborne pathogen that leads to global outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis (AGE) usually affecting less than 30 individuals. Human sapovirus (HuSaV) is an enteric virus responsible for sporadic cases and outbreaks of AGE worldwide. In a study conducted in Beijing, HuSaV detection ranked second after norovirus.
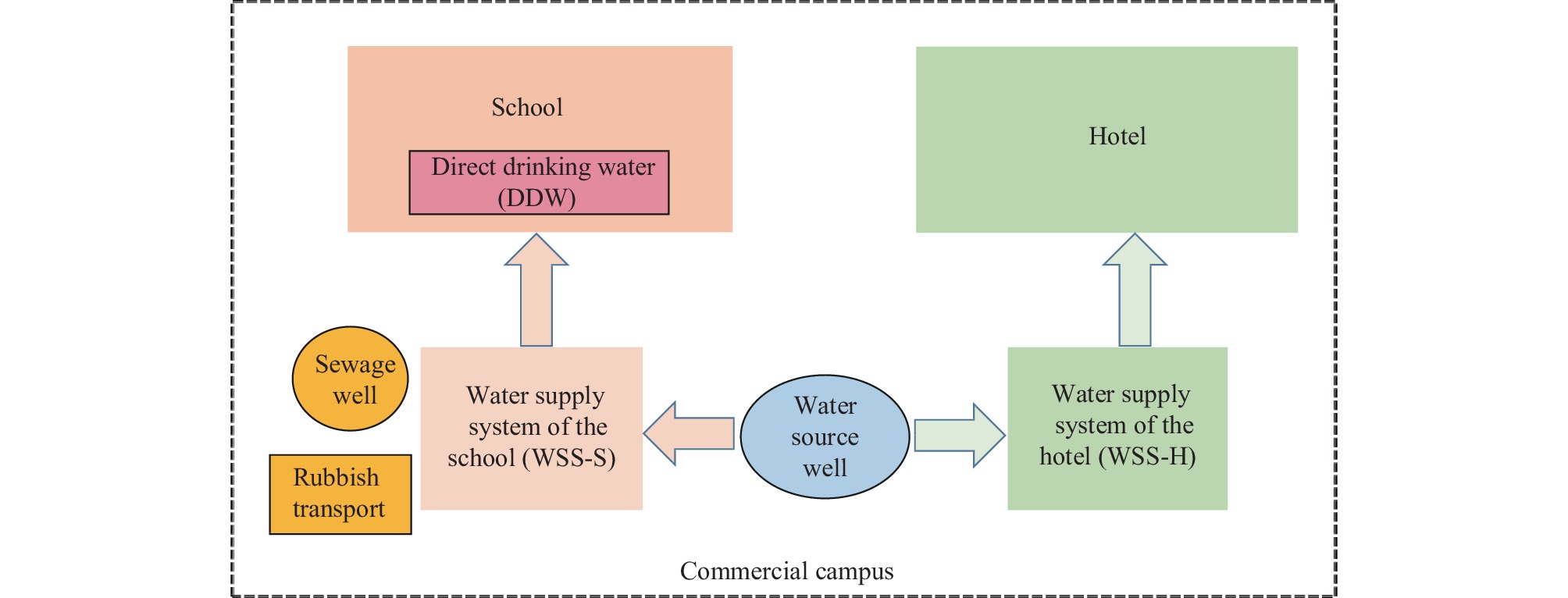
We present a discussion of the first large-scale outbreak of AGE caused by both Campylobacter coli (C. coli) and HuSaV. The outbreak involved a total of 996 patients and exhibited two distinct peaks over a period of 17 days. Through case-control studies, we identified exposure to raw water from a secondary water supply system as a significant risk factor. Among 83 patients, 49 samples tested positive for C. coli, 39 samples tested positive for HuSaV, and 27 samples tested positive for both pathogens using real-time polymerase chain reaction detection. Furthermore, whole-genome sequencing of 17 C. coli isolates obtained from 17 patients revealed that all isolates belonged to a highly clonal strain of C. coli.
Outbreaks of AGE resulting from multiple pathogen infections warrant increased attention. This report emphasizes the significance of ensuring the safety of drinking water, particularly in secondary supply systems.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed